
Polychaeta is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes. Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm and the sandworm or clam worm Alitta.

Oligochaeta is a subclass of soft-bodied animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthworms, and freshwater or semiterrestrial microdrile forms, including the tubificids, pot worms and ice worms (Enchytraeidae), blackworms (Lumbriculidae) and several interstitial marine worms.

In invertebrates, the term parapodium refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed lateral outgrowths that bear the chaetae. In several groups of sea snails and sea slugs, 'parapodium' refers to lateral fleshy protrusions.

Sabellidae, or feather duster worms, are a family of marine polychaete tube worms characterized by protruding feathery branchiae. Sabellids build tubes out of a tough, parchment-like exudate, strengthened with sand and bits of shell. Unlike the other sabellids, the genus Glomerula secretes a tube of calcium carbonate instead. Sabellidae can be found in subtidal habitats around the world. Their oldest fossils are known from the Early Jurassic.

Spirorbis borealis is a sedentary marine polychaete worm in the Serpulidae family. It is commonly called the sinistral spiral tubeworm and is the type species of the genus Spirorbis.

Sabellastarte spectabilis is a species of benthic marine polychaete worm in the Sabellidae family. It is commonly known as the feather duster worm, feather duster or fan worm. It is native to tropical waters of the Indo-Pacific but has spread to other parts of the world. It is popular in aquariums because of its distinctive appearance and its ability to remove organic particles and improve water quality.

Chaetopterus variopedatus is a species of parchment worm, a marine polychaete in the family Chaetopteridae. It is found worldwide. However, recent discoveries from molecular phylogeny analysis show that Chaetopterus variopedatus sensu Hartman (1959) is not a single species.

Phyllodocida is an order of polychaete worms in the subclass Aciculata. These worms are mostly marine, though some are found in brackish water. Most are active benthic creatures, moving over the surface or burrowing in sediments, or living in cracks and crevices in bedrock. A few construct tubes in which they live and some are pelagic, swimming through the water column. There are estimated to be more than 4,600 accepted species in the order.

Cirratulus cirratus is a species of marine polychaete worm in the family Cirratulidae. It occurs in the littoral and sub-littoral zones of the Atlantic Ocean.

Lanice conchilega, commonly known as the sand mason worm, is a species of burrowing marine polychaete worm. It builds a characteristic tube which projects from the seabed, consisting of cemented sand grains and shell fragments with a fringe at the top.

Abarenicola pacifica or the Pacific lugworm is a large species of polychaete worm found on the west coast of North America and also in Japan. The worms live out of sight in burrows under the sand and produce casts which are visible on the surface.

Lagis koreni, commonly known as the trumpet worm, is a species of marine polychaete worm found in European waters. It lives within a narrow conical tube made of grains of sand and shell fragments.

Oweniidae is a family of marine polychaete worms in the suborder Sabellida. The worms live in tubes made of sand and are selective filter feeders, detritivores and grazers.

Eudistylia polymorpha, the giant feather duster worm, is a species of marine polychaete worm belonging to the family Sabellidae. Its common name is from the crown of tentacles extended when the animal is under water.
Haplosyllis spongicola, the sponge worm, is a species of polychaete worm in the family Syllidae. It was previously classified as Syllis spongicola and is part of a species complex of closely related species that are difficult to distinguish morphologically and where the demarcation between them is unclear. It is found in shallow temperate, subtropical and tropical seas worldwide, wherever its host sponges are found.

The annelids, also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments.

Phyllodocidae is a family of polychaete worms. Worms in this family live on the seabed and may burrow under the sediment.

Scolelepis squamata is a species of polychaete worm in the family Spionidae. It occurs on the lower shore of coasts on either side of the Atlantic Ocean.
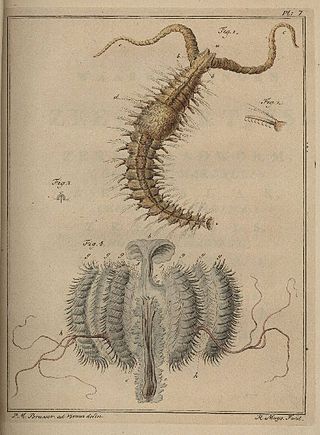
Polydora ciliata is a species of annelid worm in the family Spionidae, commonly known as a bristleworm. It is a burrowing worm and is found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and some other parts of the world.

Ramisyllis multicaudata is a species of polychaete worm in the family Syllidae. It was found in Darwin Harbour, Australia, where it was living within the tissues of a sponge of the genus Petrosia. It was the second branching species of polychaete worm to have been discovered, the first having been Syllis ramosa, a deep water species, more than a century earlier. In 2022, a second species in R. multicaudata's genus, Ramisyllis kingghidorahi, was described from specimens taken off the coast of Sado Island, Japan.



















