Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2007.

Sphenothallus is a problematic extinct genus lately attributed to the conulariids. It was widespread in shallow marine environments during the Paleozoic.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2013 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that have been described during the year 2013. The list only includes taxa at the level of genus or species.

Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2014.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2014 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that have been described during the year 2014. The list only includes taxa at the level of genus or species.
Palaeocopida is an order of ostracods in the subclass Podocopa. Most species in the suborder are extinct, and only the genera Manawa, Promanawa and Puncia in the family Punciidae are extant. The members of the family lives in high-energy shallow marine environments of New Zealand.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2017 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that are scheduled to be described during the year 2017, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to arthropod paleontology that are scheduled to occur in the year 2017.
Betty Kellett Nadeau, born Elizabeth Rosina Kellett, was an American paleontologist and micro-paleontologist who studied Palaeozoic ostracod. Numerous marine species were discovered due to the work she had done throughout her fruitful career. This work is evident to the genus Bekena named after her.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2018 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids, and other fossil arthropods of every kind that were described during the year 2018, as well as other significant discoveries, and events related to arthropod paleontology that are scheduled to occur in the year 2018.
2020 in arthropod paleontology is a list of new arthropod fossil taxa, including arachnids, crustaceans, insects, trilobites, and other arthropods that were announced or described, as well as other significant arthropod paleontological discoveries and events which occurred in 2020.
Hou Youtang was a Chinese stratigraphic paleontologist and ostracodologist and a member of the Chinese Communist Party. She was a pioneer in micropaleontology research in China and the first Chinese scholar to work on Ostracoda fossils. She is also noted for her major contributions to the oil and gas industry in China.
Phestia is an extinct genus of clam belonging to order Nuculanida and family Nuculanidae.
Septopora is an extinct genus of bryozoan belonging to the order Fenestrida. It has been found in Pennsylvanian to Permian beds in North America, South America, Australia, and southwest and east Asia.
Tabulipora is an extinct genus of bryozoan belonging to the order Trepostomida. It has been found in beds of Permian age in North America, Spitzbergen, South America, and Asia. Specimens typically form cylindrical branching colonies.
2022 in arthropod paleontology is a list of new arthropod fossil taxa, including arachnids, crustaceans, insects, trilobites, and other arthropods that were announced or described, as well as other significant arthropod paleontological discoveries and events which occurred in 2022.
Graphiadactyllis is an extinct genus of ostracod belonging to the family Quasillitidae and order Podocopida. Specimens have been found in Mississippian to Permian beds in North America, Europe, and Australia.

Amphissites is an extinct genus of ostracod belonging to the suborder Beyrichicopina and family Amphissitinae. Species belonging to the genus lived from the Devonian to the Permian in Europe, North America, Australia, and east Asia. The genus were likely deposit-feeders, and may have survived briefly into the Triassic.

Aurikirkbya is an extinct genus of ostracod belonging to the suborder Beyrichicopina and family Kirkbyidae. It is found in Pennsylvanian to Triassic beds in North America, east Asia, southwest Asia, and Europe.
Ceratobairdia is an extinct genus of ostracod belonging to the order Podocopida and family Bairdiidae. Specimens have been found in Permian to Jurassic beds in North America, China, and Europe.
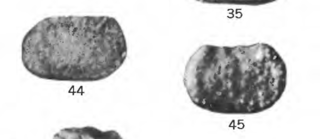
Roundyella is an extinct genus of ostracod belonging to the order Leperditellocopida and family Scrobiculidae. Specimens have been found in beds of Devonian to Triassic age in Australia, Asia, Europe, North America, and South America.




