
Bacidina is a genus of lichens in the family Ramalinaceae. It was circumscribed by Czech lichenologist Antonín Vězda in 1990, with Bacidina phacodes assigned as the type species. Vězda included 11 species in Bacidina, which was originally classified in the Lecideaceae. These species had previously been placed in genus Bacidia.
Trichothelium is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Trichotheliaceae. It has an estimated 40 species. The genus was circumscribed by the Swiss lichenologist Johannes Müller Argoviensis in 1885, with Trichothelium epiphyllum assigned as the type species.
Lasioloma is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Pilocarpaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Swedish lichenologist Rolf Santesson in 1952, with Lasioloma arachnoideum assigned as the type species. Found predominantly in tropical rainforests, genus Lasioloma contains both foliicolous (leaf-dwelling) and corticolous (bark-dwelling) species. The foliicolous species are distinguished by their woolly prothallus, a thallus that ranges from dispersed to continuous, and a hairy apothecial margin. In contrast, corticolous species typically do not have a woolly prothallus, and their thalli are usually continuous, or unbroken. Regardless of the substrate they inhabit, all known Lasioloma species are characterized by the production of campylidia and branched conidia.

Fellhanera is a genus of mostly leaf-dwelling lichens in the family Pilocarpaceae. The genus, circumscribed by lichenologist Antonín Vězda in 1986, honours Austrian lichenologist Josef Hafellner.

Calopadia is a genus of foliicolous (leaf-dwelling) lichens in the family Pilocarpaceae. It was circumscribed by Czech lichenologist Antonín Vězda in 1986.
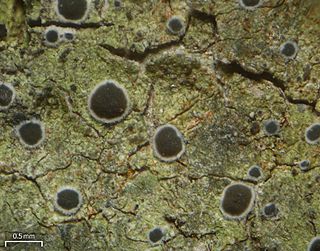
Byssoloma is a genus of leaf-dwelling lichens in the family Pilocarpaceae.

Micarea is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Pilocarpaceae. The widely distributed genus contains 126 species and new species are described actively. Species in the genus are crustose lichens and their photobiont is a single-celled green alga.

Arthothelium is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Arthoniaceae.

Enterographa is a genus of lichens in the family Roccellaceae.

Opegrapha is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Opegraphaceae. Species include:

Mazosia is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Roccellaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Italian lichenologist Abramo Bartolommeo Massalongo in 1854.

Anisomeridium is a genus of lichens in the family Monoblastiaceae. The type species was originally named Arthopyrenia xylogena by Swiss botanist Johannes Müller Argoviensis in 1883; in 1928, Maurice Choisy defined the genus Anisomeridium, designating A. xylogena the type species.

Gyalideopsis is a genus of lichens in the family Gomphillaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Czech lichenologist Antonín Vězda in 1972.

Gyalecta is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Gyalectaceae that contains 50 species. Gyalecta was circumscribed by lichenologist Erik Acharius in 1808. It forms associations with Trentepohlia algae.

Astrothelium is a large genus of corticolous (bark-dwelling) lichens in the family Trypetheliaceae. The genus is characterized by a corticate thallus and diverse ascomata structures, which can be simple, aggregated, or forming pseudostromata. Astrothelium is also notable for the carbonized walls of its ascomata, the so-called textura intricata arrangement of cells in these walls, and various forms of distoseptate, transparent spores.
André Aptroot is a Dutch mycologist and lichenologist.

Strigula is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Strigulaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1823 by English mycologist Elias Magnus Fries.

Coenogonium is a genus of filamentous lichens in the monotypic family Coenogoniaceae. It has about 90 species. Most species are leaf-dwelling or grow on bark, although a few are known to grow on rocks under certain conditions, and some are restricted to growth on termite nests. The genus was circumscribed in 1820 by German naturalist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.















