The Strait of Juan de Fuca is a body of water about 96 miles long that is the Salish Sea's main outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre of the Strait.

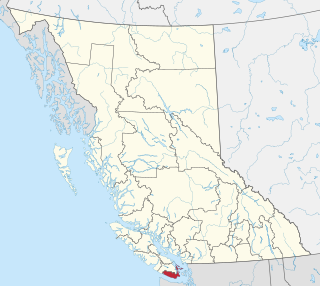
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is 456 km (283 mi) in length, 100 km (62 mi) in width at its widest point, and 32,100 km2 (12,400 sq mi) in total area, while 31,285 km2 (12,079 sq mi) are of land. The island is the largest by area and the most populous along the west coasts of the Americas.

The Township of Esquimalt is a municipality at the southern tip of Vancouver Island, in British Columbia, Canada. It is bordered to the east by the provincial capital, Victoria, to the south by the Strait of Juan de Fuca, to the west by Esquimalt Harbour and Royal Roads, to the northwest by the New Songhees 1A Indian reserve and the town of View Royal, and to the north by a narrow inlet of water called the Gorge, across which is the district municipality of Saanich. It is almost tangential to Esquimalt 1 Indian Reserve near Admirals Road. It is one of the 13 municipalities of Greater Victoria and part of the Capital Regional District.

The Strait of Georgia or the Georgia Strait is an arm of the Salish Sea between Vancouver Island and the extreme southwestern mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada, and the extreme northwestern mainland coast of Washington, United States. It is approximately 240 kilometres (150 mi) long and varies in width from 20 to 58 kilometres. Along with the Strait of Juan de Fuca and Puget Sound, it is a constituent part of the Salish Sea.
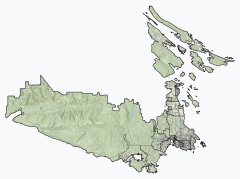
The Capital Regional District (CRD) is a local government administrative district encompassing the southern tip of Vancouver Island and the southern Gulf Islands in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The CRD is one of several regional districts in British Columbia and had an official population of 415,451 as of the Canada 2021 Census.
Juan de Fuca-Malahat is a provincial electoral district for the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia, Canada created by the 2021 British Columbia electoral redistribution that will come into effect in 2024. It has near-identical boundaries to the provincial electoral district of Malahat-Juan de Fuca in use from 1991 to 2009.

The British Columbia Coast, popularly referred to as the BC Coast or simply the Coast, is a geographic region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. As the entire western continental coastline of Canada along the Pacific Ocean is in the province, it is synonymous with being the West Coast of Canada.

Juan de Fuca Provincial Park is a provincial park located on the west coast of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. The park was established on April 4, 1996 by combining three former parks — China Beach, Loss Creek, and Botanical Beach — into one provincial park. It is the location of the majority of the Juan de Fuca Marine Trail, which is a southern compliment to the West Coast Trail within Pacific Rim National Park Reserve.

Jordan River, founded as, and still officially gazetted as, River Jordan, is a small settlement on the west coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada, approximately 70 kilometres (43 mi) west of Victoria at the mouth of the Jordan River.

The Juan de Fuca Marine Trail is a rugged 47 kilometres (29 mi) wilderness hiking trail located within Juan de Fuca Provincial Park along the southwestern coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The trail stretches from China Beach, 35 kilometres (22 mi) west of Sooke, to Botanical Beach, just outside Port Renfrew.

The Salish Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean located in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington. It includes the Strait of Georgia, the Strait of Juan de Fuca, Puget Sound, and an intricate network of connecting channels and adjoining waterways.

Loss Creek is a river in the Capital Regional District of British Columbia, Canada. Located on southern Vancouver Island, it flows through a long, steep-sided valley to the Strait of Juan de Fuca on the Pacific Ocean.

Neroutsos Inlet is an inlet on the north end of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. It is the south-east arm of Quatsino Sound.

Port San Juan is an inlet along the Pacific coast of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. It was formed from the San Juan and Leech River faults which flank the northern and southern slopes of the San Juan Valley. The San Juan and Gordon rivers empty into the inlet from the northeast.

Sombrio Beach is a beach in the western Capital Regional District, British Columbia, Canada, southeast of the settlement of Port Renfrew. It is on the southwest coast of Vancouver Island on the Strait of Juan de Fuca, west of Sombrio Point, and astride the mouth of the Sombrio River. The beach is partly within Juan de Fuca Provincial Park and is traversed by the Juan de Fuca Marine Trail. It is on the traditional territory of the Pacheedaht Nation, and it was the site of a fishing and harvesting village called Qwa:qtłis.

The San Juan Valley is a small valley located in the Capital Regional District of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada.
The Sombrio River is a river in the Capital Regional District of British Columbia, Canada. Located on southern Vancouver Island, it flows to the Strait of Juan de Fuca on the Pacific Ocean at Sombrio Beach.
Jack Elliott Creek is a river in the Renfrew Land District of British Columbia, Canada. Located on southern Vancouver Island, it flows from its source to its mouth as a right tributary of Loss Creek.
Noyse Creek is a river in the Capital Regional District of British Columbia, Canada. Located on southern Vancouver Island, it flows from its source to its mouth as a right tributary of Loss Creek. The upper reaches of the creek were originally logged in 1967-1975 and replanted. The surrounding forest is now a prime example of a 50-year old second growth eco-system.
Gain Creek is a river in the Capital Regional District of British Columbia, Canada. Located on southern Vancouver Island, it flows from its source to its mouth as a right tributary of Loss Creek.