
Ornamental plants or garden plants are plants that are primarily grown for their beauty but also for qualities such as scent or how they shape physical space. Many flowering plants and garden varieties tend to be specially bred cultivars that improve on the original species in qualities such as color, shape, scent, and long-lasting blooms. There are many examples of fine ornamental plants that can provide height, privacy, and beauty for any garden. These ornamental perennial plants have seeds that allow them to reproduce. One of the beauties of ornamental grasses is that they are very versatile and low maintenance. Almost all types of plant have ornamental varieties: trees, shrubs, climbers, grasses, succulents, aquatic plants, herbaceous perennials and annual plants. Non-botanical classifications include houseplants, bedding plants, hedges, plants for cut flowers and foliage plants. The cultivation of ornamental plants comes under floriculture and tree nurseries, which is a major branch of horticulture.

The lovebug is a species of march fly found in parts of Central America and the southeastern United States, especially along the Gulf Coast. It is also known as the honeymoon fly or double-headed bug. During and after mating, matured pairs remain together, even in flight, for up to several days.

Taxodium ascendens, also known as pond cypress, is a deciduous conifer of the genus Taxodium, native to North America. Many botanists treat it as a variety of bald cypress, Taxodium distichum rather than as a distinct species, but it differs in habitat, occurring mainly in still blackwater rivers, ponds and swamps without silt-rich flood deposits. It predominates in cypress dome habitats.

Citrus greening disease or yellow dragon disease is a disease of citrus caused by a vector-transmitted pathogen. The causative agents are motile bacteria, Liberibacter spp. The disease is transmitted by the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri, and the African citrus psyllid, Trioza erytreae, also known as the two-spotted citrus psyllid. It has no known cure. It has also been shown to be graft-transmissible.

The Florida Botanical Gardens (FBG) is a 182-acre (74 ha) botanical garden located in Largo, Florida. The park showcases flora, fauna, and natural resources in motivational surroundings that promote environmentally friendly techniques.

Imperata cylindrica is a species of perennial rhizomatous grass native to tropical and subtropical Asia, Micronesia, Melanesia, Australia, Africa, and Southern Europe. It has also been introduced to Latin America, the Caribbean, and the Southeastern United States. It is a highly flammable pyrophyte, and can spread rapidly by colonizing disturbed areas and encouraging more frequent wildfires.

Eriophyidae is a family of more than 200 genera of mites, which live as plant parasites, commonly causing galls or other damage to the plant tissues and hence known as gall mites. About 3,600 species have been described, but this is probably less than 10% of the actual number existing in this poorly researched family. They are microscopic mites and are yellow to pinkish white to purplish in color. The mites are worm like, and have only two pairs of legs. Their primary method of population spread is by wind. They affect a wide range of plants, and several are major pest species causing substantial economic damage to crops. Some species, however, are used as biological agents to control weeds and invasive plant species.

Anartia jatrophae, the white peacock, is a species of butterfly found in the southeastern United States, Central America, and throughout much of South America. The white peacock's larval hosts are water hyssop, lemon bacopa, tropical waterhyssop, frogfruit, lanceleaf frogfruit, and Carolina wild petunia . The males of the species display a unique territorial behavior, in which they stake out a territory typically 15 meters in diameter that contains larval host plants. They perch in this area and aggressively protect it from other insects and other male white peacocks.

Araujia odorata, formerly known as Morrenia odorata, the latexplant or strangler vine, is a plant in the family Apocynaceae, which is native to South America. This plant is cited in Flora Brasiliensis by Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius. The species is widely cultivated as an ornamental.

The University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (UF/IFAS) is a teaching, research and Extension scientific organization focused on agriculture and natural resources. It is a partnership of federal, state, and county governments that includes an Extension office in each of Florida's 67 counties, 12 off-campus research and education centers, five demonstration units, the University of Florida College of Agricultural and Life Sciences, three 4-H camps, portions of the UF College of Veterinary Medicine, the Florida Sea Grant program, the Emerging Pathogens Institute, the UF Water Institute and the UF Genetics Institute.
Joseph C. Joyce, executive associate vice president for agriculture and natural resources at the University of Florida is a Jacksonville, Florida native. He earned his B.S. and M.S. degrees from the University of Alabama. He received his Ph.D. from the University of Florida in 1982.

The University of Florida College of Agricultural and Life Sciences (CALS), founded in 1964, is a college of the University of Florida.

Duponchelia fovealis is a species of moth of the family Crambidae described by Philipp Christoph Zeller in 1847. It is endemic to the area surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, and the Canary Islands, but has extended its range to other parts of Africa, Europe, the Middle East and North America.

Praxelis is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Eupatorieae within the family Asteraceae.

Sagittaria kurziana, common names springtape and strap-leaf sagittaria, is a perennial aquatic plant. It grows up to 250 centimetres tall. It has long, narrow, flat leaves that float on the surface of the water, up to 250 cm long but rarely more than 15 millimetres wide. These form huge masses of ribbon-like leaves flowing back and forth with the current. Inflorescences also float on the surface, the white flowers very often submerged.

Eulophia graminea, the Chinese crown orchid, is a species of orchid native to Asia. It often develops a pseudobulb. It is considered invasive in Florida and spreads with wood chip mulch. Flowers are green and brownish purple.

Hydrolea quadrivalvis is a species of flowering plant in the family Hydroleaceae that is known by the common name of waterpod. It is native to the Southeastern United States, where it is found in the states of Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia, and Tennessee. It is also found in the state of Maryland as an introduced species.

Sacoila lanceolata, commonly referred to as leafless beaked orchid, is a species of flowering plant that grows in Florida the West Indies, Mexico, Central America, and South America. It grows in swamps and hydric hammocks including along roadsides. A varietal grows in South Florida.
Bluggoe, Orinoco, Musa'Orinoco', or burro is a cultivar of banana.
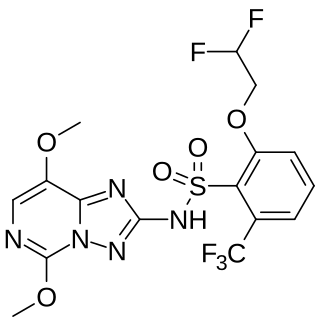
Penoxsulam is sulfonamide and triazolopyrimidine herbicide that acts as an acetolactate synthase inhibitor. It is primarily used for rice production.





















