
Poprad is a city in northern Slovakia at the foot of the High Tatra Mountains, famous for its picturesque historic centre and as a holiday resort. The largest town of the Spiš region and the largest of all towns in the vicinity of the High Tatra Mountains in both Slovakia and Poland, Poprad is the tenth largest city in Slovakia, with a population of approximately 50,000.

Spiš is a region in north-eastern Slovakia, with a very small area in south-eastern Poland. Spiš is an informal designation of the territory, but it is also the name of one of the 21 official tourism regions of Slovakia. The region is not an administrative division in its own right, but between the late 11th century and 1920 it was an administrative county of the Kingdom of Hungary.

The contemporary administrative entities roughly corresponding the traditional territory of settlement of the Rusyns. Following areas have been included which still are or up to the World War II were inhabited by each of the Rusyn sub-ethnicities mentioned below:

Prešov is a city in Eastern Slovakia. It is the seat of administrative Prešov Region and Šariš. With a population of approximately 85,000 for the city, and in total about 100,000 with the metropolitan area, it is the third-largest city in Slovakia. It belongs to the Košice-Prešov agglomeration and is the natural cultural, economic, transport and administrative center of the Šariš region. It lends its name to the Eperjes-Tokaj Hill-Chain which was considered as the geographic entity on the first map of Hungary from 1528. There are many tourist attractions in Prešov such as castles, pools and the old town.

The Nitra Region is one of the administrative regions of Slovakia. It was first established in 1923 and from 1996 exists in its present borders. It consists of seven districts and 354 municipalities, from which 16 have a town status. The economy of the region focuses more on agriculture, than in other Slovak regions. Nitra is its seat, largest city, and cultural and economic center.

Zemplín is the name of an informal traditional region located in eastern Slovakia. It includes the Slovak part of the former Zemplén county, often including the Slovak part of the Ung county.

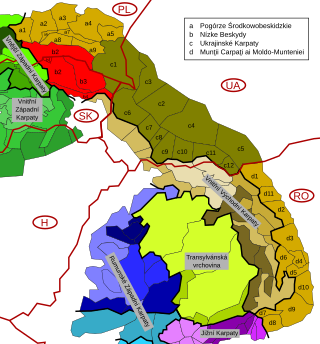
Divisions of the Carpathians are a categorization of the Carpathian mountains system.

The Žilina Region is one of the eight Slovak administrative regions and consists of 11 districts (okresy) and 315 municipalities, from which 18 have a town status. The region was established in 1923, however, in its present borders exists from 1996. It is a more industrial region with several large towns. Žilina is the region administrative center and there is a strong cultural environment in Martin.

The Banská Bystrica Region is one of the eight regions of Slovakia. It is the largest of the eight regions by area, and has a lower population density than any other region. The Banská Bystrica Region was established in 1923; its borders were last adjusted in 1996. Banská Bystrica consists of 514 municipalities, 24 of which have town status. Its administrative center is the eponymous town of Banská Bystrica, which is also the region's largest town. Other important towns are Zvolen and Lučenec.

The Košice Region is one of the eight Slovak administrative regions. The region was first established in 1923 and its present borders were established in 1996. It consists of 11 districts (okresy) and 440 municipalities, 17 of which have a town status. About one third of the region's population lives in the agglomeration of Košice, which is its main economic and cultural centre.

Stará Ľubovňa is a town with approximately 16,000 inhabitants in northeastern Slovakia. The town consists of the districts Podsadek and Stará Ľubovňa.
Abrahámovce is a village and municipality in Bardejov District in the Prešov Region of north-east Slovakia. The municipality lies at an altitude of 265 metres and covers an area of 5.899 km2. It has a population of about 342 people. The village is about 99% Slovak. The village has a public library and a football pitch.

Stará Lesná or "Old Forest" is a village and municipality in Kežmarok District in the Prešov Region in north-central Slovakia. Stará Lesná is located in an area traditionally known as Spiš and it is situated within the Slovak Tourism Region of the Tatras.

Cirocha is a right tributary of the river Laborec in the Prešov Region of eastern Slovakia. It is 50.1 km (31.1 mi) long and its drainage basin size is 499.8 km2 (193.0 sq mi). Its average flow is 2.85 m³/s in Snina.
The Low Beskids or Central Beskids are a mountain range in southeastern Poland and northeastern Slovakia. They constitute a middle (central) section of the Beskids, within the Outer Eastern Carpathians.

The Podhale-Magura Area — is a geomorphologic region of mountain ranges in northern Slovakia and southern Poland, belonging to the Outer Western Carpathians within the Carpathian Mountains system.

The Levoča Mountains is a mountain range in the Prešov Region of northern Slovakia. Geologically the range stands within the Podhale-Magura Area of the Outer Western Carpathians.

Vladimír Ledecký is a Slovak politician who was a member of the National Council of Slovakia and former state secretary at the Ministry of Investments, Regional Development and Informatization of Slovakia. He was a member of the presidency of For the People, where he acted as a guarantor for regional development. Ledecký served as mayor of Spišský Hrhov from 1998 until 2020 as well as deputy of the Prešov self-governing region from 2005 until 2022. Ledecký has been the SaS parliamentary club since 2023.




























