Trichlorosilane is an inorganic compound with the formula HCl3Si. It is a colourless, volatile liquid. Purified trichlorosilane is the principal precursor to ultrapure silicon in the semiconductor industry. In water, it rapidly decomposes to produce a siloxane polymer while giving off hydrochloric acid. Because of its reactivity and wide availability, it is frequently used in the synthesis of silicon-containing organic compounds.

Dichloromethane is an organochlorine compound with the formula CH2Cl2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odor is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is slightly polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.

Diphosgene is an organic chemical compound with the formula ClCO2CCl3. This colorless liquid is a valuable reagent in the synthesis of organic compounds. Diphosgene is related to phosgene and has comparable toxicity, but is more conveniently handled because it is a liquid, whereas phosgene is a gas.
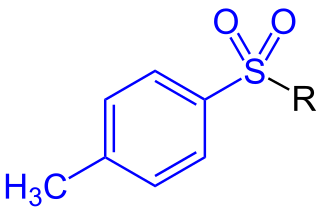
In organic chemistry, a toluenesulfonyl group (tosyl group, abbreviated Ts or Tos) is a univalent functional group with the chemical formula −SO2−C6H4−CH3. It consists of a tolyl group, −C6H4−CH3, joined to a sulfonyl group, −SO2−, with the open valence on sulfur. This group is usually derived from the compound tosyl chloride, CH3C6H4SO2Cl (abbreviated TsCl), which forms esters and amides of toluenesulfonic acid, CH3C6H4SO2OH (abbreviated TsOH). The para orientation illustrated (p-toluenesulfonyl) is most common, and by convention tosyl without a prefix refers to the p-toluenesulfonyl group.
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.

In organic chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively-charged polyatomic ions of the structure [NR4]+, where R is an alkyl group, an aryl group or organyl group. Unlike the ammonium ion and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule.
Morpholine is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula O(CH2CH2)2NH. This heterocycle features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium. For example, treating morpholine with hydrochloric acid generates the salt morpholinium chloride. It is a colorless liquid with a weak, ammonia- or fish-like odor. The naming of morpholine is attributed to Ludwig Knorr, who incorrectly believed it to be part of the structure of morphine.

Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride.
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA is also a common abbreviation. It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base.
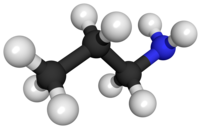
Ethylamine, also known as ethanamine, is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2NH2. This colourless gas has a strong ammonia-like odor. It condenses just below room temperature to a liquid miscible with virtually all solvents. It is a nucleophilic base, as is typical for amines. Ethylamine is widely used in chemical industry and organic synthesis.

Allylamine is an organic compound with the formula C3H5NH2. This colorless liquid is the simplest stable unsaturated amine.

Isopropylamine is an organic compound, an amine. It is a hygroscopic colorless liquid with ammonia-like odor. It is miscible with water and flammable. It is a valuable intermediate in chemical industry.

Phthalaldehyde (sometimes also o-phthalaldehyde or ortho-phthalaldehyde, OPA) is the chemical compound with the formula C6H4(CHO)2. It is one of three isomers of benzene dicarbaldehyde, related to phthalic acid. This pale yellow solid is a building block in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds and a reagent in the analysis of amino acids. OPA dissolves in water solution at pH < 11.5. Its solutions degrade upon UV illumination and exposure to air.
Methanesulfonyl chloride is an organosulfur compound with the formula CH3SO2Cl. Using the organic pseudoelement symbol Ms for the methanesulfonyl group CH3SO2–, it is frequently abbreviated MsCl in reaction schemes or equations. It is a colourless liquid that dissolves in polar organic solvents but is reactive toward water, alcohols, and many amines. The simplest organic sulfonyl chloride, it is used to make methanesulfonates and to generate the elusive molecule sulfene.
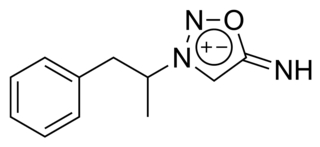
Feprosidnine (Sydnophen) is a stimulant drug which was developed in the USSR in the 1970s. It is structurally related to another Russian drug mesocarb but unlike mesocarb, was withdrawn earlier from production. In comparison with mesocarb it has own antidepressant activity, which makes it useful in treating depressions. Indications of feprosidnine included apathic, asthenic depressions, fatigue, apathic syndrome, narcolepsy and other similar conditions. Therapeutic range of doses: 10-50mg a day. Sydnophen has multiple mechanisms of action, the relative importance of which has not been clearly established. Effects on the body include reversible monoamine oxidase inhibition, cholinergic, adrenergic, opioid and nitric oxide donating actions, all of which may contribute to its pharmacological effects to some extent.
The Stieglitz rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction in organic chemistry which is named after the American chemist Julius Stieglitz (1867–1937) and was first investigated by him and Paul Nicholas Leech in 1913. It describes the 1,2-rearrangement of trityl amine derivatives to triaryl imines. It is comparable to a Beckmann rearrangement which also involves a substitution at a nitrogen atom through a carbon to nitrogen shift. As an example, triaryl hydroxylamines can undergo a Stieglitz rearrangement by dehydration and the shift of a phenyl group after activation with phosphorus pentachloride to yield the respective triaryl imine, a Schiff base.
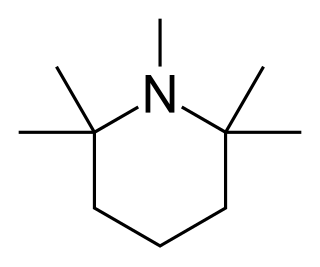
Pempidine is a ganglion-blocking drug, first reported in 1958 by two research groups working independently, and introduced as an oral treatment for hypertension.
The Hinsberg reaction is a chemical test for the detection of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. The reaction was first described by Oscar Hinsberg in 1890. In this test, the amine is shaken well with the Hinsberg reagent in the presence of aqueous alkali. A primary amine will form a soluble sulfonamide salt. Acidification of this salt then precipitates the sulfonamide of the primary amine. A secondary amine in the same reaction will directly form an insoluble sulfonamide. A tertiary amine will not react with the original reagent and will remain insoluble. After adding dilute acid this insoluble amine is converted to a soluble ammonium salt. In this way the reaction can distinguish between the three types of amines.

Trifluoroacetyl chloride (also known as TFAC) is a toxic gaseous chemical compound with the chemical formula C2ClF3O. TFAC is the perfluorinated version of acetyl chloride. The compound is a gas, but it is usually shipped as a liquid under high pressure.

Nereistoxin is a natural product identified in 1962 as the toxic organic compound N,N-dimethyl-1,2-dithiolan-4-amine. It had first been isolated in 1934 from the marine annelid Lumbriconereis heteropoda and acts by blocking the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Researchers at Takeda in Japan investigated it as a possible insecticide. They subsequently developed a number of derivatives that were commercialised, including those with the ISO common names bensultap, cartap, thiocyclam and thiosultap.