
Meniscoessus is a genus of extinct multituberculates from the Upper Cretaceous Period that lived in North America.

Cimolodon is a genus of the extinct mammal order of Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and the family Cimolodontidae. Specimens are known from the Late Cretaceous of North America.

Cimolomys is a mammal genus from the Upper Cretaceous of North America. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Cimolomyidae.

The Hell Creek Formation is an intensively studied division of mostly Upper Cretaceous and some lower Paleocene rocks in North America, named for exposures studied along Hell Creek, near Jordan, Montana. The formation stretches over portions of Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Wyoming. In Montana, the Hell Creek Formation overlies the Fox Hills Formation. The site of Pompeys Pillar National Monument is a small isolated section of the Hell Creek Formation. In 1966, the Hell Creek Fossil Area was designated as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service.

Paronychodon was a theropod dinosaur genus. It is a tooth taxon, often considered dubious because of the fragmentary nature of the fossils, which include "buckets" of teeth from many disparate times and places but no other remains, and should be considered a form taxon.
Philip Reese Bjork is an American geologist and paleontologist known for his work in unearthing dinosaur species in America.
Parictis is an extinct arctoid belonging to the family Subparictidae.

The Fort Union Formation is a geologic unit containing sandstones, shales, and coal beds in Wyoming, Montana, and parts of adjacent states. In the Powder River Basin, it contains important economic deposits of coal, uranium, and coalbed methane.

Oodectes is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from the early to middle Eocene.
This is an overview of the fossil flora and fauna of the Maastrichtian-Danian Hell Creek Formation.

The Brule Formation was deposited between 33 and 30 million years ago, roughly the Rupelian age (Oligocene). It occurs as a subunit of the White River Group in South Dakota, Nebraska, Colorado, North Dakota, and Wyoming.
The Willwood Formation is a sedimentary sequence deposited during the late Paleocene to early Eocene, or Clarkforkian, Wasatchian and Bridgerian in the NALMA classification.

The Ash Hollow Formation of the Ogallala Group is a geological formation found in Nebraska and South Dakota. It preserves fossils dating back to the Neogene period. It was named after Ash Hollow, Nebraska and can be seen in Ash Hollow State Historical Park. Ashfall Fossil Beds State Historical Park is within this formation.

The Valentine Formation is a geologic unit formation or member within the Ogallala unit in northcentral Nebraska near the South Dakota border. It preserves fossils dating to the Miocene epoch of the Neogene period and is particularly noted for Canid fossils. This unit consists of loosely-consolidated sandstone that crumbles easily. These sands carry the water of the Ogallala Aquifer and is the source of much of the water in the Niobrara River. A particular feature of the Valentine is lenticular beds of green-gray opaline sandstone that can be identified in other states, including South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, and Colorado. Although three mammalian fauna stages can be mapped throughout the range of the Ogallala, no beddings of the Ogallala are mappable and all attempts of formally applying the Valentine name to any mappable lithology beyond the type location have been abandoned. Even so, opaline sandstone has been used to refer to this green-gray opalized conglomerate sandstone that is widely found in the lower Ogallala Formation.
The Sharps Formation is a geologic formation in South Dakota. It preserves fossils dating back to the Paleogene.
The Deep River Formation is a geologic formation in Montana. It preserves fossils dating back to the Neogene period.

The Wasatch Formation (Tw) is an extensive highly fossiliferous geologic formation stretching across several basins in Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Utah and western Colorado. It preserves fossils dating back to the Early Eocene period. The formation defines the Wasatchian or Lostcabinian, a period of time used within the NALMA classification, but the formation ranges in age from the Clarkforkian to Bridgerian.

The San Jose Formation is an Early Eocene geologic formation in the San Juan Basin of New Mexico and Colorado.
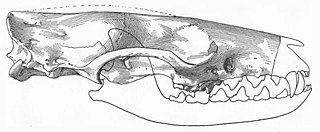
Viverravus is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Viverravinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America, Europe and Asia from the middle Paleocene to middle Eocene.

Nyctitheriidae is a family of extinct eulipotyphlan insectivores known from the Paleocene and Eocene epochs of North America and Asia and persisting into the Oligocene of Europe. Several genera, including Nyctitherium, Paradoxonycteris, and Wyonycteris, have initially been described as bats, although the family is more frequently placed in the order Eulipotyphla.














