Province of Vicenza | |
|---|---|
 Villa Cordellina Lombardi, the provincial seat | |
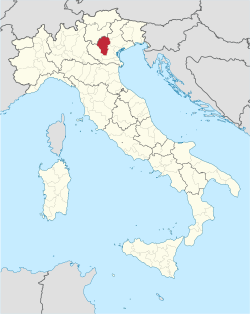 Map highlighting the location of the province of Vicenza in Italy | |
| Country | |
| Region | |
| Capital(s) | Vicenza |
| Comuni | 119 |
| Government | |
| • President | Francesco Rucco |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,722.53 km2 (1,051.17 sq mi) |
| Population (30 June 2019) | |
• Total | 938,957 |
| • Density | 340/km2 (890/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | €27.697 billion (2015) |
| • Per capita | €31,890 (2015) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 36010-36078, 36100 |
| Telephone prefix | 0424, 0444, 0445 |
| Vehicle registration | VI |
| ISTAT | 024 |
The province of Vicenza (Venetian : provincia de Vicensa; Italian : provincia di Vicenza) is a province in the Veneto region of Italy. Its capital city is Vicenza.
Contents
- Municipalities
- Economy
- Quality of life
- Transport
- Motorways
- Railway lines
- See also
- References
- External links
The province has an area of 2,722.53 km2, and a total population of 865,082 (as of 2017). There are 113 comuni (municipalities) in the province. [2] Towns in the province include Bassano del Grappa, Schio, Arzignano, Montecchio Maggiore, Thiene, Torri di Quartesolo, Noventa Vicentina, Marostica, Lonigo and Valdagno.
Population is unevenly spread throughout the province. More than 60% of the populace resides in densely industrialised areas in the eastern, western, and northern (known as Alto Vicentino) conurbations, as well as the area surrounding Bassano del Grappa. The remaining 40% reside in predominantly rural areas in the southern part of the province (the Colli Berici and Basso Vicentino) or the Asiago plateau.
Economic development in some areas is hindered by industrial and agricultural depression. Towns in the western section such as Valdagno and Montecchio Maggiore suffer from high unemployment, following a decline in steel and textile industries. The Colli Berici and Basso Vicentino remain overwhelmingly agricultural and present high levels of unemployment. The heavily industrial Alto Vicentino area alone accounts for half of the province's GDP.
Federico Faggin, an Italian physicist/electrical engineer principally responsible for the design of the first microprocessor, was born in Vicenza.