Related Research Articles
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as articular ligament, articular larua, fibrous ligament, or true ligament. Other ligaments in the body include the:

The uterus or womb is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more fertilized eggs until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment.
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.

A hamstring is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from medial to lateral, the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris).
Ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction, colloquially known as Tommy John surgery, is a surgical graft procedure where the ulnar collateral ligament in the medial elbow is replaced with either a tendon from elsewhere in the patient's body, or with one from a deceased donor. The procedure is common among collegiate and professional athletes in several sports, particularly in baseball. The surgery is performed to restore optimal function for repetitive elbow movements or specifically throwing ability, often extending the careers of professional athletes. In many athletes, the surgery is done more than once during their careers.
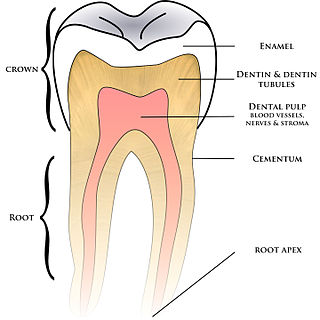
Cementum is a specialized calcified substance covering the root of a tooth. The cementum is the part of the periodontium that attaches the teeth to the alveolar bone by anchoring the periodontal ligament.

A sprain is a soft tissue injury of the ligaments within a joint, often caused by a sudden movement abruptly forcing the joint to exceed its functional range of motion. Ligaments are tough, inelastic fibers made of collagen that connect two or more bones to form a joint and are important for joint stability and proprioception, which is the body's sense of limb position and movement. Sprains may be mild, moderate, or severe, with the latter two classes involving some degree of tearing of the ligament. Sprains can occur at any joint but most commonly occur in the ankle, knee, or wrist. An equivalent injury to a muscle or tendon is known as a strain.

The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments in the human knee. The two ligaments are called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In the quadruped stifle joint, based on its anatomical position, it is also referred to as the cranial cruciate ligament. The term cruciate is Latin for cross. This name is fitting because the ACL crosses the posterior cruciate ligament to form an "X". It is composed of strong, fibrous material and assists in controlling excessive motion by limiting mobility of the joint. The anterior cruciate ligament is one of the four main ligaments of the knee, providing 85% of the restraining force to anterior tibial displacement at 30 and 90° of knee flexion. The ACL is the most frequently injured ligament in the knee.

The acromioclavicular joint, or AC joint, is a joint at the top of the shoulder. It is the junction between the acromion and the clavicle. It is a plane synovial joint.

The periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, are a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which they sit. It inserts into root cementum on one side and onto alveolar bone on the other.
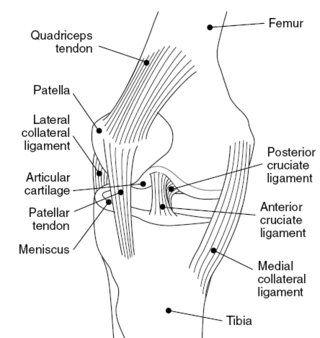
The medial collateral ligament (MCL), also called the superficial medial collateral ligament (sMCL) or tibial collateral ligament (TCL), is one of the major ligaments of the knee. It is on the medial (inner) side of the knee joint and occurs in humans and other primates. Its primary function is to resist valgus forces on the knee.

In anatomy, the alar ligaments are ligaments which connect the dens to tubercles on the medial side of the occipital condyle.

The calcaneofibular ligament is a narrow, rounded cord, running from the tip of the lateral malleolus of the fibula downward and slightly backward to a tubercle on the lateral surface of the calcaneus. It is part of the lateral collateral ligament, which opposes the hyperinversion of the subtalar joint, as in a common type of ankle sprain.

The posterior clinoid processes are the tubercles of the sphenoid bone situated at the superior angles of the dorsum sellae which represents the posterior boundary of the sella turcica. They vary considerably in size and form. The posterior clinoid processes deepen the sella turcica, and give attachment to the tentorium cerebelli, and the dura forming the floor of the hypophyseal fossa.
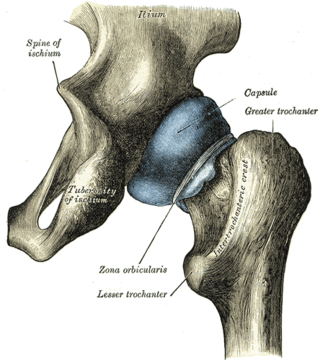
The zona orbicularis or annular ligament is a ligament on the neck of the femur formed by the circular fibers of the articular capsule of the hip joint. It is also known as the orbicular zone, ring ligament, and zonular band.

An anterior cruciate ligament injury occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is either stretched, partially torn, or completely torn. The most common injury is a complete tear. Symptoms include pain, an audible cracking sound during injury, instability of the knee, and joint swelling. Swelling generally appears within a couple of hours. In approximately 50% of cases, other structures of the knee such as surrounding ligaments, cartilage, or meniscus are damaged.

The interspinous ligaments are thin, membranous ligaments that connect adjoining spinous processes of the vertebra in the spine. They take the form of relatively weak sheets of fibrous tissue and are well developed only in the lumbar region.

The scapholunate ligament is a ligament of the wrist.

The pelvis is the lower part of an anatomical trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.
The anterolateral ligament (ALL) is a ligament on the lateral aspect of the human knee, anterior to the fibular collateral ligament.
References
- ↑ Natsis, K; Piagkou, M; Skotsimara, G; Totlis, T; Apostolidis, S; Panagiotopoulos, N. A.; Skandalakis, P (2013). "The ossified pterygoalar ligament: An anatomical study with pathological and surgical implications". Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery. 42 (5): e266–70. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2013.10.003. PMID 24290255.