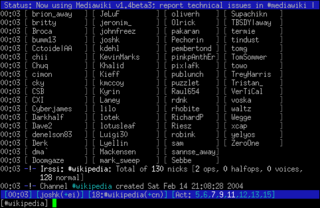
Irssi is an IRC client program for Linux, FreeBSD, macOS and Microsoft Windows. It was originally written by Timo Sirainen, and released under the terms of the GNU General Public License in January 1999.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines the application programming interface (API), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility with variants of Unix and other operating systems.

Qt is a free and open-source widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces as well as cross-platform applications that run on various software and hardware platforms such as Linux, Windows, macOS, Android or embedded systems with little or no change in the underlying codebase while still being a native application with native capabilities and speed. Qt is currently being developed by The Qt Company, a publicly listed company, and the Qt Project under open-source governance, involving individual developers and organizations working to advance Qt. Qt is available under both commercial licenses and open source GPL 2.0, GPL 3.0, and LGPL 3.0 licenses.

Wine is a free and open-source compatibility layer that aims to allow computer programs developed for Microsoft Windows to run on Unix-like operating systems. Wine also provides a software library, known as Winelib, against which developers can compile Windows applications to help port them to Unix-like systems.
Darwin is an open-source Unix-like operating system first released by Apple Inc. in 2000. It is composed of code developed by Apple, as well as code derived from NeXTSTEP, BSD, Mach, and other free software projects.
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system, which share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphical shell. The desktop environment was seen mostly on personal computers until the rise of mobile computing. Desktop GUIs help the user to easily access and edit files, while they usually do not provide access to all of the features found in the underlying operating system. Instead, the traditional command-line interface (CLI) is still used when full control over the operating system is required.
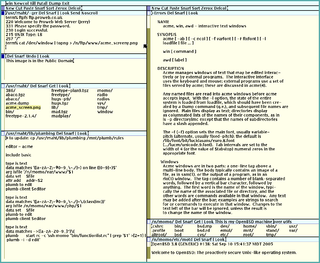
Acme is a text editor and graphical shell from the Plan 9 from Bell Labs operating system, designed and implemented by Rob Pike. It can use the Sam command language. The design of the interface was influenced by Oberon. It is different from other editing environments in that it acts as a 9P server. A distinctive element of the user interface is mouse chording.

wxWidgets is a widget toolkit and tools library for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for cross-platform applications. wxWidgets enables a program's GUI code to compile and run on several computer platforms with minimal or no code changes. A wide choice of compilers and other tools to use with wxWidgets facilitates development of sophisticated applications. wxWidgets supports a comprehensive range of popular operating systems and graphical libraries, both proprietary and free, and is widely deployed in prominent organizations.

Krusader is an advanced orthodox file manager for KDE and other desktops in the Unix world. It is similar to the console-based GNU Midnight Commander, GNOME Commander for the GNOME desktop environment, or Total Commander for Windows, all of which can trace their paradigmatic features to the original Norton Commander for DOS. It supports extensive archive handling, mounted filesystem support, FTP, advanced search, viewer/editor, directory synchronisation, file content comparisons, batch renaming, etc.
Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE) is a software interface for Unix and Unix-like computer operating systems that lets non-privileged users create their own file systems without editing kernel code. This is achieved by running file system code in user space while the FUSE module provides only a "bridge" to the actual kernel interfaces.

Linux is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution.
progeCAD is a Microsoft Windows based CAD software program for editing and printing DWG and DXF files from most versions of AutoCAD.

ngrep is a network packet analyzer written by Jordan Ritter. It has a command-line interface, and relies upon the pcap library and the GNU regex library.
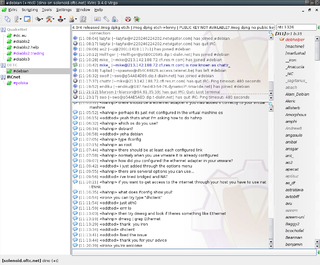
KVIrc is a graphical IRC client for Linux, Unix, Mac OS and Windows. The name is an acronym of K Visual IRC in which the K stands for a dependency to KDE, which became optional from version 2.0.0. The software is based on the Qt framework and its code is released under a modified GNU General Public License.
LibreCAD is a free computer-aided design (CAD) application for 2D design. It works on Linux, macOS, Unix and Windows operating systems.
Absoft Fortran Compilers are set of Fortran compilers for Microsoft Windows, Apple Macintosh, and Linux produced by Absoft Corporation. The compilers are source code compatible across platforms.









