
The single transferable vote (STV), sometimes known as proportional ranked choice voting (P-RCV), is a multi-winner electoral system in which each voter casts a single vote in the form of a ranked-choice ballot. Voters have the option to rank candidates, and their vote may be transferred according to alternate preferences if their preferred candidate is eliminated or elected with surplus votes, so that their vote is used to elect someone they prefer over others in the running. STV aims to approach proportional representation based on votes cast in the district where it is used, so that each vote is worth about the same as another. Formally, STV satisfies a fairness criterion known as proportionality for solid coalitions.

A Condorcet method is an election method that elects the candidate who wins a majority of the vote in every head-to-head election against each of the other candidates, that is, a candidate preferred by more voters than any others, whenever there is such a candidate. A candidate with this property, the pairwise champion or beats-all winner, is formally called the Condorcet winner. The head-to-head elections need not be done separately; a voter's choice within any given pair can be determined from the ranking.

Voting is a method by which a group, such as a meeting or an electorate, convenes together for the purpose of making a collective decision or expressing an opinion usually following discussions, debates or election campaigns. Democracies elect holders of high office by voting. Residents of a jurisdiction represented by an elected official are called "constituents", and the constituents who choose to cast a ballot for their chosen candidate are called "voters." There are different systems for collecting votes, but while many of the systems used in decision-making can also be used as electoral systems, any which cater to proportional representation can only be used in elections.
The Droop quota is the quota most commonly used in elections held under the single transferable vote (STV) system. It is also sometimes used in elections held under the largest remainder method of party-list proportional representation. Any candidate that receives quota is declared elected. Under some STV systems, especially those of the full-preferential voting variant, all the winners receive the quota, but in others, of the optional-preferential voting or semi-optional preferential voting variants, it is common for as many as three winners in a district to be elected with less than quota.
Copeland's method is a ranked voting method based on a scoring system of pairwise "wins", "losses", and "ties". The method has a long history:
The Gibbard–Satterthwaite theorem is a theorem in voting theory. It was first conjectured by the philosopher Michael Dummett and the mathematician Robin Farquharson in 1961 and then proved independently by the philosopher Allan Gibbard in 1973 and economist Mark Satterthwaite in 1975. It deals with deterministic ordinal electoral systems that choose a single winner. It states that for every voting rule, one of the following three things must hold:
- The rule is dictatorial, i.e. there exists a distinguished voter who can choose the winner; or
- The rule limits the possible outcomes to two alternatives only; or
- The rule is susceptible to tactical voting: in certain conditions, a voter's sincere ballot may not best defend their opinion.
The Hare quota is a formula used under some forms of proportional representation. In these voting systems the quota is the number of votes that guarantees a candidate, or a party in some cases, captures a seat. The Hare quota is the total number of votes divided by the number of seats to be filled. This is the simplest quota, but the Droop quota is mostly used currently.
The single transferable vote (STV) is a proportional representation voting system that elects multiple winners. It is one of several ways of choosing winners from ballots that rank candidates by preference. Under STV, an elector's vote is initially allocated to their most-preferred candidate. Candidates are elected (winners) if their vote tally reaches quota. After this 1st Count, if seats still remain open, surplus votes are transferred from winners to remaining candidates (hopefuls) according to the surplus ballots' next usable back-up preference. if no surplus votes have to be transferred, then the least-popular candidate is eliminated so the vote has chance to be placed on a candidate who can use it.
The Edmonton provincial electoral district also known as Edmonton City from 1905 to 1909, was a provincial electoral district in Alberta, Canada mandated to return members to the Legislative Assembly of Alberta from 1905 to 1917 and again from 1921 to 1959.
The Borda count electoral system can be combined with an instant-runoff procedure to create hybrid election methods that are called Nanson method and Baldwin method. Both methods are designed to satisfy the Condorcet criterion, and allow for incomplete ballots and equal rankings.
Positional voting is a ranked voting electoral system in which the options or candidates receive points based on their rank position on each ballot and the one with the most points overall wins. The lower-ranked preference in any adjacent pair is generally of less value than the higher-ranked one. Although it may sometimes be weighted the same, it is never worth more. A valid progression of points or weightings may be chosen at will or it may form a mathematical sequence such as an arithmetic progression, a geometric one or a harmonic one. The set of weightings employed in an election heavily influences the rank ordering of the candidates. The steeper the initial decline in preference values with descending rank, the more polarised and less consensual the positional voting system becomes.
The plurality criterion is a voting system criterion devised by Douglas R. Woodall for ranked voting methods with incomplete ballots. It is stated as follows:
CPO-STV, or the Comparison of Pairs of Outcomes by the Single Transferable Vote, is a ranked voting system designed to achieve proportional representation. It is a more sophisticated variant of the Single Transferable Vote (STV) system, designed to overcome some of that system's perceived shortcomings. It does this by incorporating some of the features of Condorcet's method, a voting system designed for single-winner elections, into STV. As in other forms of STV, in a CPO-STV election more than one candidate is elected and voters must rank candidates in order of preference. As of February 2021, it has not been used for a public election.
There are a number of complications and issues surrounding the application and use of single transferable vote proportional representation that form the basis of discussions between its advocates and detractors.

The matrix vote is a voting procedure which can be used when one group of people wishes to elect a smaller number of persons, each of whom is to have a different assignment. Examples of its use are
- when an association elects its executive committee; and
- when a parliament elects its all-party power-sharing coalition government.
The Borda count is a family of positional voting rules which gives each candidate, for each ballot, a number of points corresponding to the number of candidates ranked lower. In the original variant, the lowest-ranked candidate gets 0 points, the next-lowest gets 1 point, etc., and the highest-ranked candidate gets n − 1 points, where n is the number of candidates. Once all votes have been counted, the option or candidate with the most points is the winner. The Borda count is intended to elect broadly acceptable options or candidates, rather than those preferred by a majority, and so is often described as a consensus-based voting system rather than a majoritarian one.

The Wright system is a refinement of rules associated with proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV) electoral system. It was developed and written by Anthony van der Craats, a system analyst and life member of the Proportional Representation Society of Australia. It is described in a submission into a parliamentary review of the 2007 Australian federal election.
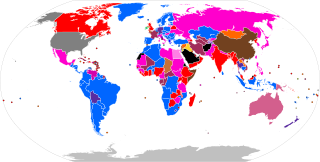
An electoral system or voting system is a set of rules that determine how elections and referendums are conducted and how their results are determined. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, non-profit organisations and informal organisations. These rules govern all aspects of the voting process: when elections occur, who is allowed to vote, who can stand as a candidate, how ballots are marked and cast, how the ballots are counted, how votes translate into the election outcome, limits on campaign spending, and other factors that can affect the result. Political electoral systems are defined by constitutions and electoral laws, are typically conducted by election commissions, and can use multiple types of elections for different offices.

The term ranked voting, also known as preferential voting or ranked choice voting, pertains to any voting system where voters use a rank to order candidates or options—in a sequence from first, second, third, and onwards—on their ballots. Ranked voting systems vary based on the ballot marking process, how preferences are tabulated and counted, the number of seats available for election, and whether voters are allowed to rank candidates equally. An electoral system that utilizes ranked voting employs one of numerous counting methods to determine the winning candidate or candidates. Additionally, in some ranked voting systems, officials mandate voters to rank a specific number of candidates, sometimes all; while in others, voters may rank as many candidates as they desire.

Hare-Clark is a type of single transferable vote electoral system of proportional representation used for elections in Tasmania and the Australian Capital Territory. The method for the distribution of preferences is similar to other voting systems in Australia, such as for the Australian Senate.







