
The Falkland Islands are a British overseas territory and, as such, rely on the United Kingdom for the guarantee of their security. The other UK territories in the South Atlantic, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, fall under the protection of British Forces South Atlantic Islands (BFSAI), formerly known as British Forces Falkland Islands (BFFI), which includes commitments from the British Army, Royal Air Force and Royal Navy. They are headed by the Commander, British Forces South Atlantic Islands (CBFSAI), a brigadier-equivalent appointment that rotates among all three services.

The Falklands War was a ten-week undeclared war between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982 over two British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands and its territorial dependency, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. The conflict began on 2 April, when Argentina invaded and occupied the Falkland Islands, followed by the invasion of South Georgia the next day. On 5 April, the British government dispatched a naval task force to engage the Argentine Navy and Air Force before making an amphibious assault on the islands. The conflict lasted 74 days and ended with an Argentine surrender on 14 June, returning the islands to British control. In total, 649 Argentine military personnel, 255 British military personnel, and three Falkland Islanders were killed during the hostilities.
This is a list of the naval forces from the United Kingdom that took part in the Falklands War, often referred to as "the Task Force" in the context of the war. For a list of naval forces from Argentina, see Argentine naval forces in the Falklands War.
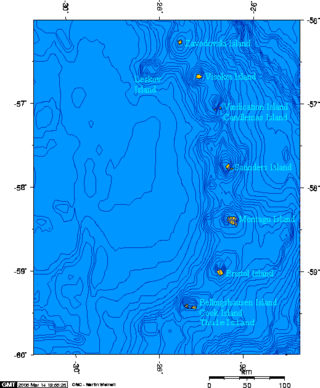
Operation Keyhole was a British special operation to recapture Thule Island in the South Sandwich Islands during the Falklands War. The operation took place from 19 to 20 June 1982.

HMS Brilliant was a Type 22 frigate of the Royal Navy.

HMS Sheffield was a Type 42 guided missile destroyer and the second Royal Navy ship to be named after the city of Sheffield in Yorkshire. Commissioned on 16 February 1975 the Sheffield was part of the Task Force 317 sent to the Falkland Islands during the Falklands War. She was struck and heavily damaged by an Exocet air-launched anti-ship missile from an Argentine Super Étendard aircraft on 4 May 1982 and foundered while under tow on 10 May 1982.

RFA Diligence was a forward repair ship of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary. Launched in 1981 as a support ship for North Sea oil rigs, she was chartered by the British government to support naval activities during the 1982 Falklands War and was later bought outright as a fleet maintenance vessel. She gave assistance to the damaged USS Tripoli and Princeton in the 1991 Gulf War, and to Sri Lanka after the 2005 tsunami. She typically had deployments of 5-8 years in support of the Trafalgar-class submarine on duty east of Suez, with a secondary role as a mothership for British and US minesweepers in the Persian Gulf. Until 2016 Diligence was set to go out of service in 2020. However in August 2016, the UK Ministry of Defence placed an advert for the sale of RFA Diligence. As of 2016 the option for the delivery of future operational maintenance and repair capability for the RFA remained under consideration. However, the 2021 British defence white paper made no specific mention of the need for this capability. In April 2023, it was revealed that the ship was to be scrapped after no suitable buyers materialised, & she was moved out of 3 Basin across to Fareham Trots to await her final journey to the scrapyard.

RFA Fort Austin is a retired British Fort Rosalie-class dry stores ship of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary.

RFA Fort Rosalie was the lead ship of her class of Royal Fleet Auxiliary fleet replenishment ships. Fort Rosalie was originally named RFA Fort Grange, but was renamed in May 2000 to avoid confusion with the now-decommissioned RFA Fort George. On 31 March 2021, the ship was withdrawn from service.

HMS Yarmouth was the first modified Type 12 frigate of the Rothesay class to enter service with the Royal Navy.

Corbeta Uruguay base was an Argentine military outpost established in November 1976 on Thule Island, Southern Thule, in the South Sandwich Islands. It was vacated and mostly demolished in 1982 following Britain's victory against Argentina in the Falklands War.
Operation Journeyman was a Royal Navy operation in which a naval taskforce was secretly sent to the Falkland Islands in November 1977 to prevent an Argentine invasion.

Admiral of the Fleet John David Elliott Fieldhouse, Baron Fieldhouse, was a Royal Navy officer. He commanded five submarines and a frigate before achieving higher command from the 1970s. Following the invasion of the Falkland Islands by Argentine forces in April 1982, Fieldhouse was appointed Commander of the Task Force given responsibility for "Operation Corporate", the mission to recover the Falkland Islands. The campaign ended in the surrender of Argentine forces in June 1982. He became First Sea Lord and Chief of Naval Staff in December that year and, in that role, persuaded the British Government to fund the replacement of ships lost in the Falklands War. He went on to be Chief of the Defence Staff from 1985 until his retirement in 1988.
These are some of the key weapons of the Falklands War used by both sides.

HMS Endurance was a Royal Navy ice patrol vessel that served from 1967 to 1991. She came to public notice when she was involved in the Falklands War of 1982. The final surrender of the war, in the South Sandwich Islands, took place aboard Endurance.

RFA Wave Ruler is a Wave-class fast fleet tanker of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA) of the United Kingdom tasked with providing fuel, food, fresh water, ammunition and other supplies to Royal Navy vessels around the world.

The 1982 British military campaign to recapture the Falkland Islands depended on complex logistical arrangements. The logistical difficulties of operating 7,000 nautical miles from home were formidable. The Argentine invasion of the Falkland Islands came at a time when the Royal Navy was experiencing a reduction in its amphibious capability, but it still possessed the aircraft carriers HMS Hermes and Invincible, the landing platform dock (LPD) ships HMS Fearless and Intrepid, and six landing ship logistics (LSL) ships. To provide the necessary logistic support, the Royal Navy's ships were augmented by ships taken up from trade (STUFT).
The Battle of San Carlos was a battle between aircraft and ships that lasted from 21 to 25 May 1982 during the British landings on the shores of San Carlos Water in the 1982 Falklands War. Low-flying land-based Argentine jet aircraft made repeated attacks on ships of the British Task Force.

The Ol-class tankers were Royal Fleet Auxiliary "fast fleet tankers" tasked with providing fuel, food, fresh water, ammunition and other supplies to Royal Navy vessels around the world.
Junella was a fishing trawler, best known for her service with the Royal Navy during the Falklands War. She was built in 1975 for J Marr & Son, a Hull-based fishing company. On 11 April 1982 she was taken up from trade by the British government and commissioned into the Royal Navy. She was fitted with Second World War era minesweeping gear at Rosyth Dockyard, manned by Royal Navy sailors and allocated to the 11th Mine Countermeasures Squadron. She sailed on 26 April but was unable to commence sweeping until after the 14 June Argentine surrender. In the meantime she was utilised to transfer troops and stores between ships and landed special forces troops at San Carlos. Demining operations commenced on 21 June. Junella returned to the United Kingdom on 11 August, carrying a defused Argentine mine.
















