
Xenacanthida is an order or superorder of extinct shark-like chondrichthyans known from the Carboniferous to Triassic. They were native to freshwater, marginal marine and shallow marine habitats. Some xenacanths may have grown to lengths of 5 m (16 ft). Most xenacanths died out at the end of the Permian in the End-Permian Mass Extinction, with only a few forms surviving into the Triassic.
The Climatiiformes is an order of extinct fish belonging to the class Acanthodii. Like most other "spiny sharks", the Climatiiformes had sharp spines. These animals were often fairly small in size and lived from the Late Silurian to the Early Carboniferous period. The type genus is Climatius. The order used to be subdivided into the suborders Climatiida and Diplacanthida, but subsequently Diplacanthida has been elevated to a separate order, the Diplacanthiformes. The Diplacanthiformes take their name from Diplacanthus, first described by Agassiz in 1843. Family Gyracanthidae is sometimes rejected from this order.

Strepsodus is a genus of rhizodont lobe-finned fish that lived throughout the Carboniferous period. Fossils have been found in eastern Canada, Britain, and Queensland, Australia; indeterminate species of Strepsodus have also been found in the late Devonian deposits of Turkey, Iran and Colombia. A large individual is measured up to 3.5 metres (11.5 ft) long.

Sphenacanthus is an extinct genus of a chondrichtyan xenacanthiform that belongs to the Sphenacanthidae family and lived from the Late Devonian, through Carboniferous until the Late Permian period in Scotland, Spain, Russia and Brazil. It lived 359 million years ago, and probably it was one of the first member of the elasmobranchians, the lineage that leads to the modern sharks. Sphenacanthus probably hunts small fishes and, unlike their modern-day relatives, its inhabited fresh water lagoons. Sphenacanthus had seven fins, two in the upper part and five in the underside, and it had a heterodont dentition and mandibles relatively long and deeper. Sphenacanthus serrulatus is still only known from incomplete neurocranial remains and associated dermal material. These suggest that it was a relatively large shark, probably well over one meter in length when fully grown. Its body form was probably similar to that of other phalacanthous sharks.

Gnathorhiza is an extinct genus of prehistoric lobe-finned fish (lungfish) which lived from the Carboniferous period to the Early Triassic epoch. It is the only known lungfish genus to have crossed the Permo-Triassic boundary. Several species have been described, ranging in size from 5 to 50 centimeters.
Ligulalepis is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish. Ligulalepis was first described from isolated scales found in the Taemas-Wee jasper limestones of New South Wales by Dr Hans-Peter Schultze (1968) and further material described by Burrow (1994). A nearly complete skull found in the same general location was described in Nature by Basden et al. (2000) claiming the genus was closely related to basal ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygii). In 2015 Flinders University student Benedict King found a more complete new skull of this genus which was formally described by Clement et al. (2018), showing the fish to be on the stem of all osteichthyans.

Nerepisacanthus is an extinct genus of acanthodian, probably acritolepid, from Middle Silurian deposits of New Brunswick, Canada. Nerepisacanthus is known from many incomplete but articulated specimens. It was collected from the Cunningham Creek Formation, near Nerepis, southern New Brunswick. It was first named by Carole J. Burrow in 2011 and the type species is Nerepisacanthus denisoni. Additional specimen is known from Bertie Formation, making that species the oldest near-complete acanthodian.
Mcmurdodus is an extinct genus of chondrichthyan belonging to the family Mcmurdodontidae. It contains one species, Mcmurdodus featherensis, from the Middle Devonian of Antarctica. The Australian species M. whitei was previously included in the genus too, but was moved to a new genus, Maiseyodus, in 2021.

The Battery Point Formation is a geologic formation in Quebec. It preserves fossils dating back to the early Emsian to early Eifelian the lower Devonian period.
The York River Formation is a geologic formation in Quebec. It preserves fossils dating back to the Devonian period.
The Campbellton Formation is a geologic formation in New Brunswick. It preserves fossils dating back to the latest Pragian and Emsian of the Devonian period.
Cladodus is an extinct genus of cartilaginous fishes in the family Ctenacanthidae. As the name implies, they are a type of cladodont, primitive sharks with teeth designed to snag fish and swallow them whole, instead of sawing off chunks to swallow.

Thrinacodus is an extinct genus of basal elasmobranch, found worldwide from the Late Devonian-Lower Carboniferous. The type species is Thrinacodus nanus. Most species are only known from their tricuspid teeth. T. gracia, originally placed in the separate genus Thrinacoselache from the Serpukhovian-aged Bear Gulch Limestone, of what is now Montana, is known from full body impressions, showing a long, slender eel-like body up to a metre in length, with an elongate rostrum. Stomach contents of T. gracia include remains of crustaceans and small chondrichthyan fish. It is a member of the Phoebodontiformes.
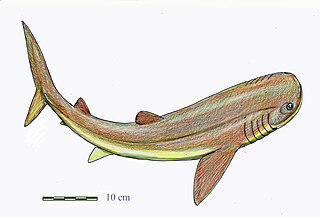
Gladbachus is an extinct genus of chondrichthyan.

Gyracanthides is an extinct genus of acanthodian gnathostome, known from Devonian to Early Carboniferous.

Ageleodus is an extinct genus of cartilaginous fish from the Paleozoic era. It is known from two species, both of which are based upon isolated teeth. A. pectinatus is known from the Carboniferous of Europe and North America. A. altus was described in 2006 from the Carboniferous of Australia. Four teeth from the Tournaisian deposits of Canning Basin probably present another Australian species although their shape is likely caused by physical wear rather than species features. This genus is also known from the Famennian of the Catskill formation at the Red Hill Site in Hyner, Pennsylvania. A study of 382 specimens from the site showed the strong heterodonty of this genus, which varies widely in tooth length and cusp number. This study described them as A. pectinatus, but the paper which described A. altus tentatively labeled them Ageleodus cf. A. altus. While generally considered a chondrichthyan, it has eluded classification into any known order or family.

Gyracanthidae is an family of extinct fish belonging to the class Acanthodii, known from early Devonian to late Carboniferous. Members are characterized by large, broad-based, paired fin spines with the pectoral fin spines having a distinct longitudinal curvature. Although it is originally classified in order Climatiiformes, but later study questioned this.
Acanthodopsis is a genus of Acanthodian fish from the family Acanthodidae. It lived during the Carboniferous period. Acanthodopsis fossils have been discovered in Australia and England. The largest species could have reached up to 75 cm in length while others were much smaller.










