
Cornwall is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised by Cornish and Celtic political groups as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, Devon to the east, and the English Channel to the south. The largest urban area in the county is a conurbation that includes the former mining towns of Redruth and Camborne, and the county town is the city of Truro.
Cornish is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family. Along with Welsh and Breton, Cornish is descended from the Common Brittonic language spoken throughout much of Great Britain before the English language came to dominate. For centuries, until it was pushed westwards by English, it was the main language of Cornwall, maintaining close links with its sister language Breton, with which it was mutually intelligible, perhaps even as long as Cornish continued to be spoken as a vernacular. Cornish continued to function as a common community language in parts of Cornwall until the mid 18th century, and there is some evidence for traditional speakers of the language persisting into the 19th century.

The River Fowey is a river in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom.

Saint Austell is a town in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, 10 miles (16 km) south of Bodmin and 30 miles (48 km) west of the border with Devon.

The history of Cornwall goes back to the Paleolithic, but in this period Cornwall only had sporadic visits by groups of humans. Continuous occupation started around 10,000 years ago after the end of the last ice age. When recorded history started in the first century BCE, the spoken language was Common Brittonic, and that would develop into Southwestern Brittonic and then the Cornish language. Cornwall was part of the territory of the tribe of the Dumnonii that included modern-day Devon and parts of Somerset. After a period of Roman rule, Cornwall reverted to rule by independent Romano-British leaders and continued to have a close relationship with Brittany and Wales as well as southern Ireland, which neighboured across the Celtic Sea. After the collapse of Dumnonia, the remaining territory of Cornwall came into conflict with neighbouring Wessex.

St Columb Major is a town and civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. Often referred to locally as St Columb, it is approximately seven miles (11 km) southwest of Wadebridge and six miles (10 km) east of Newquay The designation Major distinguishes it from the nearby settlement and parish of St Columb Minor on the coast. An electoral ward simply named St Columb exists with a population at the 2011 census of 5,050. The town is named after the 6th-century AD Saint Columba of Cornwall, also known as Columb.
The constitutional status of Cornwall has been a matter of debate and dispute. Cornwall is an administrative county of England.

The culture of Cornwall forms part of the culture of the United Kingdom, but has distinct customs, traditions and peculiarities. Cornwall has many strong local traditions. After many years of decline, Cornish culture has undergone a strong revival, and many groups exist to promote Cornwall's culture and language today.

The Cornish people or Cornish are an ethnic group native to, or associated with Cornwall and a recognised national minority in the United Kingdom, which can trace its roots to the Brittonic Celtic ancient Britons who inhabited Great Britain from somewhere between the 11th and 7th centuries BC and inhabited Britain at the time of the Roman conquest. Many in Cornwall today continue to assert a distinct identity separate from or in addition to English or British identities. Cornish identity has also been adopted by some migrants into Cornwall, as well as by emigrant and descendant communities from Cornwall, the latter sometimes referred to as the Cornish diaspora. Although not included as a tick-box option in the UK census, the numbers of those writing in a Cornish ethnic and national identity are officially recognised and recorded.

Castle an Dinas is an Iron Age hillfort at the summit of Castle Downs near St Columb Major in Cornwall, UK and is considered one of the most important hillforts in the southwest of Britain. It dates from around the 3rd to 2nd century BCE and consists of three ditch and rampart concentric rings, 850 feet (260 m) above sea level. During the early 1960s it was excavated by a team led by Dr Bernard Wailes of the University of Pennsylvania during two seasons of excavation.

Sithney is a village and civil parish in the West of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. Sithney is north of Porthleven. The population including Boscadjack and Crowntown at the 2011 census was 841.
The Institute of Cornish Studies is a research institute affiliated with the University of Exeter. Formerly located at Pool, near Redruth, then in Truro, it is now on the University's Penryn Campus near Penryn, Cornwall.
Philip John Payton is a British-Australian historian and Emeritus Professor of Cornish and Australian Studies at the University of Exeter and formerly Director of the Institute of Cornish Studies based at Tremough, just outside Penryn, Cornwall. An Australian citizen, he is Professor of History at Flinders University in Adelaide, South Australia.

Cornish nationalism is a cultural, political and social movement that seeks the recognition of Cornwall – the south-westernmost part of the island of Great Britain – as a nation distinct from England. It is usually based on three general arguments:
Cornish Americans are Americans who describe themselves as having Cornish ancestry, an ethnic group of Brittonic Celts native to Cornwall and the Scilly Isles, part of England in the United Kingdom. Although Cornish ancestry is not recognized on the United States Census, Bernard Deacon at the Institute of Cornish Studies estimates there are close to two million people of Cornish descent in the U.S., compared to half a million in Cornwall itself and only half of those Cornish by descent.

Cornish Australians are citizens of Australia who are fully or partially of Cornish heritage or descent, an ethnic group native to Cornwall in the United Kingdom.
Cornish surnames are surnames used by Cornish people and often derived from the Cornish language such as Jago, Trelawney or Enys. Others have strong roots in the region and many in the UK with names such as Eddy, Stark or Rowe are likely to have Cornish origins. Such surnames for the common people emerged in the Middle Ages, although the nobility probably had surnames much earlier on. Not until the later Middle Ages did it become necessary for a common man to have a surname. Most surnames were fully established throughout Cornwall by the end of the 15th century. Cornish surnames can be found throughout the world as part of the Cornish diaspora.
The Battle of Hehil was a battle won by a force of Britons, probably against the Anglo-Saxons of Wessex around the year 720. The location is unknown, except that it was apud Cornuenses.
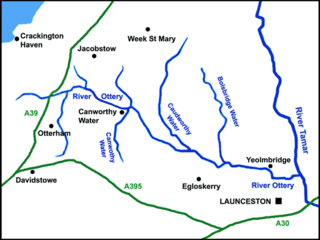
The River Ottery is a small river in northeast Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The river is about twenty miles (32 km) long from its source southeast of Otterham to its confluence with the River Tamar at Nether Bridge, two miles (3.2 km) northeast of Launceston.
Presented below is an alphabetical index of articles related to Cornwall:













