Related Research Articles

In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep.

The North American plate is a tectonic plate containing most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of 76 million km2 (29 million sq mi), it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific plate.

The richly textured landscape of the United States is a product of the dueling forces of plate tectonics, weathering and erosion. Over the 4.5 billion-year history of the Earth, tectonic upheavals and colliding plates have raised great mountain ranges while the forces of erosion and weathering worked to tear them down. Even after many millions of years, records of Earth's great upheavals remain imprinted as textural variations and surface patterns that define distinctive landscapes or provinces.

Mother lode is a principal vein or zone of gold or silver ore. The term is also used colloquially to refer to the real or imaginary origin of something valuable or in great abundance.
In geology, a terrane is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate and accreted or "sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its distinctive geologic history, which is different from the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton.

The Arabian-Nubian Shield (ANS) is an exposure of Precambrian crystalline rocks on the flanks of the Red Sea. The crystalline rocks are mostly Neoproterozoic in age. Geographically – and from north to south – the ANS includes parts of Israel, Jordan, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Yemen, and Somalia. The ANS in the north is exposed as part of the Sahara Desert and Arabian Desert, and in the south in the Ethiopian Highlands, Asir province of Arabia and Yemen Highlands.
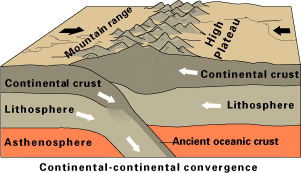
In geology, continental collision is a phenomenon of plate tectonics that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of subduction, whereby the subduction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together. Continental collision is only known to occur on Earth.

The Smartville Block, also called the Smartville Ophiolite, Smartville Complex, or Smartville Intrusive Complex, is a geologic terrane formed in the ocean from a volcanic island arc that was accreted onto the North American Plate during the late Jurassic. The collision created sufficient crustal heating to drive mineral-laden water up through numerous fissures along the contact zone. When these cooled, among the precipitating minerals was gold. Associated with the Western Metamorphic Belt of the Sierra Nevada foothills it extends from the central Sierra Nevada mountain range, due west, under a section of the Central Valley and California Coast Ranges, in northern California. The ophiolitic sequence found in this terrane is one of several major ophiolites found in California. Ophiolites are crustal and upper-mantle rocks from the ocean floor that have been moved on land. Ophiolites have been studied extensively regarding the movement of crustal rocks by plate tectonics.
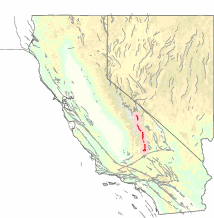
The Sierra Nevada Fault is an active seismic fault along the eastern edge of the Sierra Nevada mountain block in California. It forms the eastern escarpment of the Sierra Nevada, extending roughly 600 km (370 mi) from just north of the Garlock Fault to the Cascade Range.

The Trans-Hudson orogeny or Trans-Hudsonian orogeny was the major mountain building event (orogeny) that formed the Precambrian Canadian Shield and the North American Craton, forging the initial North American continent. It gave rise to the Trans-Hudson orogen (THO), or Trans-Hudson Orogen Transect (THOT), which is the largest Paleoproterozoic orogenic belt in the world. It consists of a network of belts that were formed by Proterozoic crustal accretion and the collision of pre-existing Archean continents. The event occurred 2.0–1.8 billion years ago.

The Olympic–Wallowa lineament (OWL) is a series of geologic structures oriented from northwest to southeast for 650 km (400 mi) across Washington and northeast Oregon in the United States, passing through the Seattle area and including notable features east of the Cascade Range such as the Yakima Fold Belt and Wallowa Mountains. It was first reported by cartographer Erwin Raisz in 1945 on a relief map of the continental United States. Some geologists have questioned the existence of a geological relationship between the individual structures along the lineament suggesting it is an optical illusion. The origin of this feature in its entirety is not well understood with multiple hypotheses on the subject. The Olympic–Wallowa lineament likely predates the Columbia River Basalt Group.
This is a list of articles related to plate tectonics and tectonic plates.

The Ramapo Fault zone is a system of faults between the northern Appalachian Mountains and Piedmont areas to the east. Spanning more than 185 miles (298 km) in New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania, it is perhaps the best known fault zone in the Mid-Atlantic region, and some small earthquakes have been known to occur in its vicinity. Recently, public knowledge about the fault has increased, especially after the 1970s, when the fault's proximity to the Indian Point nuclear plant in New York was noted.
The Sierra Nevada–Great Valley Block (SNGV) is a section of the Earth's crust in California encompassing most of the region east of the Great Valley fault system which runs along the eastern foot of the Coast Ranges, and west of the Sierra Nevada Fault which runs along the foot of the Sierra Nevada's eastern scarp. To the south, the block is bounded by the Garlock Fault. The northern bound is not well defined at present, but generally runs along a line extending across the northern Sacramento Valley.

The Puget Sound faults under the heavily populated Puget Sound region of Washington state form a regional complex of interrelated seismogenic (earthquake-causing) geologic faults. These include the:
The Pharusian Ocean is an ancient ocean that existed on Earth from 800 to 635 million years ago, between the break-up of the Rodinia supercontinent and the start of formation of the Pannotia supercontinent.

Most of central and northern California rests on a crustal block (terrane) that is being torn from the North American continent by the passing Pacific plate of oceanic crust. Southern California lies at the southern end of this block, where the Southern California faults create a complex and even chaotic landscape of seismic activity.
The Romeral fault system is a megaregional system of major parallel and anastomosing faults in the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes and the Cauca, Amagá, and Sinú-San Jacinto Basins. The system spans across ten departments of Colombia, from northeast to south Bolívar, Sucre, Córdoba, Antioquia, Caldas, Risaralda, Quindío, Valle del Cauca, Cauca and Nariño. The fault zone extends into Ecuador where it is known as the Peltetec fault system. The in detail described part of the Romeral fault system south of Córdoba has a total length of 697.4 kilometres (433.3 mi) with a cumulative length of 1,787.9 kilometres (1,110.9 mi) and runs along an average north to south strike of 017.6 ± 16, cross-cutting the central-western portion of Colombia.

The geology of Kyrgyzstan began to form during the Proterozoic. The country has experienced long-running uplift events, forming the Tian Shan mountains and large, sediment filled basins.
The geology of Romania is structurally complex, with evidence of past crustal movements and the incorporation of different blocks or platforms to the edge of Europe, driving recent mountain building of the Carpathian Mountains. Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the southeast, Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, and Moldova to the east.
References
- ↑ https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/recenteqscanv/fault/197.html USGS . accessed 12.2.2010