Related Research Articles
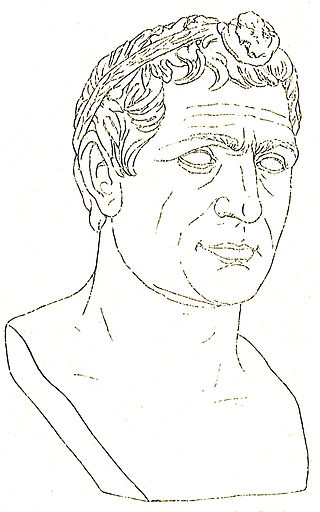
Agathocles was a Greek tyrant of Syracuse (317–289 BC) and self-styled king of Sicily (304–289 BC).

This article concerns the period 309 BC – 300 BC.
This article concerns the period 289 BC – 280 BC.

Ptolemy V Epiphanes Eucharistos was the King of Ptolemaic Egypt from July or August 204 BC until his death in 180 BC.
Timaeus of Tauromenium was an ancient Greek historian. He was widely regarded by ancient authors as the most influential historian between the time of Ephorus and Polybius. In the words of scholar Lionel I. C. Pearson, Timaeus "maintained his position as the standard authority on the history of the Greek West for nearly five centuries."

Demetrius I Anicetus, also called Damaytra was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek king, who ruled areas from Bactria to ancient northwestern India. He was the son of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom's ruler Euthydemus I and succeeded him around 200 BC, after which he conquered extensive areas in what is now southern Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan and India.

Lysimachus was a Thessalian officer and successor of Alexander the Great, who in 306 BC, became King of Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedon.

Burebista was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61 BC to 45/44 BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area located between the Danube, Tisza, and Dniester rivers, and modern day Romania and Moldova. In the 7th and 6th centuries BC it became home to the Thracian peoples, including the Getae and the Dacians. From the 4th century to the middle of the 2nd century BC the Dacian peoples were influenced by La Tène Celts who brought new technologies with them into Dacia. Sometime in the 2nd century BC, the Dacians expelled the Celts from their lands. Dacians often warred with neighbouring tribes, but the relative isolation of the Dacian peoples in the Carpathian Mountains allowed them to survive and even to thrive. By the 1st century BC the Dacians had become the dominant power.

Agathocles I Dicaeus was a Greco-Bactrian/Indo-Greek king, who reigned between around 190 and 180 BC, likely of the dynasty of Diodotus I, due to his commemoration of Antiochus Nicator.

Pantaleon, also known as Panteleimon (Παντελεήμων), was a Greek king who reigned some time between 190–180 BC in Bactria and India. He was a younger contemporary or successor of the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius, and is sometimes believed to have been his brother and/or subking.
Agathocles was a prince of Macedonian and Thessalian descent. He was the son of Lysimachus and his first wife, Nicaea a daughter of Antipater, the regent of Alexander the Great's Empire. His full blooded siblings were his younger sisters Eurydice and Arsinoe I.
Agathocles is a Greek name. The most famous person called Agathocles was Agathocles of Syracuse, the tyrant of Syracuse. The name is derived from Ancient Greek: ἀγαθός, romanized: agathos, lit. 'good' and Ancient Greek: κλέος, romanized: kleos, lit. 'glory'.

Samuil Micu Klein was a Romanian Greek-Catholic theologian, historian, philologist and philosopher, a member of the Enlightenment-era movement of Transylvanian School. He is the author of Elementa linguae daco-romanae sive valachicae, a book which is the reference point for the start of Modern Romanian language period.
Theoxena was a Greek Macedonian noblewoman. Through her mother's second marriage, she was a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty and through marriage was a queen of Sicily, Magna Graecia.
Archagathus was a Syracusan Greek Prince of Magna Graecia.
Archagathus was a Syracusan from Magna Graecia prince and Ptolemaic official who lived around the late second half of the 4th century BC and first half of the 3rd century BC.
Theoxena, also known as Theoxena the Younger to distinguish her from her mother, was a Syracusan Greek Princess of Magna Graecia and was a noblewoman of high status.
Ptolemy Epigonos was a Greek Prince from Asia Minor who was of Macedonian and Thessalian descent.

The Battle of White Tunis was fought between Carthage and the tyrant Agathocles of Syracuse in 310 BC. It was the first large battle of the Agathocles' military expedition to Libya. Even though heavily outnumbered by the Carthaginian army, the soldiers of Agathocles were far more experienced in warfare than the Carthaginian citizen soldiers. Another important factor was the terrain, which prevented the Carthaginians from using their numbers to outflank Agathocles. The Carthaginian suffered a serious defeat, which caused some of the Carthaginian allies to change their allegiance to Agathocles.

Post-Mauryan coinage refers to the period of coinage production in India, following the breakup of the Maurya Empire.
References
- Dicţionar de istorie veche a României ("Dictionary of ancient Romanian history") (1976) Editura Ştiinţifică şi Enciclopedică, pp. 504