Related Research Articles
The Romanian state was formed in 1859 through a personal union of the Danubian Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia. The new state, officially named Romania since 1866, gained independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1877. During World War I, after declaring its neutrality in 1914, Romania fought together with the Allied Powers from 1916. In the aftermath of the war, Bukovina, Bessarabia, Transylvania, and parts of Banat, Crișana, and Maramureș became part of the Kingdom of Romania. In June–August 1940, as a consequence of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact and Second Vienna Award, Romania was compelled to cede Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina to the Soviet Union and Northern Transylvania to Hungary. In November 1940, Romania signed the Tripartite Pact and, consequently, in June 1941 entered World War II on the Axis side, fighting against the Soviet Union until August 1944, when it joined the Allies and recovered Northern Transylvania.

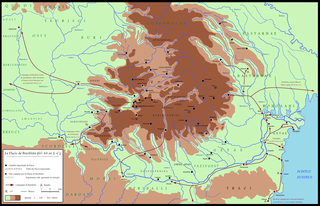
Sarmizegetusa Regia was the capital and the most important military, religious and political centre of the Dacians before the wars with the Roman Empire. Built on top of a 1200 m high mountain, the fortress, consisting of six citadels, was the core of a strategic and defensive system in the Orăștie Mountains.

The Dacians were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area includes mainly the present-day countries of Romania and Moldova, as well as parts of Ukraine, Eastern Serbia, Northern Bulgaria, Slovakia, Hungary and Southern Poland. The Dacians and the related Getae spoke the Dacian language, which has a debated relationship with the neighbouring Thracian language and may be a subgroup of it. Dacians were somewhat culturally influenced by the neighbouring Scythians and by the Celtic invaders of the 4th century BC.

Burebista was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61 BC to 45/44 BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area located between the Danube, Tisza, and Dniester rivers, and modern day Romania and Moldova. In the 7th and 6th centuries BC it became home to the Thracian peoples, including the Getae and the Dacians. From the 4th century to the middle of the 2nd century BC the Dacian peoples were influenced by La Tène Celts who brought new technologies with them into Dacia. Sometime in the 2nd century BC, the Dacians expelled the Celts from their lands. Dacians often warred with neighbouring tribes, but the relative isolation of the Dacian peoples in the Carpathian Mountains allowed them to survive and even to thrive. By the 1st century BC the Dacians had become the dominant power.

Balchik is a town and seaside resort on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast in the Southern Dobruja area of northeastern Bulgaria. It is in Dobrich Province, 35 km southeast of Dobrich and 42 km northeast of Varna. It sprawls scenically along hilly terraces descending from the Dobruja plateau to the sea, and is often called "The White City" because of its white cliffs.

Argedava was potentially an important Dacian town mentioned in the Decree of Dionysopolis (48 BC), and maybe located at Popești, a district in the town of Mihăilești, Giurgiu County, Muntenia, Romania.

The Burs were a Dacian tribe living in Dacia in the 1st and 2nd centuries A.D., with their capital city at Buridava.

Mihăilești is a town located in Giurgiu County, Muntenia, Romania. It administers three villages: Drăgănescu, Novaci and Popești. It officially became a town in 1989, as a result of the Romanian rural systematization program.
Teurisci was a Dacian tribe at the time of Ptolemy. They were originally considered a branch of the Celtic Taurisci (Noricum), who moved to Upper Tisza. However, the archaeology shows that Celts have been absorbed by Dacians, at some point creating a Celto-Dacian cultural horizon in the upper Tisza.

Argidava was a Dacian fortress town close to the Danube, inhabited and governed by the Albocense. Located in today's Vărădia, Caraș-Severin County, Romania.
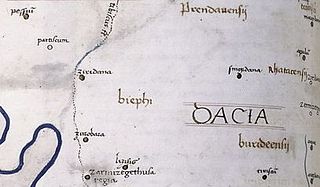
Zurobara was a Dacian town located in the northwest of today's Romanian Banat. It was positioned by the Tibiscus (Timiș) river, north of Sarmizegetusa Regia and south of Ziridava.

Dava was a Geto-Dacian name for a city, town or fortress. Generally, the name indicated a tribal center or an important settlement, usually fortified. Some of the Dacian settlements and the fortresses employed the Murus Dacicus traditional construction technique.
Akornion was an important citizen of the Ionian Greek colony of Dionysopolis.
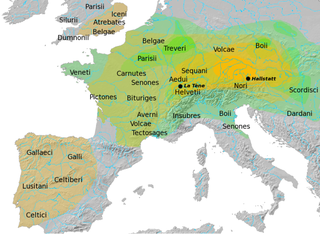
The appearance of Celts in Transylvania can be traced to the later La Tène period . Excavation of the great La Tène necropolis at Apahida, Cluj County, by S. Kovacs at the turn of the 20th century revealed the first evidence of Celtic culture in Romania. The 3rd–2nd century BC site is remarkable for its cremation burials and chiefly wheel-made funeral vessels.

Romanian archaeology begins in the 19th century.

Milliarium of Aiton is an ancient Roman milliarium (milestone) discovered in the 1758 in Aiton commune, near Cluj-Napoca, Romania. Dating from 108 AD, shortly after the Roman conquest of Dacia, the milestone shows the construction of the road from Potaissa to Napoca, by demand of the Emperor Trajan. It indicates the distance of ten thousand feet (P.M.X.) to Potaissa. This is the first epigraphical attestation of the settlements of Potaissa and Napoca in Roman Dacia.

Ziridava was a Dacian town located between Apulon and Tibiscum, mentioned by Ptolemy in the area of the Dacian tribe of Biephi.
This section of the timeline of Romanian history concerns events from Late Neolithic until Late Antiquity, which took place in or are directly related with the territory of modern Romania.
The history of Dacia comprises the events surrounding the historical region roughly corresponding to the present territory of Romania and Moldova and inhabited by the Getae and Dacian peoples, with its capital Sarmizegetusa Regia.
References
- Crisan, Ion Horatiu (1978). "Burebista and His Time". Bucharest: Bibliotheca Historica Romaniae.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - Daicoviciu, Hadrian (1972). "Dacii". Bucharest: Editura Enciclopedica Româna.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - Mihailov, Georgi (1970). "Inscriptiones graecae in Bulgaria repertae" (in Latin and Ancient Greek). 1 (2nd ed.). Sofia: In aedibus typographicis Academiae Litterarum Bulgaricae.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Oltean, Ioana Adina (2007). Dacia: landscape, colonisation and romanisation. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-41252-0.
- Pârvan, Vasile (1923). Consideraţiuni asupra unor nume de râuri daco-scitice (PDF). Bucharest. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-09-17. Retrieved 2011-10-19.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Dittenberger, Wilhelm (1898). Sylloge Inscriptionum Graecarum. Vol. 2 (2 ed.). Leipzig.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Dittenberger, Wilhelm; Hiller, Friedrich (1917). Sylloge Inscriptionum Graecarum. Vol. 2 (3 ed.). Leipzig.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Kalinka, Ernst (1905). "Antike Denkmäler in Bulgaria". Schriften der Balkankommission. Vol. 4. Vienna.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)