
Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of pelagic fish, mostly from the family Scombridae. They are found in both temperate and tropical seas, mostly living along the coast or offshore in the oceanic environment.

Carcharhiniformes, the ground sharks, are the largest order of sharks, with over 270 species. They include a number of common types, such as catsharks, swellsharks, and the sandbar shark.

Schindleria is a genus of marine fish. It was the only genus of family Schindleriidae, among the Gobioidei of order Perciformes but is now classified under the Gobiidae in the Gobiiformes. The type species is S. praematura, Schindler's fish. The Schindleria species are known generically as Schindler's fishes after German zoologist Otto Schindler (1906–1959), or infantfishes. They are native to the southern Pacific Ocean, from the South China Sea to the Great Barrier Reef off eastern Australia.

Citharichthys is a genus of flatfish in the large-tooth flounder family, Paralichthyidae. They have both eyes on the left sides of their heads. They are native to the oceans around the Americas, with a single species, C. stampflii off the West African coast. Most are found in relatively shallow depths, but the genus also includes species found in deep water and species that enter fresh water.

Eleotridae is a family of fish commonly known as sleeper gobies, with about 34 genera and 180 species. Most species are found in the tropical Indo-Pacific region, but there are also species in subtropical and temperate regions, warmer parts of the Americas and near the Atlantic coast in Africa. While many eleotrids pass through a planktonic stage in the sea and some spend their entire lives in the sea; as adults, the majority live in freshwater streams and brackish water. One of its genera, Caecieleotris, is troglobitic. They are especially important as predators in the freshwater stream ecosystems on oceanic islands such as New Zealand and Hawaii that otherwise lack the predatory fish families typical of nearby continents, such as catfish. Anatomically, they are similar to the gobies (Gobiidae), though unlike the majority of gobies, they do not have a pelvic sucker.
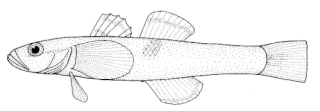
Graham's gudgeon, Grahamichthys radiata, is a species of goby of the family Thalasseleotrididae, the only member of the genus Grahamichthys. This species is found in rock pools and in the neritic zone, to 50 metres (160 ft) in depth, where sand or mud is lies around and partially buries rocks, shells, or other objects. It is unusual for a goby, in that it lives in loose schools. The generic name is a compound formed from the surname Graham in honour of David H. Graham who wrote A Treasury of New Zealand Fishes which was published in 1953 and therefore is an allusion to this taxon being endemic to New Zealand and the Greek ichthys meaning "fish".
Awaous is a genus of fish in the family Gobiidae, the gobies. They are native to fresh, marine and brackish waters from Africa to the Americas.

The leaf goblinfish is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a waspfish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. This is the only species in the monotypic genus Neovespicula. It is found in coastal habitats of the Indo-West Pacific region.
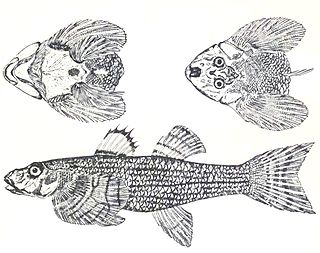
The loach goby, Rhyacichthys aspro, is a goby belonging to the family Rhyacichthyidae. It is not fished commercially.

Fish are very diverse animals and can be categorised in many ways. This article is an overview of some of ways in which fish are categorised. Although most fish species have probably been discovered and described, about 250 new ones are still discovered every year. According to FishBase about 34,800 species of fish had been described as of February 2022, which is more than the combined total of all other vertebrate species: mammals, amphibians, reptiles and birds.

Rhyacichthys is a genus of fish belonging to the family Rhyacichthyidae. They occur in the Indo-Pacific region.
Rhyacichthys guilberti is a goby belonging to the family Rhyacichthyidae. This fish only occurs in the Northern Province of New Caledonia and in Vanuatu. It is found in only two rivers. Its maximum standard length of about 240 mm. Its population on New Caledonia was estimated at less than 400 individuals, but it is now thought to have been extirpated from that island, it remains common on Vanuatu.
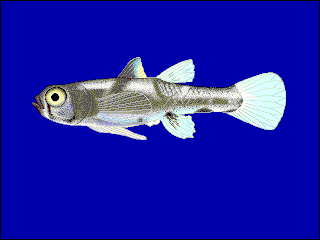
Pandaka is a genus of fish in the goby subfamily, Gobionellinae, native to fresh, brackish and marine waters of Asia and the western Pacific Ocean. Some species in the genus are among the smallest fish in the world; the male P. pygmaea can be just 9 mm (0.35 in) in standard length at maturity.

Milyeringidae, the blind cave gobies, is a small family of gobies, in the order Gobiiformes. There are two genera and six species within the family, which is considered to be a subfamily of the Eleotridae by some authorities. Milyeringidae includes one genus (Milyeringa) restricted to caves in the North West Cape region of Australia and the other (Typhleotris) to underground water systems in Madagascar. They are all troglobitic species and have lost their eyes.
Protogobius attiti is a species of loach goby which is endemic to nine rivers in South Province, New Caledonia. It occurs in rivers with ultramafic beds. It prefers areas where there is a gravel substrate under overhanging vegetation in slower reaches of fast flowing, clear streams. The rocks and gravel in the areas in which it occurs are usually coated with detritus. When threatened it buries itself in the gravel leaving its eyes, mouth and first dorsal fin above the substrate. Its main prey is small freshwater crustaceans, especially the abundant transparent shrimp which occur in these streams. It is threatened by nickel mining which creates sediments which blanker the rocks on which it hides and destroys the algae its prey feed on. The specific name honours a Melanesian chief of Goro, New Caledonia.
Belobranchus segura is a species of eleotrid sleeper goby which has been found in Indonesia on Halmahera, in Papua Barat and also on the Solomon Islands. It is an anadromous species in which the eggs are laid over rocky and gravel bottoms in freshwater streams. The free-swimming larvae then drift downstream to the sea where they undergo a planktonic stage before migrating up streams to mature and breed. It feeds on small crustaceans and fish. The specific name honours the French hydrobiologist Gilles Segura for his contribution to the study of fish faunas.

Thalasseleotris is a genus of gobies comprising two species in the family Thalasseleotrididae from the south-western Pacific Ocean in the seas off Australia and New Zealand. The generic name is derived from the Greek Thalassa meaning "sea" and the generic name Eleotris as at the time it was named the genus was considered to be in the family Eleotridae.
The Wirz's goby, Oxuderces wirzi, is a species of goby found in Oceania from Papua New Guinea and northern Australia.

Oxuderces dentatus, is a species of goby found in the Indo-West Pacific from India, to Viet Nam, to Macao, China, Malaysia and Indonesia.













