
Automobile roads in Belarus are classified into several categories.

Automobile roads in Belarus are classified into several categories.
The state-owned roads of common access are managed by the Belavtodor department of the Ministry of Transport and Communications of Belarus. [1] They are classified into republican roads and local roads. Automobile roads may also be owned by persons, businesses, state enterprises, and military.
Belarus has an extensive system of 4-laned dual carriageways and expressways, currently in expansion. Currently they are:
| Highway | Route | Length | European road | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Border of Poland at Brest – Minsk to border with Russia (on to Moscow) | 611 km (380 mi) | (entire route) | Entrances to Dziaržynsk, Pružany, Brest Airport, Brest, Kobryn |
| | Minsk – Minsk International Airport | 34 km (21 mi) | ||
| | Minsk – Viciebsk | 253 km (157 mi) | Entrances to Lahojsk, "Khatyn" memorial complex and Biešankovičy | |
| | Minsk – Smilavičy – Červień – Bierazino – Mahilioŭ | 182 km (113 mi) | Entrance to Mahilioŭ Airport | |
| | Minsk – Homieĺ | 282 km (175 mi) | (entire route) | Entrances to Babrujsk and Žlobin |
| | Minsk – Lida – Hrodna to the border with Poland | 262 km (163 mi) | (Minsk–Volozhin) | Entrances to Valožyn, Lida, Hrodna Airport and Hrodna |
| | Minsk – Border with Lithuania at Kammeny Log | 139 km (86 mi) | (entire route) | Concurrent with M6 from Minsk to Volozhin; entrance to Volozhin |
| | Border with Russia at Ezerische via Vitebsk, Orsha, Mogilev, and Gomel to border with Ukraine at Nowa Huta | 456 km (283 mi) | (entire route) | Entrances to Vitebsk Airport, Orsha, Kopysov, Shklov, Mogilev, Bykhov and Gomel |
| | Ring road around Minsk | 56 km (35 mi) | Entrance to pension | |
| | Border with Russia – Gomel – Kalinkavichy – Pinsk – Kobryn | 526 km (327 mi) | Entrances to Gomel, Petrikov, Zhitkovichi and Luninets | |
| | Border with Lithuania at Benyakoni – Lida – Slonim – intersection with P2 near Byten | 186 km (116 mi) | (entire route) | Entrance to "Radon" sanatorium |
| | Kobryn – border with Ukraine at Mokrany | 55 km (34 mi) | (entire route) | |
| | Outer ring road around Minsk | 160 km (99 mi) (planned) 47 km (29 mi) (in operation) | Vitebsk–Grodno section opened in 2015 | |

Vitebsk Region or Vitebsk Oblast or Viciebsk Voblasts is a region (oblast) of Belarus with its administrative center being Vitebsk. It is located near the border with Russia.

Minsk Region or Minsk Oblast or Minsk Voblasts is one of the regions of Belarus. Its administrative center is Minsk, although it is a separate administrative territorial entity of Belarus. As of 2011, the region's population is 1,411,500.

Operation Bagration was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation, a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front of World War II, just over 2 weeks after the start of Operation Overlord in the west, causing the Germans to have to fight on two major fronts at the same time. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of 34 divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. It was the biggest defeat in German military history, with around 450,000 German casualties, while 300,000 other German soldiers were cut off in the Courland Pocket.

Orsha is a city in Belarus in the Vitebsk Region, on the fork of the Dnieper and Arshytsa rivers.

The 16th Army was a field army of the Red Army during the Russian Civil War era. It was originally formed as the Western Army on November 15, 1918, by the Russian SFSR for the purpose of recovering territories lost by the Russian Empire during the First World War and establishing Soviet republics in those territories. The Western Army engaged various local forces from the Baltic States, Belarus, Poland and Ukraine, and its actions contributed to starting the Polish–Soviet War of 1919–1920. The army fought in the Polish–Soviet War under the command of Nikolai Sollogub and advanced westwards into Poland in July 1920 before being thrown back during the Battle of Warsaw in August. The army retreated east into Belarus and was disbanded in May 1921.

The Russo-Polish War of 1654–1667, also called the Thirteen Years' War and the First Northern War, was a major conflict between the Tsardom of Russia and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Between 1655 and 1660, the Swedish invasion was also fought in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and so the period became known in Poland as "The Deluge" or Swedish Deluge.
The Pripyat Marshes massacres were a series of mass murders, carried out by German military forces, against Jewish civilians in Belarus and Ukraine, during July–August 1941. SS leader Heinrich Himmler ordered these operations, which were carried out by units of the Wehrmacht. These units were ordered to kill as many Jews as possible, in a region in and around the Pripyat Marshes, comprising nine raions of the Byelorussian SSR and three raions of the Ukrainian SSR.

The Vitebsk–Orsha offensive was part of the Belorussian strategic offensive of the Red Army in summer 1944, commonly known as Operation Bagration. During the offensive, Soviet troops captured Vitebsk and Orsha. A Soviet breakthrough during the offensive helped achieve the encirclement of German troops in the subsequent Minsk offensive.

The European route E95 is a road in Europe and a part of the United Nations International E-road network. Approximately 2,527 kilometres (1,570 mi) long, it connects St Petersburg with Merzifon in north central Turkey. Between its northern terminus in Russia and its southern end, it passes in addition through Belarus and Ukraine. Between the ports of Odessa / Chornomorsk on Ukraine's southern coast and ports of Turkey vehicles are required to cross the Black Sea by ferry over a distance of 731 kilometres (454 mi).
The Battle of Ula or Battle of Chashniki was fought during the Livonian War on 26 January 1564 between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Tsardom of Russia on the Ula River north of Chashniki in the Vitebsk Region. The Russian troops, unarmed and moving in a loose formation, were taken by complete surprise and defeated, losing their large wagon train.
2012–13 Belarusian Cup was the twenty second season of the Belarusian annual cup competition. Contrary to the league season, it is conducted in a fall-spring rhythm. The first games were played on 13 June 2012. Winners of the Cup qualified for the second qualifying round of the 2013–14 UEFA Europa League.

In the history of Poland, a royal city or royal town was an urban settlement within the crown lands.
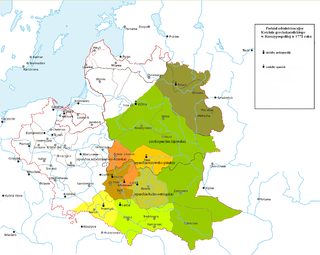
The Archeparchy of Polotsk(-Vitebsk) was an eparchy of the Ruthenian Uniate Church in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1596 to 1839.
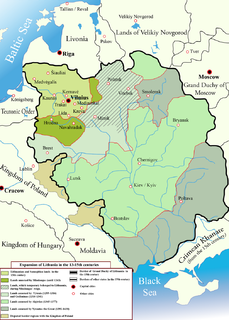
The Lithuanian-Muscovite War of 1512-1522 was a military conflict between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Ruthenia, which included Ukrainian and Belarusian lands, and the Grand Duchy of Moscow for Russian border lands.
Lithuanians in Belarus have a long history, as Belarus was part of Lithuania for more than half a millenium from the 13th century onwards. The land of what is now Belarus was originally inhabited by Balts, while Slavs arrived to those lands only during the late Early Middle Ages.