
Bury St Edmunds, commonly referred to locally as Bury is a cathedral as well as market town and civil parish in the West Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England. The town is best known for Bury St Edmunds Abbey and St Edmundsbury Cathedral. Bury is the seat of the Diocese of St Edmundsbury and Ipswich of the Church of England, with the episcopal see at St Edmundsbury Cathedral. In 2011 it had a population of 45,000. The town, originally called Beodericsworth, was built on a grid pattern by Abbot Baldwin around 1080. It is known for brewing and malting and for a British Sugar processing factory, where Silver Spoon sugar is produced. The town is the cultural and retail centre for West Suffolk and tourism is a major part of the economy.

St Edmundsbury was a local government district and borough in Suffolk, England. It was named after its main town, Bury St Edmunds. The second town in the district was Haverhill. The population of the district was 111,008 at the 2011 Census.
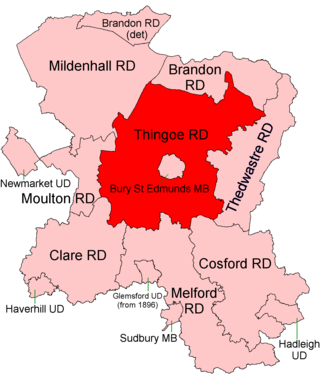
Thingoe Rural District was a rural district in the county of West Suffolk, England between 1894 and 1974. It was named after the ancient Hundred of Thingoe and administered from Bury St Edmunds, which it surrounded.

Bury St Edmunds was a constituency in Suffolk from 1621 to 2024, most recently represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament from 2015 to 2024 by Jo Churchill, a Conservative.

Troston is a village and civil parish in Suffolk, England, five miles north-east of Bury St Edmunds. Its parish church contains rare mediaeval wall paintings, including dragon-slaying and the Martyrdom of St Edmund.

Culford is a village and civil parish about 4 miles (6 km) north of Bury St Edmunds and 62 miles (100 km) north east of London in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk, England.

Whepstead is a village and civil parish in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England, located south of Bury St Edmunds. Once the property of Bury Abbey it became a possession of the Drury family at the Dissolution of the Monasteries in the 16th century. Whepstead Church is dedicated to St Petronilla the only such dedication in England.

Ampton is a village and civil parish in the West Suffolk District of Suffolk, England, about five miles north of Bury St Edmunds.
Bradfield Combust with Stanningfield is a civil parish about 6 miles south of Bury St Edmunds, in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk, England.
The Saxhams is a civil parish in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England. Located around two miles west of Bury St Edmunds, the parish covers the villages of Great Saxham and Little Saxham, as well as the Saxham Industrial Estate on the A14. In 2005 its population was 300. The parish was formed in 1998 from "Great Saxham" and "Little Saxham" and part of Risby.

Ixworth is a village and civil parish in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk, England, 6 miles (9.7 km) north-east of Bury St Edmunds on the A143 road to Diss and 9 miles (14 km) south-east of Thetford. The parish had a population of 2,365 at the 2011 Census.

Westley is a village and civil parish in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England. It is located south of Junction 42 of the A14 providing primary access to adjacent market towns Bury St Edmunds (East) and Newmarket (West). The village consists of two central roads: Fornham Lane and Hill Road running north and south through the parish, with adjoining roads accommodating Westley's total population of 183.

Ousden is a village and civil parish in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England. It is located around 6 miles (10 km) west of Bury St Edmunds and 72 miles (116 km) north of London, and as of 2011, its population is 266. The village has an Anglican church of St Peter's and a chapel in the cemetery dedicated to St Barnabas.

Nowton is a small village and civil parish in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England. Located on the southern edge of Bury St Edmunds, in 2005 its population was estimated to be 140. At the 2011 census 163 people were recorded as living in the village.

Hawkedon is a village and civil parish in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England. Located around 7 miles (11 km) south-south-west of Bury St Edmunds, the parish also contains the hamlet of Thurston End, and in 2005 had a population of 120. The majority of the village is classed as a conservation area.

The Davers Baronetcy, of Rougham in the County of Suffolk, was a title in the Baronetage of England. It was created on 12 May 1682 for Robert Davers, who had made a great fortune in Barbados as a plantation owner before acquiring the Rougham estate in Suffolk. The second and fourth Baronets represented Bury St Edmunds and Suffolk in Parliament. The sixth Baronet sat as Member of Parliament for Weymouth and Bury St Edmunds. Despite having an alleged nine illegitimate children, the 6th Baronet left his estates to his nephew, Frederick Hervey, 1st Marquess of Bristol, and his baronetcy became extinct.

West Suffolk District is a local government district in Suffolk, England. It was established in 2019 as a merger of the previous Forest Heath District with the Borough of St Edmundsbury. The council is based in Bury St Edmunds, the district's largest town. The district also contains the towns of Brandon, Clare, Haverhill, Mildenhall and Newmarket, along with numerous villages and surrounding rural areas. In 2021 it had a population of 180,820.

Rougham is a village and former civil parish 19 miles (31 km) north west of Ipswich, now in the parish of Rushbrooke with Rougham, in the West Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England. Until April 2019 Rougham was in the St Edmundsbury district. In 1961 the parish had a population of 777. Rougham is also a ward, in 2011 the ward had a population of 2341. The ward touches Chadacre, Thurston, Rattlesden, The Fornhams & Great Barton, Moreton Hall, Lavenham, Horringer and Southgate. Rougham is pronounced "Ruff'm". In 1958 the parish had settlements at Mouse Lane estate, Rougham Green, Kingshall Street and Chapmans Close.

Rushbrooke is a village and former civil parish on the River Lark, 20 miles (32 km) north west of Ipswich, now in the parish of Rushbrooke with Rougham, in the West Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England. Until April 2019 Rushbrooke was in the St Edmundsbury district. In 1961 the parish had a population of 58.
Thingoe South Division is an electoral division in Suffolk which returns one county councillor to Suffolk County Council.


















