
Syracuse is a city in and the county seat of Onondaga County, New York, United States. It is the fifth-most populous city in the state of New York following New York City, Buffalo, Rochester, and Yonkers.

The State University of New York is a system of public institutions of higher education in New York. It is the largest comprehensive system of universities, colleges, and community colleges in the United States, with a total enrollment of 424,051 students, plus 2,195,082 adult education students, spanning 64 campuses across the state. Led by Chancellor Kristina M. Johnson, the SUNY system has 91,182 employees, including 32,496 faculty members, and some 7,660 degree and certificate programs overall and a $10.7 billion budget. The University at Buffalo, founded by U.S. President Millard Fillmore, is the SUNY campus with the highest enrollment, most number of applicants and an endowment more than double of any other SUNY.

The State University of New York at Binghamton, is a public research university with campuses in Binghamton, Vestal, and Johnson City, New York. It is one of the four university centers in the State University of New York (SUNY) system. As of Fall 2018, 17,768 undergraduate and graduate students attend the university.

Upstate New York is the portion of the U.S. state of New York lying north of the New York metropolitan area. The Upstate region includes most of the land area of the state of New York, but a minority of the state's population. Although the precise boundary is debated, Upstate New York excludes New York City and Long Island, and most definitions of the region exclude all or part of Westchester and Rockland counties. Major cities in Upstate New York, from east to west, include Albany, Utica, Binghamton, Syracuse, Rochester, and Buffalo.

The State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry (ESF) is a public university in Syracuse, New York. It is part of the State University of New York (SUNY) system. ESF is immediately adjacent to Syracuse University, within which it was founded, and with whom it maintains a special relationship. It also operates facilities in the Adirondack Park, the Thousand Islands, elsewhere in central New York, and Costa Rica. The college's curricula focus on the understanding, management, and sustainability of the environment and natural resources.

The New York State College of Veterinary Medicine is a college of veterinary medicine at Cornell University, Ithaca, New York. Founded in 1894, it is the first statutory college established by the State University of New York (SUNY) system.

Central New York is the central region of New York State, roughly including the following counties and cities:

SUNY Downstate Health Sciences University (Downstate) is a public medical school and hospital in New York City. It is part of the State University of New York (SUNY) system and the only academic medical center for health education, research, and patient care serving Brooklyn’s 2.5 million residents. As of Fall 2018, it had a total student body of 1,846 and approximately 8,000 faculty and staff.
Albany Medical College (AMC) is a medical school located in Albany, New York, United States. It was founded in 1839 by Alden March and James H. Armsby and is one of the oldest medical schools in the nation. The college is part of the Albany Medical Center, which includes the Albany Medical Center Hospital.
Herman Gates Weiskotten (1884-1972) served as dean of Syracuse University medical school from 1922 to 1951. During his final year, the school had been renamed SUNY Upstate Medical University.
The University of the State of New York (USNY), its policy-setting Board of Regents, and its administrative arm, the New York State Education Department, oversee all public primary, middle-level, and secondary education in the state. The New York City Department of Education, which manages the public school system in New York City, is the largest school district in the United States, with more students than the combined population of eight U.S. states. Over 1 million students are taught in more than 1,200 separate schools.
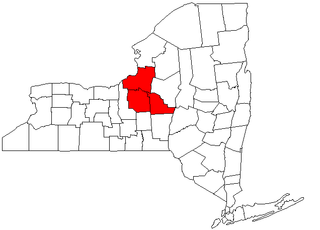
The Syracuse Metropolitan Statistical Area, as defined by the United States Census Bureau, is an area consisting of three counties in central New York, anchored by the city of Syracuse. As of the 2010 census, the MSA had a population of 662,577. In the 2000 census, the MSA had a population of 650,154.

Geneva Medical College was founded on September 15, 1834, in Geneva, New York, as a separate department (college) of Geneva College, currently known as Hobart and William Smith Colleges. In 1871, the medical school was transferred to Syracuse University in Syracuse, New York. In 1950, the university sold the college to the State University of New York (SUNY) for $1, where it remains today.

Michael M. Meguid is Professor of Surgery Emeritus at Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, New York.

University Hill is a neighborhood and business district in Syracuse, New York, located east and southeast of Downtown Syracuse, on one of the larger hills in Syracuse. The neighborhood is bounded on the west by Almond Street and Interstate 81. It continues east to Ostrom Avenue and Thornden Park, where it borders the Westcott and University neighborhoods. Interstate 690 currently serves as the neighborhood's northern boundary.
Frank Aram Oski was an American pediatrician. After holding several faculty positions at medical schools, he spent several years as the chair of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. He was the founder and editor of the journal Contemporary Pediatrics, and he edited one of the most widely read textbooks in pediatrics.
Patricia Joy Numann is an American endocrine surgeon. She is the founder of the Association of Women Surgeons, former president of the American College of Surgeons, and professor emeritus at the State University of New York Upstate Medical University.

Hezekiah Joslyn was an American physician and abolitionist.



















