
Myles Standish was an English military officer and colonist. He was hired as military adviser for Plymouth Colony in present-day Massachusetts, United States by the Pilgrims. Standish accompanied the Pilgrims on the ship Mayflower and played a leading role in the administration and defense of Plymouth Colony from its foundation in 1620. On February 17, 1621, the Plymouth Colony militia elected him as its first commander and continued to re-elect him to that position for the remainder of his life. Standish served at various times as an agent of Plymouth Colony on a return trip to England, as assistant governor of the colony, and as its treasurer.

East Bridgewater is a town in Plymouth County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 14,440 at the 2020 census. It is also a part of Massachusetts' 8th congressional district, of which it is represented by Stephen Lynch.

Plymouth Colony was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on the Mayflower at a location that had previously been surveyed and named by Captain John Smith. The settlement served as the capital of the colony and developed as the town of Plymouth, Massachusetts. At its height, Plymouth Colony occupied most of the southeastern portion of Massachusetts. Many of the people and events surrounding Plymouth Colony have become part of American folklore, including the American tradition of Thanksgiving and the monument of Plymouth Rock.

Massasoit Sachem or Ousamequin was the sachem or leader of the Wampanoag confederacy. Massasoit means Great Sachem. Massasoit was not his name but a title. English colonists mistook Massasoit as his name and it stuck.

The Spencer–Peirce–Little Farm is a Colonial American farm located at 5 Little's Lane, Newbury, Massachusetts, United States, in the midst of 231 acres (93 ha) of open land bordering the Merrimack River and Plum Island Sound. The farmhouse, dating to c. 1690, was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1968 as an extremely rare 17th-century stone house in New England. It is now a nonprofit museum owned and operated by Historic New England and open to the public several days a week during the warmer months; an admission fee is charged for non Members.
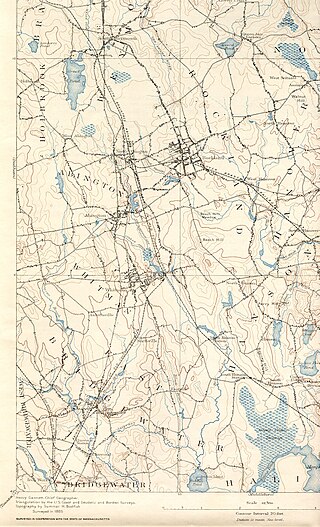
The Satucket River is 5.5-mile-long (8.9 km) river in southeastern Massachusetts within the Taunton River Watershed. It flows generally west from Robbins Pond in East Bridgewater, and into the Matfield River.

The Bay Circuit Trail and Greenway or Bay Circuit is a Massachusetts rail trail and greenway connecting the outlying suburbs of Boston from Plum Island in Newburyport to Kingston Bay in Duxbury, a distance of 200 miles (320 km).

Cole's Hill is a National Historic Landmark containing the first cemetery used by the Mayflower Pilgrims in Plymouth, Massachusetts in 1620. The hill is located on Carver Street near the foot of Leyden Street and across the street from Plymouth Rock. Owned since 1820 by the preservationist Pilgrim Society, it is now a public park.

Ross Farm is a historic farmhouse at 123 Meadow Street in Northampton, Massachusetts. Its importance rests in its significance as the site of a utopian community that operated there from 1841 to 1845, and for its use as a site on the Underground Railroad. Once part of a 300-acre (120 ha) parcel, the property has been reduced to 2.25 acres (0.91 ha), whose only significant structure is the farmhouse which was built in 1825.

Burial Hill is a historic cemetery or burying ground on School Street in Plymouth, Massachusetts. Established in the 17th century, it is the burial site of several Pilgrims, the founding settlers of Plymouth Colony. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2013.

Brook Farm is a historic country estate farm at 4203 Twenty Mile Stream Road in Cavendish, Vermont. It includes one of the state's grandest Colonial Revival mansion houses, and surviving outbuildings of a model farm of the turn of the 20th century. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1993. The property is now home to the Brook Farm Vineyard.

The Clymer House is a historic house at 31 Clymer Road in Harrisville, New Hampshire. Built in 1932, it is a finely crafted example of Colonial Revival architecture, built in conscious imitation of an earlier form that might have occupied the same site. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1988.

The Frost Farm is a historic farmstead at 18 Fairwood Drive in Dublin, New Hampshire, United States. Built in 1855 and extensively restyled in 1910, it is a good example of a Georgian Revival summer house, with expansive views of nearby Mount Monadnock. The property was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1983. It is now home to the Fairwood Bible Institute.

The Crows Nest is a historic farmstead property at 35 Sturgis Drive in Wilmington, Vermont. The 75-acre (30 ha) property includes rolling woods and a hay meadow, and a small cluster of farm outbuildings near the main house, a c. 1803 Cape style building. The property typifies early Vermont farmsteads, and is now protected by a preservation easement. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1998.

The Fox–Cook Farm is a historic farm property on Cook Drive in Wallingford, Vermont. Established in the 1790s, it is one of the oldest surviving farmsteads in the Otter Creek valley south of Wallingford village. It includes a c. 1800 Cape style farmhouse and a c. 1850 barn, among other outbuildings. The property was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1986.

The Isaac M. Raymond Farm, now Uphill Farm, is a historic farm property on North Bridgewater Road in Woodstock, Vermont, United States. The farm is the reduced core of a larger farm property accumulated in the first half of the 19th century by Isaac Raymond, and revived as a gentleman's farm in 1940. The property includes an altered 1805 Cape style farmhouse and 20th-century Colonial Revival farm buildings. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1993.

Field Farm is a historic farm property on Fuller Mountain Road in Ferrisburgh, Vermont. Developed around the turn of the 19th century, the property includes an early farmhouse and barn, as well as outbuildings representative of Vermont's trends in agriculture over two centuries. The property was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1995.

The Woodbridge Farm is a historic farm property on Woodbridge Road in Salem, Connecticut. The property was developed by Nathaniel Woodbridge in 1791, and it had more than 200 years of cultivation, and many decades of ownership by the Woodbridge family. The property includes an early farmstead, remade in the early 20th century into a Colonial Revival country house. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1997.

Myles Standish Park is a municipal park in the town of Duxbury, Massachusetts. It consists of a 1-acre (0.40 ha) parcel of land encompassing the former site of the home of the early Pilgrim settler Myles Standish. The park was established in 1929 after the land was given to the town by the Myles Standish Monument Association. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2021.

The Anthony–Corwin Farm is a historic farmhouse located at 244 West Mill Road near Long Valley in Washington Township, Morris County, New Jersey. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on May 1, 1992, for its significance in architecture. The 11.5-acre (4.7 ha) farm overlooks the valley formed by the South Branch Raritan River. The farmhouse is part of the Stone Houses and Outbuildings in Washington Township Multiple Property Submission (MPS).























