
Salak is a species of palm tree native to Java and Sumatra in Indonesia. It is cultivated in other regions of Indonesia as a food crop, and reportedly naturalized in Bali, Lombok, Timor, Maluku, and Sulawesi.

Pinus wallichiana is a coniferous evergreen tree native to the Himalaya, Karakoram and Hindu Kush mountains, from eastern Afghanistan east across northern Pakistan and north west India to Yunnan in southwest China. It grows in mountain valleys at altitudes of 1800–4300 m, reaching 30–50 m (98–164 ft) in height. It favours a temperate climate with dry winters and wet summers. In Pashto, it is known as Nishtar.

Salacca is a genus of about 20 species of palms native to Southeast Asia and the eastern Himalayas. They are dioecious and pollinated by Curculionidae beetles.

Ulmus wallichianaPlanch., the Himalayan elm, also known as the Kashmir elm and Bhutan elm, is a mountain tree ranging from central Nuristan in Afghanistan, through northern Pakistan and northern India to western Nepal at elevations of 800–3000 m. Although dissimilar in appearance, its common name is occasionally used in error for the cherry bark elm Ulmus villosa, which is also endemic to the Kashmir, but inhabits the valleys, not the mountain slopes. The species is closely related to the wych elm U. glabra.

Ulmus 'Lobel' is a Dutch hybrid cultivar raised at the Dorschkamp Research Institute for Forestry & Landscape Planning, Wageningen, from a crossing of clone '202' with '336'. 'Lobel' was cloned in 1962 and released for sale in 1973.
Ulmus 'Stavast' is a Dutch hybrid elm cultivar raised at the Dorschkamp Research Institute for Forestry & Landscape Planning, Wageningen, as clone '622' from the crossing of 'Commelin' with clone '202', itself a hybrid of the Exeter Elm Ulmus 'Exoniensis' and Himalayan Elm Ulmus wallichiana.

Taxus wallichiana, the Himalayan yew, is a species of yew, native to the Himalaya and parts of south-east Asia. The species has a variety of uses in traditional medicine. It is currently classified as endangered by the IUCN.
The elm Ulmus wallichiana subsp. xanthoderma was identified by Melville and Heybroek after the latter's expedition to the Himalaya in 1960. The tree is of more western distribution than subsp. wallichiana, from Afghanistan to Kashmir.
Ulmus wallichiana subsp. wallichiana was identified by Melville and Heybroek after the latter's expedition to the Himalaya in 1960.
Ulmus wallichiana var. tomentosa was identified by Melville & Heybroek after the latter's expedition to the Himalaya in 1960.

Salacca ramosiana is a species of palm in the genus Salacca. It is native to the Philippines and to the Island of Borneo. It has a palm with pinnate fronds and long sharp spines along the margins of the petioles.

Calameae is a palm tree tribe in the subfamily Calamoideae. The type genus is Calamus and many of its members are rattans.

Iguanura is a monoecious genus of flowering plant in the palm family from Southeast Asia, commonly called pinang. Closely related to the Heterospathe palms, they are noted for producing a wide variety of fruit forms. Its name combines the Spanish word for "lizard" with the Greek word for "tail".

Utricularia scandens is a small, probably annual carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. It has a wide native distribution that includes Africa and Asia. U. scandens grows as a terrestrial plant in wet grasslands and bogs at lower altitudes around sea level up to 2,300 m (7,546 ft). It was originally described by Ludwig Benjamin in 1847. There is a significant amount of synonymy established for this species, in part because of its large distribution and variable morphology.

The Western Himalayan subalpine conifer forests is a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion of the middle and upper elevations of the western Middle Himalayas of Nepal, India, and Pakistan.
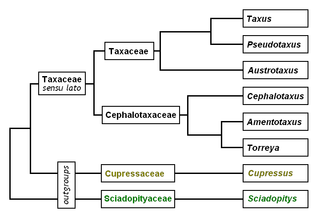
Yew is a common name given to various species of trees.

The flowering plant species formerly known as (i.a.) Selinum tenuifoliumFranch. is a member of the family Apiaceae now known correctly as Ligusticopsis wallichiana
Microtropis wallichiana is a species of small tree in the family Celastraceae. It is native to India and Sri Lanka. Its leaves are simple, opposite, decussate, and estipulate. The tree is about 15m high. Branchlets are yellowish in mature trees and darker in the youngest. The fruit is a capsule, 1-seeded; flowers are bisexual with 5 petals. Flowering and fruiting occur in December and January.
Salacca affinis, also known as red salak, red snakefruit salak, red snakefruit, buah ridan salak, buah ridan, linsum, salak hutan, buah manau, kelubi, buah rotan, and ridan, is a flowering shrub in the family Arecaceae. The specific epithet (affinis) comes from Latin "ad finis", meaning "at the boundary", and refers to its resemblance with the congener species Salacca zalacca.

Khao Nam Khang National Park is a national park in Thailand. It was declared the 65th national park on July, 22 1990.













