The geography of Croatia is defined by its location—it is described as located at the crossroads of Central Europe and Southeast Europe, or within the wider region of Southern Europe. Croatia's territory covers 56,594 km2 (21,851 sq mi), making it the 127th largest country in the world. Bordered by Slovenia in the northwest, Hungary in the northeast, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia in the east, Montenegro in the southeast and the Adriatic Sea in the south, it lies mostly between latitudes 42° and 47° N and longitudes 13° and 20° E. Croatia's territorial waters encompass 18,981 square kilometres (7,329 sq mi) in a 12 nautical miles wide zone, and its internal waters located within the baseline cover an additional 12,498 square kilometres (4,826 sq mi).

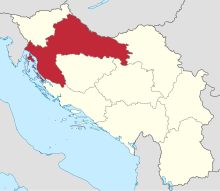
Vukovar-Srijem County, Vukovar-Sirmium County or Vukovar-Syrmia County, named after the eponymous town of Vukovar and the region of Syrmia, is the easternmost Croatian county. It includes the eastern parts of the region of Slavonia and the western parts of the region of Syrmia, as well as the lower Sava river basin, Posavina and Danube river basin Podunavlje. Due to the overlapping definitions of geographic regions, division on Slavonia and Syrmia approximately divides the county vertically into north-west and south-east half, while division on Posavina and Podunavlje divides it horizontally on north-east and south-west half.

The Srem District is one of seven administrative districts of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It lies in the geographical regions of Srem and Mačva. According to the 2022 census results, it has a population of 282,547 inhabitants. The administrative center is the city of Sremska Mitrovica.

The Drina Banovina or Drina Banate was a province (banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. Its capital was Sarajevo and it included portions of present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. It was named after the Drina River and, like all Yugoslav banovinas, was intentionally not based on ethnic boundaries. As a result of the creation of the Banovina of Croatia in 1939, its territory was reduced considerably.

Danube Banovina or Danube Banate, was a banovina of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. This province consisted of the geographical regions of Syrmia, Bačka, Banat, Baranya, Šumadija, and Braničevo. The capital city of the Danube Banovina was Novi Sad. The province was named after the Danube River.

The Vrbas Banovina or Vrbas Banate, was a province (banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. It was named after the Vrbas River and consisted mostly of territory in western Bosnia with its capital at Banja Luka. Dvor district of present-day Croatia was also part of the Vrbas Banovina.
Podunavlje is the name of the Danube river basin parts located in Croatia and Serbia. Podunavlje is located on the southern edge of Pannonian Basin. In its wider meaning, the Croatian term refers to the area around the entire flow of the river Danube.

The Drava Banovina or Drava Banate, was a province (banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. This province consisted of most of present-day Slovenia and was named for the Drava River. The capital city of the Drava Banovina was Ljubljana.

The Littoral Banovina or Littoral Banate, was a province (banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1939. This province consisted of much of the Croatian region of Dalmatia and parts of present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina and was named for its coastal (maritime) location. The capital city of the Littoral Banovina was Split.

The Zeta Banovina, was a province (banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. This province consisted of all of present-day Montenegro as well as adjacent parts of Central Serbia, Croatia, Kosovo and Bosnia and Herzegovina. It was named after the Zeta River which also gave its name to the medieval state of Zeta that roughly corresponds to modern-day Montenegro. The capital of Banovina was Cetinje.

The Morava Banovina or Morava Banate, was a province (banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. This province consisted of parts of present-day Central Serbia and it was named after the Morava Rivers. The capital city of the Morava Banovina was Niš.

The Banovina of Croatia or Banate of Croatia was an administrative subdivision (banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1939 and 1941. It was formed by a merger of Sava and Littoral banovinas into a single autonomous entity, with small parts of the Drina, Zeta, Vrbas and Danube banovinas also included. Its capital was Zagreb and it included most of present-day Croatia along with portions of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. Its sole Ban during this period was Ivan Šubašić.
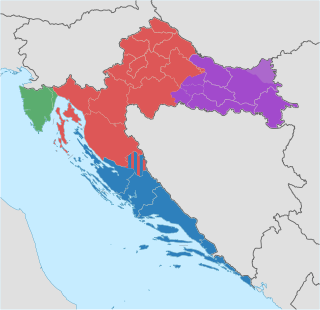
Though the Republic of Croatia administratively consists of twenty counties, it is traditionally divided into four historical and cultural regions: Croatia proper, Dalmatia, Istria, and Slavonia. These are further divided into other, smaller regions.

Banovina or Banija is a geographical region in central Croatia, between the Sava, Una, Kupa and Glina rivers. The main towns in the region include Petrinja, Glina, Kostajnica, and Dvor. There is no clear geographical border of the region towards the west and the neighboring region of Kordun. The area of Banovina is today administratively almost entirely located within the Sisak-Moslavina County.

Ban of Croatia was the title of local rulers or office holders and after 1102, viceroys of Croatia. From the earliest periods of the Croatian state, some provinces were ruled by bans as a ruler's representative (viceroy) and supreme military commander. In the 18th century, Croatian bans eventually became the chief government officials in Croatia.

Yugoslavia had various administrative divisions throughout its 74 years of existence.
The subdivisions of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia existed successively in three different forms. From 1918 to 1922, the Kingdom of Yugoslavia maintained the pre-World War I subdivisions of Yugoslavia's predecessor states. In 1922, the state was divided into 33 oblasts or provinces and, in 1929, a new system of nine banates was implemented.

Slabinja is a village in the Sisak-Moslavina County in the central part of Croatia. It is in the Una Valley near the border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, 12.6 kilometres (7.8 mi) southeast of the town of Hrvatska Kostajnica, 9.7 kilometres (6 mi) northwest of the village of Hrvatska Dubica, and 106 kilometres (66 mi) southeast of Croatian capital Zagreb, at the south fringe of the Banovina region. Slabinja is a dormitory village with a resident population of just over 250 people.

Posavina is a geographical region that stretches along the Sava river, encompassing only the inner areas of the Sava river basin, that are adjacent or near to the Sava river itself, namely catch region spanning from the Julian Alps in the northwest to the confluence with the Danube in the southeast. It passes through several countries of former Yugoslavia, namely Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. In Slovene, the term Posavina is not used to describe the parts of Slovenia that lie by the Sava river. Instead, the terms Posavje, Zasavje and Zgornjesavska dolina are used.
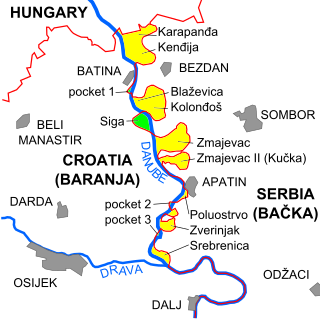
The border between Croatia and Serbia in the area of the Danube is disputed, an important part of their broader diplomatic relations. While Serbia claims that the thalweg of the Danube valley and the centreline of the river represents the international border between the two countries, Croatia disagrees, claiming that the international border lies along the boundaries of the cadastral municipalities located along the river—departing from the course at several points along a 140-kilometre (87 mi) section. The cadastre-based boundary reflects the course of the Danube which existed in the 19th century, before anti-meandering and hydrotechnical engineering works altered its course. The area size of the territory in dispute is reported variously, up to 140 km2.