
Inostrancevia is an extinct genus of large carnivorous therapsids which lived during the Late Permian in what are now Siberia, Russia and Southern Africa. The first-known fossils of this gorgonopsian were discovered in the Northern Dvina, where two almost complete skeletons were exhumed. Subsequently, several other fossil materials were discovered in various oblasts, and these finds will lead to a confusion about the exact number of valid species in the country, before only three of them were officially recognized: I. alexandri, I. latifrons and I. uralensis. More recent research carried out in South Africa has discovered fairly well-preserved remains of the genus, being attributed to the species I. africana. An isolated left premaxilla suggests that Inostrancevia also lived in Tanzania during the earliest Lopingian age. The whole genus is named in honor of Alexander Inostrantsev, professor of Vladimir P. Amalitsky, the paleontologist who described the taxon.

Ericiolacerta is an extinct genus of small therocephalian therapsids from the early Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. Ericiolacerta, meaning "hedgehog lizard", was named by D.M.S. Watson in 1931. The species E. parva is known from the holotype specimen which consists of a nearly complete skeleton found in the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone within the Katberg Formation of the Beaufort Group in South Africa, and from a partial jaw found in the Lower Triassic Fremouw Formation in Antarctica. Ericiolacerta was around 20 centimetres (7.9 in) in length, with long limbs and relatively small teeth. It probably ate insects and other small invertebrates. The therocephalians – therapsids with mammal-like heads – were abundant in Permian times, but only a few made it into the Triassic. Ericiolacerta was one of those. It is possible that they gave rise to the cynodonts, the only therapsid group to survive into post-Triassic times. Cynodonts gave rise to mammals.

Therocephalia is an extinct clade of eutheriodont therapsids from the Permian and Triassic periods. The therocephalians ("beast-heads") are named after their large skulls, which, along with the structure of their teeth, suggest that they were carnivores. Like other non-mammalian synapsids, therocephalians were once described as "mammal-like reptiles". Therocephalia is the group most closely related to the cynodonts, which gave rise to the mammals, and this relationship takes evidence in a variety of skeletal features. Indeed, it had been proposed that cynodonts may have evolved from therocephalians and so that therocephalians as recognised are paraphyletic in relation to cynodonts.

The theriodonts are a major group of therapsids which appeared during the Middle Permian and which includes the gorgonopsians and the eutheriodonts, itself including the therocephalians and the cynodonts.

Hovasaurus is an extinct genus of basal diapsid reptile. It lived in what is now Madagascar during the Late Permian and Early Triassic, being a survivor of the Permian–Triassic extinction event and the paleontologically youngest member of the Tangasauridae. Fossils have been found in the Permian Lower and Triassic Middle Sakamena Formations of the Sakamena Group, where it is amongst the commonest fossils. Its morphology suggests an aquatic ecology.

Parotosuchus is an extinct genus of capitosaurian temnospondyls within the family Mastodonsauridae. Fossils are known from the Early Triassic of Europe, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica. It was about 2 metres (6.6 ft) long and likely lived in aquatic environments such as lakes and rivers. Parotosuchus was covered in a scaly skin, unlike the smooth skin of modern-day amphibians, and probably moved with an eel-like motion in the water.
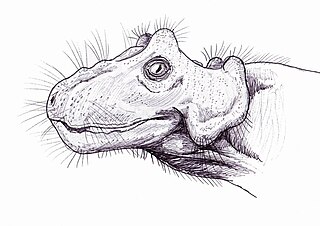
Paraburnetia is an extinct genus of biarmosuchian therapsids from the Late Permian of South Africa. It is known for its species P. sneeubergensis and belongs to the family Burnetiidae. Paraburnetia lived just before the Permian–Triassic mass extinction event.
Antecosuchus is an extinct genus of bauriid therocephalians.
Promoschorhynchus is a genus of akidnognathid therocephalians from the Late Permian and Early Triassic of South Africa. Unlike many other therapsids, Promoschorhynchus survived the Permian-Triassic extinction event.
Malasaurus is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids which lived in South east Finland, North west Russia. The type species is Malasaurus germanus.

Madysaurus is an extinct genus of cynodonts which existed in Kyrgyzstan. It was first named by Leonid Petrovich Tatarinov in 2005. Madysaurus is known from the Madygen Formation, a Triassic Lagerstätte that also includes well-preserved remains of insects and small reptiles like Sharovipteryx and Longisquama. Madysaurus is one of the most primitive cynodonts and is placed in its own family, Madysauridae.
Neotrirachodon is an extinct genus of therapsids which existed in Russia during the Middle Triassic period. Its type and only species is Neotrirachodon expectatus.

Akidnognathidae is an extinct family of therocephalian therapsids from the Late Permian and Early Triassic of South Africa, Russia and China. The family includes many large-bodied therocephalians that were probably carnivorous, including Moschorhinus and Olivierosuchus. One akidnognathid, Euchambersia, may even have been venomous. Akidnognathids have robust skulls with a pair of large caniniform teeth in their upper jaws. The family is morphologically intermediate between the more basal therocephalian group Scylacosauridae and the more derived group Baurioidea.
Scalenodon is an extinct genus of traversodontid cynodonts from the Middle Triassic of Africa and possibly Russia. The type species S. angustifrons was named in 1946 and several other species were named in the following years. Most of the species from Africa are now thought to belong to different genera than Scalenodon.

Perplexisaurus is a genus of therocephalian therapsid from the Middle to Late Permian Deltavjatia vjatkensis Assemblage Zone, Vanyushonki Member of the Urpalov Formation of Russia. It was described by L. P. Tatarinov in 1997, and the type species is P. foveatus. A new species, P. lepusculus, was described by M.F. Ivachnenko in 2011, from Russia.

Blattoidealestes is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsid from the Middle Permian of South Africa. The type species Blattoidealestes gracilis was named by South African paleontologist Lieuwe Dirk Boonstra from the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone in 1954. Dating back to the Middle Permian, Blattoidealestes is one of the oldest therocephalians. It is similar in appearance to the small therocephalian Perplexisaurus from Russia, and may be closely related.
Scalopodon is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids from the Late Permian of Russia. The type species Scalopodon tenuisfrons was named in 1999 from the Kotelnichsky District of Kirov Oblast. Scalopodon is known from a single fragmentary holotype specimen including the back of the skull, the left side of the lower jaw and isolated postorbital and prefrontal bones. The skull was found in the Deltavjatia Assemblage Zone, which dates back to the early Wuchiapingian about 260 million years ago. Distinguishing features of Scalopodon include narrow frontal bones and a distinctive sagittal crest along the parietal region at the back of the skull. Scalopodon was originally classified in the family Scaloposauridae, and was the first scaloposaurid found in Russia. More recent studies of therocephalians have found scaloposaurids like Scalopodon to be juvenile forms of larger therocephalians and do not consider Scaloposauridae to be a valid group. Scalopodon and most other scaloposaurids are now classified as basal members of Baurioidea.

Karenites is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids from the Late Permian of Russia. The only species is Karenites ornamentatus, named in 1995. Several fossil specimens are known from the town of Kotelnich in Kirov Oblast.
Lycideops is an extinct genus of therocephalians from the Late Permian of South Africa. The type species is Lycideops longiceps, named in 1931 by South African paleontologist Robert Broom. Fossils of Lycideops come from the Dicynodon Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group. Lycideops is a member of the family Lycideopidae. Like other lycideopids, Lycideops has a long snout.

Leonid Petrovich Tatarinov was a Russian and Soviet paleontologist and evolutionary biologist. He was an Academician of the USSR Academy of Sciences (1981) and Russian Academy of Sciences (1991), director of the Paleontological Institute and editor-in-chief of Paleontological journal. His research interests were in the comparative anatomy of vertebrates, tetrapod phylogeny, and evolution.












