Squalidae, more commonly known as dogfish, dog sharks, or spiny dogfish, are one of several families of sharks categorized under Squaliformes, making it the second largest order of sharks, numbering 119 species across 7 families. Having earned their name after a group of fishermen reportedly observed the species chasing down smaller fish in dog-like packs, dogfish have slender, streamlined bodies, usually more compact in comparison to other species, and a pointed snout. Dogfish likewise have two dorsal fins, each with smooth spines, but no anal fin, and their skin is generally rough to the touch. As the species reaches adulthood, males usually measure a maximum of 100 cm, while females typically measure 125 cm long. The species therefore exhibits female-dominant sexual dimorphism.
Squalus is a genus of dogfish sharks in the family Squalidae. Commonly known as spurdogs, these sharks are characterized by smooth dorsal fin spines, teeth in upper and lower jaws similar in size, caudal peduncle with lateral keels; upper precaudal pit usually present, and caudal fin without subterminal notch. In spurdogs, the hyomandibula is oriented at a right angle to the neurocranium, while in other sharks, the hyomandibula runs more parallel to the body. This led some to think that the upper jaw of Squalus would not be as protractile as the jaws of other sharks. However, a study that compared different jaw suspension types in sharks showed that this is not the case and that Squalus is quite capable of protruding its upper jaw during feeding.

The Somniosidae are a family of sharks in the order Squaliformes, commonly known as sleeper sharks. The common name "sleeper shark" comes from their slow swimming, low activity level, and perceived non-aggressive nature.

The plunket shark or Plunket's shark is a sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found around south eastern Australia, and New Zealand, at depths of between 220 and 1,550 m over continental shelves. It reaches a length of 130 cm.

The longnose velvet dogfish is a sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found circumglobally in southern hemisphere subtropical seas, at depths of between 230 and 1,500 m. It reaches a length of 130 cm. It has a diet consisting of predominantly mesopelagic fishes and squids.
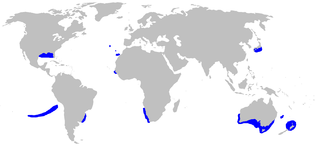
The roughskin dogfish is a sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found around the world on continental shelves in tropical, subtropical and temperate seas, at depths of between 100 and 1,500 m. It reaches a length of 121 cm.

Somniosus is a widely distributed genus of deepwater dogfish sharks in the family Somniosidae. Several members of the genus are believed to attain lengths up to 7 m (23 ft), thus ranking among the largest of sharks.

The Portuguese dogfish or Portuguese shark, is a species of sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae. This globally distributed species has been reported down to a depth of 3,675 m (12,057 ft), making it the deepest-living shark known. It inhabits lower continental slopes and abyssal plains, usually staying near the bottom. Stocky and dark brown in color, the Portuguese dogfish can be distinguished from similar-looking species by the small spines in front of its dorsal fins. Its dermal denticles are also unusual, resembling the scales of a bony fish. This species typically reaches 0.9–1 m (3.0–3.3 ft) in length; sharks in the Mediterranean Sea are much smaller and have distinct depth and food preferences.

The largespine velvet dogfish is a shark of the family Somniosidae, found on the lower continental slopes between latitudes 50°S and 54°S in the southeast Pacific Ocean from the Straits of Magellan, and the southwest Pacific from New Zealand, at depths of between 650 and 920 m. Its length is up to 68 cm. It was originally in the genus Centroscymnus because of the shape of its dermal denticles and dorsal fin spines but some argued to put this in the Scymnodon genus because of its shape of dermal denticles. While some wanted to allocate these in Centroscymnus because of the shape of its lower teeth but later it was allocated to a distinct genus called the Proscymnodon.
Centroscymnus is a genus of squaliform sleeper sharks in the family Somniosidae and of the phylum chordata.
Scymnodalatias is a genus of squaliform sharks in the family Somniosidae.

The Japanese velvet dogfish is a harmless deepwater sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found in the northwest Pacific from Suruga Bay and adjacent waters of Japan at depths of between 500 and 800 metres. Reproduction is ovoviviparous.

The knifetooth dogfish, is a harmless sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found in the eastern Atlantic, from Scotland to Spain, Portugal, and Senegal, and the southwest Pacific from New Zealand, between latitudes 58°N and 15°N, at depths of between 200 and 1,600 m. Its length is up to 1.1 metres (3.6 ft).

The velvet dogfish, the only member of the genus Zameus, is a small sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found around the world between latitudes 64°N and 48°S, from the surface to 2,000 m.

The brown lanternshark or bristled lanternshark is a little-known species of deep-sea dogfish shark in the family Etmopteridae. It is found off Japan and New Zealand, and possibly also South Africa and Australia, typically deeper than 300 m (980 ft). This species can be distinguished from other lanternsharks by its coloration, which is a uniform dark gray or brown without the ventral surface being much darker and clearly delineated from the rest of the body. The brown lanternshark feeds on small bony fishes, cephalopods, and crustaceans. Reproduction is ovoviviparous, with females giving birth to 9–18 young. An unusually high proportion of individuals in Suruga Bay are hermaphrodites, with both male and female characteristics.

The southern sleeper shark, or Whitley's sleeper shark, is a deepwater benthopelagic sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae found in the southern and subantarctic extremes of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans, and some northern reaches of the Antarctic oceans. It has been recorded near the southernmost areas of South America, near South Africa, southern Australia, Tasmania and New Zealand, as well as more remote locations in the south-central Indian Ocean.
The frog shark is a very rare species of squaliform shark mainly found in deep water in the Pacific Ocean. It is in the sleeper shark family Somniosidae with the Greenland shark.













