
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type of axle is referred to as a spindle.

Yari (槍) is the term for a traditionally-made Japanese blade in the form of a spear, or more specifically, the straight-headed spear. The martial art of wielding the yari is called sōjutsu.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

Scipionyx was a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Italy, around 113 million years ago.

Shenzhousaurus is a genus of basal ornithomimosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of China.
In human anatomy, the body of femur is the almost cylindrical, long part of the femur. It is a little broader above than in the center, broadest and somewhat flattened from before backward below. It is slightly arched, so as to be convex in front, and concave behind, where it is strengthened by a prominent longitudinal ridge, the linea aspera.

Spur gears or straight-cut gears are the simplest type of gear. They consist of a cylinder or disk with teeth projecting radially. Viewing the gear at 90 degrees from the shaft length the tooth faces are straight and aligned parallel to the axis of rotation. Looking down the length of the shaft, a tooth's cross section is usually not triangular. Instead of being straight the sides of the cross section have a curved form to achieve a constant drive ratio. Spur gears mesh together correctly only if fitted to parallel shafts. No axial thrust is created by the tooth loads. Spur gears are excellent at moderate speeds but tend to be noisy at high speeds.

An ice tool is a specialized elaboration of the modern ice axe, used in ice climbing, mostly for the more difficult configurations. Ice tools are used two to a person for the duration of a pitch, and thus in some circumstances such as top-rope-anchored climbs, a pair may be shared among two or more people, where only one of them at a time is climbing. In contrast a classical "ice axe" is used one to a person for the hours or days a party is traveling across snow or glacier. In communities where it is common to refer to an "ice tool" simply as an "ice axe", classic "ice axes" are often referred to as "traveling axes", "walking axes", or "general mountaineering axes" to distinguish them from "tools".

An iron is a type of club used in the sport of golf to propel the ball towards the hole. Irons typically have shorter shafts and smaller clubheads than woods, the head is made of solid iron or steel, and the head's primary feature is a large, flat, angled face, usually scored with grooves. Irons are used in a wide variety of situations, typically from the teeing ground on shorter holes, from the fairway or rough as the player approaches the green, and to extract the ball from hazards, such as bunkers or even shallow water hazards.

Peloroplites is a monospecific genus of nodosaurid dinosaur from Utah that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Mussentuchit Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation. The type and only species, Peloroplites cedrimontanus, is known from a partial skull and postcranial skeleton. It was named in 2008 by Kenneth Carpenter and colleagues. Peloroplites was 6 metres long and weighed 2 tonnes, making it one of the largest known nodosaurids, and came from a time when ankylosaurids and nodosaurids were attaining large sizes.

Asilisaurus ; from Swahili, asili, and Greek, σαυρος is an extinct genus of silesaurid archosaur. The type species is Asilisaurus kongwe.Asilisaurus fossils were uncovered in the Manda Beds of Tanzania and date back to the early Carnian, making it one of the oldest known members of the Avemetatarsalia. It was the first non-dinosaurian dinosauriform recovered from Africa. The discovery of Asilisaurus has provided evidence for a rapid diversification of avemetatarsalians during the Middle Triassic, with the diversification of archosaurs during this time previously only documented in pseudosuchians.

A cue stick is an item of sporting equipment essential to the games of pool, snooker and carom billiards. It is used to strike a ball, usually the cue ball. Cues are tapered sticks, typically about 57–59 inches long and usually between 16 and 21 ounces (450–600 g), with professionals gravitating toward a 19-ounce (540 g) average. Cues for carom tend toward the shorter range, though cue length is primarily a factor of player height and arm length. Most cues are made of wood, but occasionally the wood is covered or bonded with other materials including graphite, carbon fiber or fiberglass. An obsolete term for a cue, used from the 16th to early 19th centuries, is billiard stick.

Jesairosaurus is an extinct genus of early archosauromorph reptile known from the Illizi Province of Algeria. It is known from a single species, Jesairosaurus lehmani. Although a potential relative of the long-necked tanystropheids, this lightly-built reptile could instead be characterized by its relatively short neck as well as various skull features.
Panguraptor is a genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur known from fossils discovered in Lower Jurassic rocks of southern China. The type and only known species is Panguraptor lufengensis. The generic name refers to the deity Pangu but also to the supercontinent Pangaea for which in a geological context the same characters are used: 盘古. Raptor means "seizer", "robber" in Latin. The specific name is a reference to the Lufeng Formation. The holotype specimen was recovered on 12 October 2007 from the Lufeng Formation of Yunnan, which is noted for sauropodomorph fossils. It was described in 2014 by You Hai-Lu and colleagues.

Meroktenos is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period of what is now Lesotho.

Rativates is a genus of ornithomimid theropod dinosaur from the Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta. The type species is Rativates evadens.
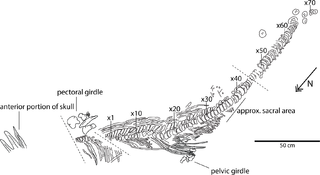
Keilhauia is a genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur, a type of dolphin-like, large-eyed marine reptile, from the Early Cretaceous shallow marine Slottsmøya Member of the Agardhfjellet Formation in Svalbard, Norway. The genus contains a single species, K. nui, known from a single specimen discovered in 2010 and described by Delsett et al. in 2017. In life, Keilhauia probably measured approximately 4 metres (13 ft) in length; it can be distinguished by other ophthalmosaurids by the wide top end of its ilium and the relatively short ischiopubis compared to the femur. Although it was placed in a basal position within the Ophthalmosauridae by phylogenetic analysis, this placement is probably incorrect.
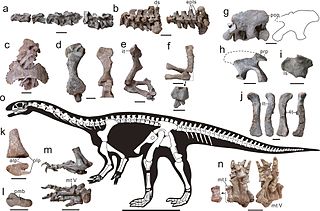
Xingxiulong is a genus of bipedal sauropodiform from the Early Jurassic of China. It contains a single species, X. chengi, described by Wang et al. in 2017 from three specimens, two adults and an immature individual, that collectively constitute a mostly complete skeleton. Adults of the genus measured 4–5 metres (13–16 ft) long and 1–1.5 metres tall. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that Xingxiulong is most closely related to its contemporary Jingshanosaurus, although an alternative position outside of both the Sauropodiformes and Massospondylidae is also plausible.
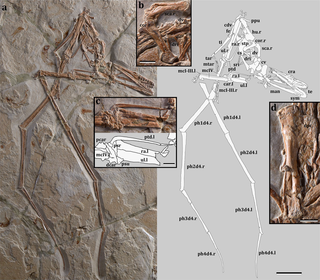
Mimodactylus is a genus of mimodactylid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous of what is now Lebanon.


















