
Coelacanths are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods than to ray-finned fish.

Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the class Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods. The mouths of lungfish typically bear tooth plates, which are used to crush hard shelled organisms.

Sarcopterygii — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii — is a taxon of the bony fish known as the lobe-finned fish or sarcopterygians, characterised by prominent muscular limb buds (lobes) within the fins, which are supported by articulated appendicular skeletons. This is in contrast to the other clade of bony fish, the Actinopterygii, which have only skin-covered bony spines (lepidotrichia) supporting the fins.

Tiktaalik is a monospecific genus of extinct sarcopterygian from the Late Devonian Period, about 375 Mya, having many features akin to those of tetrapods. Tiktaalik is estimated to have had a total length of 1.25–2.75 metres (4.1–9.0 ft) based on various specimens.

Styloichthys is a prehistoric sarcopterygian, lobe-finned fish which lived during the Early Devonian (Lochkovian) period of East Yunnan, South China.

Megalichthyidae is an extinct family of tetrapodomorphs which lived from the Middle–Late Devonian to the Early Permian. They are known primarily from freshwater deposits, mostly in the Northern Hemisphere, but one genus (Cladarosymblema) is known from Australia, and the possible megalichthyid Mahalalepis is from Antarctica.
Euporosteus is an extinct genus of prehistoric sarcopterygian or lobe-finned fish.
Lochmocercus is an extinct genus of prehistoric coelacanth fishes which lived during the Carboniferous Period.
Heimenia is an extinct genus of prehistoric sarcopterygian or lobe-finned fish.
Hainbergia is an extinct genus of prehistoric sarcopterygian or lobe-finned fish.

Mylacanthus is an extinct genus of prehistoric coelacanth lobe-finned fish that lived during the Smithian age of the Early Triassic epoch in what is now Svalbard.
Sassenia is an extinct genus of prehistoric coelacanth lobe-finned fish that lived during the Early Triassic epoch in what is now East Greenland and Svalbard.
Youngichthys is an extinct genus of prehistoric sarcopterygians or lobe-finned fish from the upper Permian (Changhsingian) comprising a single species, Youngichthys xinghuansis. The single specimen of the fish was discovered in Zhejiang Province, China in 1981.
Westollrhynchus is an extinct genus of prehistoric sarcopterygians or lobe-finned fish containing only one recognized species, Westrollrhynchus lehmanni.
Swenzia is an extinct genus of coelacanthid fish from the late Jurassic of France. It contains a single species, S. latimerae, which was originally described as Wenzia latimerae. Because the generic name Wenzia was already preoccupied by a snail, the generic name was amended to Swenzia. It is the fossil genus most closely related to the living coelacanth, Latimeria.
Tarachomylax is an extinct genus of prehistoric sarcopterygians or lobe-finned fish.
Spermatodus is an extinct genus of prehistoric coelacanth lobe-finned fish, which lived during the Artinskian age of the Cisuralian epoch in what is now Oklahoma and Texas, United States.
Scleracanthus is an extinct genus of prehistoric coelacanth lobe-finned fish. It lived during the Early Triassic epoch in what is now Spitsbergen, Svalbard.
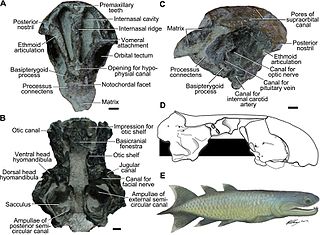
Qingmenodus is a genus of prehistoric lobe-finned fish. Fossils of Qingmenodus were found in China and date back to the Early Devonian period. Qingmenodus reveals the first well-ossified otoccipital braincase in onychodonts. Palaeontologists believe that Qingmenodus was one of the oldest onychodont fish.

The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion. It was during this time that the early chordates developed the skull and the vertebral column, leading to the first craniates and vertebrates. The first fish lineages belong to the Agnatha, or jawless fish. Early examples include Haikouichthys. During the late Cambrian, eel-like jawless fish called the conodonts, and small mostly armoured fish known as ostracoderms, first appeared. Most jawless fish are now extinct; but the extant lampreys may approximate ancient pre-jawed fish. Lampreys belong to the Cyclostomata, which includes the extant hagfish, and this group may have split early on from other agnathans.













