
Bavayia is a genus of lizards in the family Diplodactylidae. Species in the genus Bavayia are also known commonly as New Caledonian geckos or bavayias. The genus is native to the remote New Caledonia and Loyalty Islands. The 41 species are moderately small to medium-sized geckos, and are distinguished from other genera by their tail length and the shape of their digits.

Eurydactylodes is a small genus of geckos commonly referred to as chameleon geckos from the subfamily Diplodactylidae, endemic to New Caledonia and few adjacent islands. Within the Diplodactylidae, Eurydactylodes resides in the Carphodactylini tribe, and consists of four species. All species share similar morphology as well as lifestyle and habits. The first of the Eurydactylodes species to be classified, E. vieillardi, was discovered in 1869.

Caledoniscincus is a genus of lizards in the family Scincidae (skinks). The genus is endemic to New Caledonia.

Graciliscincus is a lizard genus in the family Scincidae. The genus is indigenous to New Caledonia.
Nannoscincus is a genus of small skinks, lizards in the family Scincidae. The genus is endemic to New Caledonia.
Phoboscincus is a small genus of skinks, lizards in the family Scincidae. There are two known species in the genus Phoboscincus. Both species are found on various island of New Caledonia.
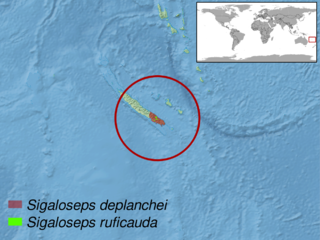
Sigaloseps is a genus of skinks which inhabit the moist, closed forest of southern New Caledonia.

Mniarogekko chahoua, commonly known as the mossy New Caledonian gecko, short-snouted New Caledonian gecko, Bavay's giant gecko, or mossy prehensile-tailed gecko, is an arboreal gecko found natively on the southern portion of the island of New Caledonia and on the outlying islands of Île des Pins.

The terror skink, also called commonly Bocourt's terrific skink, Bocourt's eyelid skink and Bocourt's skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to the Île des Pins, a small islet off the coast of New Caledonia. First described in 1876, the species was presumed to be extinct, but was rediscovered in 1993, and since then several individuals have been seen. Because of its small area of occupation and small population size, the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being "critically endangered".
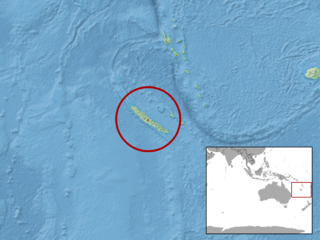
Geoscincus is a monotypic genus of skinks: the only accepted species is Geoscincus haraldmeieri.
Émile Deplanche was a French physician and naturalist.

Eurydactylodes vieillardi, sometimes known commonly as Bavay's gecko or Vieillard's chameleon gecko, is a species of lizard in the family Diplodactylidae. The species is endemic to Grande Terre in New Caledonia.

Caledoniscincus chazeaui, also known commonly as Chazeau's litter skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to New Caledonia.
Epibator greeri, also known commonly as Greer's tree skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to New Caledonia.

Lioscincus steindachneri, also known commonly as the white-lipped forest skink or Steindachner's ground skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to New Caledonia.

Lioscincus vivae is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to New Caledonia.
Nannoscincus slevini, also known commonly as Slevin's elf skink and Slevin's dwarf skink, is an endangered species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to New Caledonia.
Phasmasaurus tillieri, commonly known as Tillier's maquis skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. It is endemic to New Caledonia.

Phoboscincus garnieri, also known commonly as Garnier's giant skink and Garnier's skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to New Caledonia.

Saproscincus challengeri, also known commonly as the Border Ranges shadeskink, Challenger's skink, the challenging shade skink, and the orange-tailed shadeskink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to New South Wales and Queensland in Australia.














