
The Battle of Moorefield was a cavalry battle in the American Civil War, which took place on August 7, 1864. The fighting occurred along the South Branch of the Potomac River, north of Moorefield, West Virginia, in Hardy County. The National Park Service groups this battle with Early's Washington Raid and operations against the B&O Railroad, and it was the last major battle in the region before General Philip Sheridan took command of Union troops in the Shenandoah Valley. This Union triumph was the third of three major victories for Brigadier General William W. Averell, who performed best when operating on his own.
The 23rd Ohio Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during much of the American Civil War. It served in the Eastern Theater in a variety of campaigns and battles, and is remembered with a stone memorial on the Antietam National Battlefield not far from Burnside's Bridge.
The Battle of Charleston was a Confederate victory in Kanawha County, Virginia, on September 13, 1862, during the American Civil War. Troops led by Major General William W. Loring defeated a Union force led by Colonel Joseph Andrew Jackson Lightburn. This battle, which featured extensive use of artillery but few casualties, was the second major fight in Loring's Kanawha Valley Campaign of 1862 that succeeded in driving Union forces out of the Kanawha River Valley. All points in the Kanawha River Valley were in the southwestern part of Virginia at the time of the battle, but are now part of the state of West Virginia.

The Battle of Droop Mountain occurred in Pocahontas County, West Virginia, on November 6, 1863, during the American Civil War. A Union brigade commanded by Brigadier General William W. Averell defeated a smaller Confederate force commanded by Brigadier General John Echols and Colonel William L. "Mudwall" Jackson. Confederate forces were driven from their breastworks on Droop Mountain, losing weapons and equipment. They escaped southward through Lewisburg, West Virginia; hours before a second Union force commanded by Brigadier General Alfred N. Duffié occupied the town.

The 1st West Virginia Cavalry Regiment served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Although it started slowly, it became one of the most active and effective of the West Virginia Civil War regiments—and had 14 Medal of Honor recipients, the most for any West Virginia regiment during the war. It was originally called the 1st Virginia Cavalry, not to be confused with the Confederate 1st Virginia Cavalry. Some reports added "Union," "Loyal" or "West" when identifying this regiment. After the Unionist state of West Virginia was officially admitted to the Union in 1863, the regiment became the 1st West Virginia Cavalry Regiment. The National Park Service identifies it as the 1st Regiment, West Virginia Cavalry.

The 2nd West Virginia Cavalry Regiment served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was organized in Parkersburg, Virginia during September 1861. Most of the original members of this regiment were from southeastern Ohio, and planners thought that this regiment would become the 4th Ohio Cavalry. Their application was rejected by the governor of Ohio, so the unit became the 2nd Regiment of Loyal Virginia Volunteer Cavalry. The "Loyal Virginia" part of the name was replaced with "West Virginia" after the state of West Virginia was officially admitted to the Union in 1863. Today, the National Park Service lists them as 2nd Regiment, West Virginia Cavalry under a heading of Union West Virginia Volunteers.
Simmonds' Battery Kentucky Light Artillery was an artillery battery that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was sometimes referred to as the 1st Kentucky Independent Battery, and has the distinction of being the only Kentucky unit in U.S. service to serve in the eastern theater.
The 13th Ohio Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War.
The 11th Ohio Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War.

The Battle of Scary Creek was a minor battle fought on July 17, 1861, during the American Civil War in Scary across the Kanawha River from present day Nitro in Putnam County, West Virginia. It was the first Confederate victory in Kanawha Valley.
The 28th Ohio Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was frequently referred to as the 2nd German Ohio Regiment.
The western Virginia campaign, also known as operations in western Virginia or the Rich Mountain campaign, occurred from May to December 1861 during the American Civil War. Union forces under Major General George B. McClellan invaded the western portion of Virginia to prevent Confederate occupation; this area later became the state of West Virginia. West Virginians on both sides would fight in the campaign while a Unionist convention in Wheeling would appoint their choice for a Unionist governor for Virginia, Francis H. Pierpont, and promote the creation of a new state in western Virginia. Large scale Confederate forces would gradually abandon the region, leaving it to small local brigades to maintain hold on southern and eastern sections for much of the war.

William Henry Powell was an American soldier who fought for the Union in the American Civil War. He was a leader in the iron and nail business before the war, and his leadership abilities proved useful in the military. Powell began as a captain, and quickly ascended to higher roles in the cavalry, including commanding a regiment, a brigade, and then a division. Powell was awarded his country's highest award for bravery during combat, the Medal of Honor, for heroism at Sinking Creek, Virginia, when, as leader of a group of 22 men, he captured an enemy camp and took over 100 prisoners. This was accomplished without the loss of any of his men on November 26, 1862. He was honored with the award on July 22, 1890.

The Wytheville Raid or Toland's Raid was an attack by an undersized Union brigade on a Confederate town during the American Civil War. Union Colonel John Toland led a brigade of over 800 men against a Confederate force of about 130 soldiers and 120 civilians. The location of Wytheville, the county seat of Wythe County in southwestern Virginia, had strategic importance because of a nearby lead mine and the railroad that served it. This mine supplied lead for about one third of the Confederate Army's munitions, while the Virginia & Tennessee Railroad transported Confederate troops and supplies; plus telegraph wires along the railroad line were vital for communications. In addition to logistics of moving the lead to bullet manufacturing facilities, this rail line also connected an important salt works of an adjacent county with the wider Confederacy.

The 14th Pennsylvania Cavalry Regiment was a cavalry regiment of the Union Army during the American Civil War. Most of its fighting happened in the last half of 1863 and full year 1864. The regiment fought mainly in West Virginia and Virginia, often as part of a brigade or division commanded by Brigadier General William W. Averell and later Brigadier General William Powell.

The Battle of Lewisburg occurred in Greenbrier County, Virginia, on May 23, 1862, during the American Civil War. A Union brigade commanded by Colonel George Crook soundly defeated a larger Confederate force commanded by Brigadier General Henry Heth. Panicked Confederate forces escaped by crossing and burning a bridge across the Greenbrier River.

The Kanawha Valley Campaign of 1862 was Confederate Major General William W. Loring's military campaign to drive the Union Army out of the Kanawha River Valley during the American Civil War. The campaign took place from September 6 through September 16, 1862, although an important raid that had impact on the campaign started on August 22. Loring achieved success after several skirmishes and two battles, and Union troops retreated to the Ohio River and the safety of the state of Ohio.

The Battle of Fayetteville occurred in Fayette County, Virginia, on September 10, 1862, during the American Civil War. A Confederate Army, consisting of multiple brigades commanded by Major General William W. Loring, drove away a Union brigade commanded by Colonel Edward Siber. The battle is part of the Kanawha Valley Campaign of 1862.
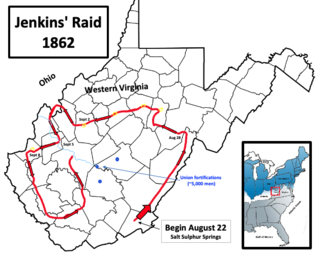
Jenkins' Trans-Allegheny Raid was a Confederate cavalry expedition in the American Civil War that took place in Western Virginia and Ohio during August and September 1862. The raid was led by Brigadier General Albert G. Jenkins, and it started on August 22 as a preliminary step in Confederate Major General William W. Loring's military campaign to drive the Union Army out of the Kanawha River Valley. That campaign, known as the Kanawha Valley Campaign of 1862, took place from September 6 through September 16. The purpose of Jenkins' raid was to get behind the Union Army outposts located near the beginning of the Kanawha River, and cut off their main route of retreat to the safety of Ohio.

The Battle of Kanawha Gap, also known as the Battle of Chapmanville, was a Civil War battle fought near Chapmanville, West Virginia on September 25, 1861, as part of the Western Virginia campaign. A column of Union soldiers from the Kanawha Brigade commanded by Col. Piatt and Col. Enyart, set out on an expedition from Camp Enyart to attack a Confederate camp near Chapmanville and drive Confederate forces from the Kanawha valley.

















