
Eriophorum angustifolium, commonly known as common cottongrass or common cottonsedge, is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. Native to North America, North Asia, and Northern Europe, it grows on peat or acidic soils, in open wetland, heath or moorland. It begins to flower in April or May and, after fertilisation in early summer, the small, unremarkable brown and green flowers develop distinctive white bristle-like seed-heads that resemble tufts of cotton; combined with its ecological suitability to bog, these characteristics give rise to the plant's alternative name, bog cotton.

Sparganium (bur-reed) is a genus of flowering plants, described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1753. It is widespread in wet areas in temperate regions of both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The plants are perennial marsh plants that can grow to 3.5 m, with epicene flowers.

Sagittaria latifolia is a plant found in shallow wetlands and is sometimes known as broadleaf arrowhead, duck-potato, Indian potato, or wapato. This plant produces edible tubers that have traditionally been extensively used by the indigenous peoples of the Americas.

Luronium natans is a species of aquatic plant commonly known as the floating water-plantain. It is the only recognized species in the genus Luronium, native to western and central Europe, from Spain to Britain to Norway east to Ukraine.

Sparganium natans is a species of bur-reed known by the common names least bur-reed and small bur-reed. It is a water circumboreal plant inhabiting North America, Europe, West Asia and Japan. It is usually found submersed in shallow, calm water. This bur-reed has thin, flexible, grasslike leaves which float in the water. Plants that spend more time out of water at the waterline are tougher and have shorter leaves. The plant bears two inflorescences, the staminate type being a rounded white filamentous ball and the pistillate type a sphere of thick, green, pointy peduncles. The fruits are small green or brown achenes.

Galium angustifolium is a species of flowering plant in the coffee family known by the common name narrowleaf bedstraw. It is native to California and Baja California, where it is most commonly found at low elevations in the mountains.

Sparganium eurycarpum is a species of bur-reed known by the common names broadfruit bur-reed and giant bur-reed. It is native to wetlands in Eurasia and North America. It is a clonal perennial, spreading by below-ground rhizomes. The common name, bur-reed, arises from the distinctive round clusters of fruits that take the form of a mace. It can be distinguished from all other species of bur-reed by the presence of two stigmas.

Ambrosia psilostachya is a species of ragweed known by the common names Cuman ragweed and perennial ragweed, and western ragweed.

Enhalus is a monotypic genus of marine flowering plants. The sole species is Enhalus acoroides. Enhalus is large seagrass native to coastal waters of the tropical Indian and Western Pacific Oceans. It is the only species of seagrass that does aerial surface pollination in which the pollen and the styles remain dry. Enhalus is surface pollinated with male flowers that detach from the plant to float on the surface until they reach a female flower where pollination can occur. Enhalus acoroides is considered a slow-growing, "climax" species.

Sparganium erectum, the simplestem bur-reed or branched bur-reed, is a perennial plant species in the genus Sparganium.

Persicaria amphibia is a species of flowering plant in the knotweed family known by several common names, including longroot smartweed, water knotweed, water smartweed, and amphibious bistort. It is native to much of North America, Asia, Europe, and parts of Africa, and it grows elsewhere as an introduced species and sometimes a noxious weed.

Potamogeton nodosus is a species of aquatic plant known by the common names longleaf pondweed and Loddon pondweed. It is native to Eurasia and the Americas, where it is widespread and can be found in water bodies such as ponds, lakes, ditches, and streams. This is a perennial herb producing a thin, branching stem easily exceeding a meter in maximum length. The leaves are linear to widely lance-shaped and up to 15 centimeters long by 4 wide. Both floating leaves and submerged leaves are borne on long petioles, a distinguishing characteristic. The inflorescence is a spike of many small flowers arising from the water on a peduncle.

Sparganium emersum is a species of flowering plant in the cat-tail family known by the common names European bur-reed and unbranched bur-reed. It has a circumboreal distribution, occurring throughout the northern latitudes of Eurasia and North America. It is an aquatic plant, growing in shallow water bodies such as ponds and streams. It can become abundant at times. It is a perennial herb producing a floating stem up to 2 meters long. The leaves may be limp and floating or stiff and erect, emerging above the water surface. The leaves are flat and straplike, sometimes with a triangular, keeled base that can help distinguish it from the similar Sparganium angustifolium. It is monoecious, individual plants bearing both male and female inflorescences. These are spherical, the male inflorescence a ball of stamens and the female inflorescence a ball of developing fruits growing beneath the male spheres.

Xanthium spinosum is a species of flowering plant in the aster family known by many common names, including spiny cocklebur, prickly burweed and Bathurst burr. This species is part of the genus Xanthium that encompasses 25 different species of flowering plants of the daisy family, Asteraceae, and sunflower tribe.

Zizania texana is a rare species of grass known by the common name Texas wild rice. It is endemic to Texas, where it is found only on the upper San Marcos River in Hays County. It is threatened by the loss and degradation of its habitat. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.

Damasonium minus is a species of flowering plant in the water-plantain family known by the common names starfruit and star-fruit. It is native to Australia, where it occurs everywhere except the Northern Territory. It is perhaps best known as an agricultural weed. It is a major weed of Australian rice crops.

Sparganium glomeratum, the clustered bur-reed, is a species of bur-reed. It is a water plant native to high elevation lakes and marshes of Europe, Asia, and North America. North American populations were doubted as introduced due to its scarce and scattered populations, but a recent herbarium survey found more localities of the species in the central of Canada, concluding the species as circumpolar species.
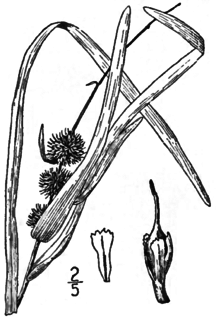
Sparganium americanum, American bur-reed, is a perennial plant found in the United States of America and Canada. Though this species resembles a grass, it is a type of bur-reed. This species is important for conservation purposes because it has the ability to remove nitrogen and phosphorus runoff from water, like many other wetland species. By doing this it protects waterways from excess nitrogen which can cause eutrophication. This increased nitrogen is especially a problem during the farmers’ growing season. During this same time frame the S. americanum is growing and taking up nitrogen.
Pilea fairchildiana, or previously known as Sarcopilea domingensis, is a succulent plant endemic to the Constanza Mountains of the Dominican Republic. It was thought to be under a monospecific genus (Sarcopilea), but with new phylogenetic information is now placed under the genus Pilea.


















