
Atracidae is a family of mygalomorph spiders, commonly known as Australian funnel-web spiders or atracids. It has been included as a subfamily of the Hexathelidae, but is now recognised as a separate family. All members of the family are native to Australia. Atracidae consists of three genera: Atrax, Hadronyche, and Illawarra, comprising 35 species. Some members of the family produce venom that is dangerous to humans, and bites by spiders of six of the species have caused severe injuries to victims. The bites of the Sydney funnel-web spider and northern tree-dwelling funnel-web spider are potentially deadly, but no fatalities have occurred since the introduction of modern first-aid techniques and antivenom.

The Sydney funnel-web spider is a species of venomous mygalomorph spider native to eastern Australia, usually found within a 100 km (62 mi) radius of Sydney. It is a member of a group of spiders known as Australian funnel-web spiders. Its bite is capable of causing serious illness or death in humans if left untreated.

Selenocosmia crassipes, synonym Phlogius crassipes, also known as the "Queensland whistling tarantula", "barking spider" or "bird-eating tarantula" is a species of tarantula native to the east coast of Queensland, Australia. The name "whistling tarantula" comes from its ability to produce a hissing noise when provoked, a trait it shares with other Australian theraphosids. This hissing is produced by the spider stridulating a patch of setae associated with its chelicerae. It has also been called the "eastern tarantula". The species name crassipes is Latin for "fat leg" referring to the relatively fat front legs.

Idiopidae, also known as armored or spiny trapdoor spiders, is a family of mygalomorph spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1889.

Nemesiidae is a family of mygalomorph spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1889, and raised to family status in 1985. Before becoming its own family, it was considered part of "Dipluridae". The family is sometimes referred to as wishbone spiders due to the shape of their burrows.

Idiosoma is a genus of Australian armoured trapdoor spiders that was first described by Anton Ausserer in 1871. Originally placed with the Ctenizidae, it was moved to the armoured trapdoor spiders in 1985. The name is derived from the Greek ἴδιος, meaning "individual, unique", and σῶμα, meaning "body", referring to the distinctive structure of the abdomen.

Porrhothele antipodiana, the black tunnelweb spider, is a species of mygalomorph spider that lives in New Zealand. It is the most common and widespread of several species in the genus Porrhothele, and is especially common in the greater Wellington region where the vagrant mature males are often encountered in or around dwellings. This species is one of New Zealand's most studied spiders. In New Zealand, the common name "tunnelweb spider" is also often used to refer to members of the genus Hexathele. Neither should be confused with their distant relatives, the highly venomous Australian funnel-web spiders.

Stanwellia is a genus of South Pacific mygalomorph spiders in the family Pycnothelidae. It was first described by W. J. Rainbow & R. H. Pulleine in 1918. Originally placed with the curtain-web spiders, it was transferred to the funnel-web trapdoor spiders in 1985, then to the Pycnothelidae in 2020. It is a senior synonym of Aparua.

Tarantulas comprise a group of large and often hairy spiders of the family Theraphosidae. As of December 2023, 1,100 species have been identified, with 166 genera. The term "tarantula" is usually used to describe members of the family Theraphosidae, although many other members of the same infraorder (Mygalomorphae) are commonly referred to as "tarantulas" or "false tarantulas". Some of the more common species have become popular in the exotic pet trade. Many New World species kept as pets have setae known as urticating hairs that can cause irritation to the skin, and in extreme cases, cause damage to the eyes.

The Sydney brown trapdoor spider is a spider in the family Idiopidae, found primarily around Sydney, Australia. It is usually shy and retiring and is often confused with the Sydney funnel-web spider, which is one of the most venomous spiders in the world.

Selenocosmia stirlingi is a species of tarantula that is native to the arid regions of Australia. It is sometimes also referred to as a barking spider or whistling spider as this species, like many tarantulas, can stridulate to produce a "hissing" sound when disturbed or threatened. This species is largely fossorial, living in burrows deep underground, however males are sometimes encountered during the breeding season.
Atrax yorkmainorum is a venomous species of Australian funnel-web spider belonging to the Atracidae family and is found in forests in the vicinity of Canberra and south-eastern New South Wales. The genus Atrax was first documented in 1877 and the Atrax yorkmainorum species was first described in 2010.
Ummidia algarve is a spider species found in Portugal. Unlike other known Ummidia species, it creates a trapdoor at the entrance of the burrow.

Eucteniza is a genus of trapdoor spiders in the family Euctenizidae containing at least 14 species occurring in Mexico and the southern United States. Species are distinguished by a softened rear portion of the carapace, and males possess large spines on the first two pairs of walking legs that are used to hold females during mating. Like other trapdoor spiders they create burrows with a hinged lid, from which they await passing insects and other arthropods to prey upon. Many species are known from only one or two localities, or from only male specimens. More species are expected to be discovered. Eucteniza is closely related to spiders of the genera Entychides and Neoapachella.
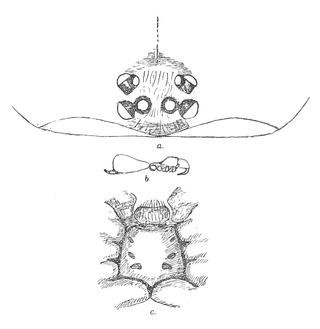
Cantuaria dendyi is a species of trapdoor spider in the family Idiopidae. It can be found in the South Island of New Zealand and is limited to the Christchurch and Banks Peninsula area.

Cantuaria borealis is a native New Zealand species of trapdoor spider.

Tasmanicosa godeffroyi, a wolf spider, is a mid sized spider found in some states of Australia. It is perhaps the most commonly noticed of the wolf spiders in Australia. It is variable in pattern and colour, though the underside of the abdomen is black. Wolf spiders tend to rest at the entrance of their burrows, and their eyes reflect the light of passing cars or torchlight. The burrow has a thin veil of silk, without a lid, unlike some other wolf spiders. The burrow is circular in cross section and travels down for around 15 cm, then parallel with the ground for the next 15 cm. The body length of the female is up to 27 mm, the male 25 mm.

Arbanitis robertsi is a species of tube-dwelling spider in the family Idiopidae found in and near rainforests in New South Wales and Queensland, Australia. A mid to large sized spider which builds a tube of web that extends from the burrow. The tube is attached to rocks, tree ferns or the base of trees. Thousands of these tubes were recorded by Sid Jackson in November 1922 at the south eastern end of Wallis Lake. "Up to three feet long, and half an inch wide". Situated on damp ground, close to freshwater streams.
Proshermacha tepperi, also known as the Lidless Banksia Trapdoor Spider, is a species of mygalomorph spider in the Anamidae family. It is endemic to Australia. It was described in 1901 by British arachnologist Henry Roughton Hogg.
Stanwellia nebulosa, also known as the nebular trapdoor spider, is a species of mygalomorph spider in the Pycnothelidae family. It is endemic to Australia. It was described in 1918 by Australian arachnologists William Joseph Rainbow and Robert Henry Pulleine.
















