
The Triassic is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic.

The Siberian Traps are a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest known volcanic events in the last 500 million years.
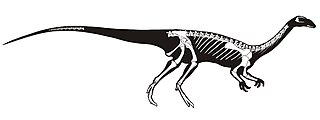
Saturnalia is an extinct genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur known from the Late Triassic Santa Maria Formation of Rio Grande do Sul, southern Brazil. It contains one species, Saturnalia tupiniquim. It is one of the earliest known dinosaurs.

The Early Jurassic Epoch is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, 201.3 Ma, and ends at the start of the Middle Jurassic 174.7 ±0.8 Ma.
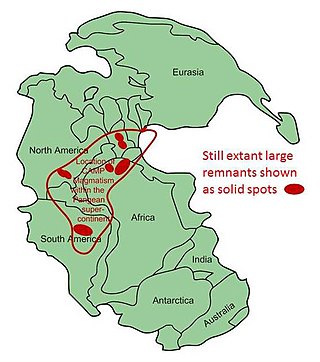
The Central Atlantic magmatic province (CAMP) is the Earth's largest continental large igneous province, covering an area of roughly 11 million km2. It is composed mainly of basalt that formed before Pangaea broke up in the Mesozoic Era, near the end of the Triassic and the beginning of the Jurassic periods. The subsequent breakup of Pangaea created the Atlantic Ocean, but the massive igneous upwelling provided a legacy of basaltic dikes, sills, and lavas now spread over a vast area around the present central North Atlantic Ocean, including large deposits in northwest Africa, southwest Europe, as well as northeast South America and southeast North America. The name and CAMP acronym were proposed by Andrea Marzoli and adopted at a symposium held at the 1999 Spring Meeting of the American Geophysical Union.

In the geologic timescale, the Anisian is the lower stage or earliest age of the Middle Triassic series or epoch and lasted from 247.2 million years ago until 242 million years ago. The Anisian Age succeeds the Olenekian Age and precedes the Ladinian Age.

The Carnian is the lowermost stage of the Upper Triassic Series. It lasted from 237 to 227 million years ago (Ma). The Carnian is preceded by the Ladinian and is followed by the Norian. Its boundaries are not characterized by major extinctions or biotic turnovers, but a climatic event occurred during the Carnian and seems to be associated with important extinctions or biotic radiations. Another extinction occurred at the Carnian-Norian boundary, ending the Carnian age.

The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and 247.2 Ma. Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages.

In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between 247.2 Ma and 237 Ma. It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages.

The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch of the Triassic Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between 237 Ma and 201.4 Ma. It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian ages.

The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and 251.2 Ma. The Induan is sometimes divided into the Griesbachian and the Dienerian subages or substages. The Induan is preceded by the Changhsingian and is followed by the Olenekian.

The Chinle Formation is an Upper Triassic continental geological formation of fluvial, lacustrine, and palustrine to eolian deposits spread across the U.S. states of Nevada, Utah, northern Arizona, western New Mexico, and western Colorado. In New Mexico, it is often raised to the status of a geological group, the Chinle Group. Some authors have controversially considered the Chinle to be synonymous to the Dockum Group of eastern Colorado and New Mexico, western Texas, the Oklahoma panhandle, and southwestern Kansas. The Chinle Formation is part of the Colorado Plateau, Basin and Range, and the southern section of the Interior Plains. A probable separate depositional basin within the Chinle is found in northwestern Colorado and northeastern Utah. The southern portion of the Chinle reaches a maximum thickness of a little over 520 meters (1,710 ft). Typically, the Chinle rests unconformably on the Moenkopi Formation.

Probainognathia is one of the two major subgroups of the clade Eucynodontia, the other being Cynognathia. The earliest forms were carnivorous and insectivorous, though some groups eventually also evolved herbivorous diets. The earliest and most basal probainognathian is the Middle Triassic (Anisian) aged Lumkuia, from South Africa, though probainognathians would not become prominent until the mid Norian stage of the Late Triassic. Three groups survived the extinction at the end of Triassic: Tritheledontidae and Tritylodontidae, which both survived until the Jurassic—the latter even into the Cretaceous —and Mammaliaformes, which includes the mammals.

São Gabriel is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.

Cyclotosaurus is an extinct genus of temnospondyl within the family Mastodonsauridae. It was of great size for an amphibian, had an elongated skull up to 56 cm (22 in).

Metoposauridae is an extinct family of trematosaurian temnospondyls. The family is known from the Triassic period. Most members are large, approximately 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) long and could reach 3 m long. Metoposaurids can be distinguished from the very similar mastodonsauroids by the position of their eyes, placed far forward on the snout.

Trematosauridae is a family of large marine temnospondyls with several included genera.
Bukobaja is an extinct genus of mastodonsaurid temnospondyl from the middle Triassic of Russia. It contains a single species, Bukobaja enigmatica. Bukobaja mainly occurs in the Bukobay Svita as part of the Ladinian?-age "Mastodonsaurus fauna", a section of Russian Triassic biostratigraphy characterized by "Mastodonsaurus" torvus. It was also present in the underlying Donguz Svita. Bukobaja appears to be a valid genus similar to, yet distinct from, Mastodonsaurus. Despite appearing to possess several unique features, Bukobaja is still known from very few remains. This has led to difficulties in determining its relations more precisely than "Mastodonsauridae incertae sedis". It has also been compared to trematosaurids.
Malutinisuchus is an extinct genus of Archosauromorph. The genus was named in 1986 with the description of the type species M. gratus. Malutinisuchus is known from Ladinian-age Middle Triassic deposits in the Bukobay and Rassypnaya localities in Orenburg Oblast, Russia. In Russia, deposits of this age are referred to the Bukobay Gorizont.
The Norian is a division of the Triassic Period. It has the rank of an age (geochronology) or stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227 to 208.5 million years ago. It was preceded by the Carnian and succeeded by the Rhaetian.
















