
The inline-four engine or straight-four engine is a four-cylinder internal combustion engine in which the cylinders are mounted in a straight line or plane along the crankcase. The single bank of cylinders may be oriented in either a vertical or an inclined plane with all the pistons driving a common crankshaft. Where it is inclined, it is sometimes called a slant-four. In a specification chart or when an abbreviation is used, an inline-four engine is listed either as I4 or L4.

The Junkers Jumo 205 aircraft engine was the most famous of a series of aircraft diesel engines that were the first, and for more than half a century the only successful aviation Diesel powerplants. The Jumo 204 first entered service in 1932. Later engines of this type comprised the experimental Jumo 206 and Jumo 208, with the Jumo 207 produced in some quantity for the Junkers Ju 86P and -R high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft, and the 46-meter wingspan, six-engined Blohm & Voss BV 222 Wiking flying boat. All three of these variants differed in stroke and bore and supercharging arrangements. In all more than 900 of these engines were produced, in the 1930s and through most of World War II.

The Mitsubishi Astron or 4G5/4D5 engine, is a series of straight-four internal combustion engines first built by Mitsubishi Motors in 1972. Engine displacement ranged from 1.8 to 2.6 litres, making it one of the largest four-cylinder engines of its time.

The Mitsubishi Sirius or 4G6/4D6 engine is the name of one of Mitsubishi Motors' four series of inline-four automobile engines, along with Astron, Orion, and Saturn.

The J-series is Honda's fourth production V6 engine family introduced in 1996, after the C-series, which consisted of three dissimilar versions. The J-series engine was designed in the United States by Honda engineers. It is built at Honda's Anna, Ohio and Lincoln, Alabama engine plants.

GMC Truck produced a unique 60 degree V6 engine family from 1959 through 1974, in gasoline and Diesel versions. V8 and V12 derivatives of the basic design were also produced. Examples of this engine family were found in pickup trucks, Suburbans, heavier trucks and motor coaches.

The Prince G-series engine was the company's only straight-four and straight-six engines which began production in 1955. A number of variations were made, with both OHV and OHC heads. A diesel four-cylinder with 1.9 L (1,862 cc) was also built, called the D-6. The G series was used in the Skyline, the Laurel, and the Gloria from the 1950s to the early 1970s.

The Honda D series inline-four cylinder engine is used in a variety of compact models, most commonly the Honda Civic, CRX, Logo, Stream, and first-generation Integra. Engine displacement ranges between 1.2 and 1.7 liters. The D Series engine is either SOHC or DOHC, and might include VTEC variable valve timing. Power ranges from 66 PS (49 kW) in the Logo to 130 PS (96 kW) in the Civic Si. D-series production commenced 1984 and ended 2005. D-series engine technology culminated with production of the D15B 3-stage VTEC (D15Z7) which was available in markets outside of the United States. Earlier versions of this engine also used a single port fuel injection system Honda called PGM-CARB, signifying the carburetor was computer controlled.
The Honda F-Series engine was considered Honda's "big block" SOHC inline four, though lower production DOHC versions of the F-series were built. It features a solid iron or aluminum open deck cast iron sleeved block and aluminum/magnesium cylinder head.
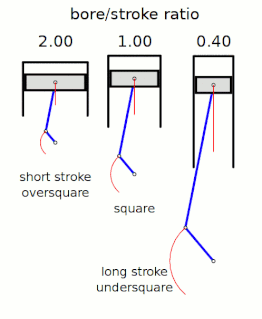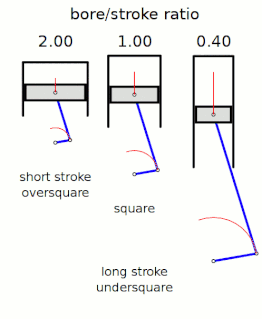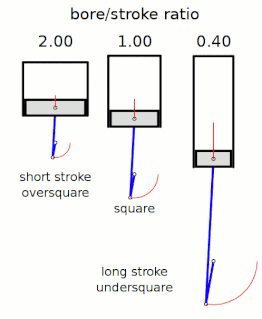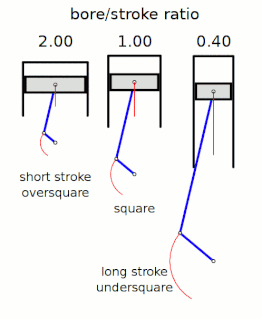
In a reciprocating piston engine, the stroke ratio, defined by either bore/stroke ratio or stroke/bore ratio, is a term to describe the ratio between cylinder bore diameter and piston stroke length. This can be used for either an internal combustion engine, where the fuel is burned within the cylinders of the engine, or external combustion engine, such as a steam engine, where the combustion of the fuel takes place outside the working cylinders of the engine.

The PSA TU engine is a family of small four-cylinder engines used in the Peugeot and Citroën range of cars. It was introduced in 1986 with the Citroën AX, replacing the X family, although it shared many components with its predecessor. The TU is available in either petrol or a naturally aspirated diesel variant, the latter called TUD.
The N series is Honda's first automotive diesel engine, an inline-four for medium-sized vehicles. It uses common rail direct injection, which Honda brands as i-CTDi. The most notable feature is the aluminium block, which uses proprietary technology in the manufacturing process to provide light weight and high rigidity. Roller chains drive two overhead camshafts. A variable-geometry turbocharger and intercooler are used.

The Hall-Scott A-7 was an early aircraft engine manufactured by the Hall-Scott company of Berkeley, California. Of straight-4 configuration, it developed 100 horsepower (75 kW). These engines suffered from reliability problems and were prone to catch fire while in operation.
The EA827 family of petrol engines was initially developed by Audi under Ludwig Kraus leadership and introduced in 1972 by the B1-series Audi 80, and went on to power many Volkswagen Group models. This is a very robust water-cooled engine configuration for four- up to eight- cylinders, and is still in production. In Brasil this engine is produced under name Volkswagen AP AP.
The Sunbeam Pathan, also known as the Sunbeam P.1, was a 1920s British diesel aero engine.

The Opel cam-in-head engine (CIH) is a family of automobile engines built by former General Motors subsidiary Opel from 1965 until 1998. Both four- and six-cylinder inline configurations were produced. The name derives from the location of the camshaft, which was neither cam-in-block nor a true overhead camshaft. In the CIH engine the camshaft is located in the cylinder head but sits alongside the valves rather than above them. The overhead valves are actuated through very short tappets and rocker arms. The four-cylinder CIH was largely supplanted by the Family II unit as Opel/Vauxhall's core mid-size engine in the 1980s. A four-cylinder version of the CIH remained in limited production until 1998, and six-cylinder versions of the CIH until 1995.
The Beardmore Cyclone was an aero engine produced by William Beardmore & Co with the aim of producing an engine generating a high power output at low revolutions by designing an engine of large displacement. The design did not enter volume production.












