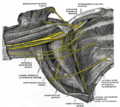
| Subclavian nerve | |
|---|---|
 Diagram of the right brachial plexus. Subclavian nerve labelled at top right. | |
 The right brachial plexus with its short branches, viewed from in front. Subclavian nerve not visible. | |
| Details | |
| From | Upper trunk (C5-C6) of brachial plexus |
| To | Sometimes the accessory phrenic nerve |
| Innervates | Subclavius muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus subclavius |
| TA98 | A14.2.03.013 |
| TA2 | 6412 |
| FMA | 65280 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The subclavian nerve, also known as the nerve to the subclavius, is a small branch of the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It contains axons from C5 and C6. It innervates the subclavius muscle.