Related Research Articles

Alchemy is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD. Greek-speaking alchemists often referred to their craft as “the Art” (τέχνη) or “Knowledge” (ἐπιστήμη), and it was often characterised as mystic (μυστική), sacred (ἱɛρά), or divine (θɛíα).
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during reactions with other substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds.
A chemical element is a chemical substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions. The basic particle that constitutes a chemical element is the atom. Elements are identified by the number of protons in their nucleus, known as the element's atomic number. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8, meaning each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its nucleus. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, known as isotopes of the element. Two or more atoms can combine to form molecules. Chemical compounds are molecules made of atoms of different elements, while mixtures contain atoms of different elements not necessarily combined as molecules. Atoms can be transformed into different elements in nuclear reactions, which change an atom's atomic number.

The phlogiston theory, a superseded scientific theory, postulated the existence of a fire-like element dubbed phlogiston contained within combustible bodies and released during combustion. The name comes from the Ancient Greek φλογιστόνphlogistón, from φλόξphlóx (flame). The idea of a phlogistic substance was first proposed in 1667 by Johann Joachim Becher and later put together more formally in 1703 by Georg Ernst Stahl. Phlogiston theory attempted to explain chemical processes such as combustion and rusting, now collectively known as oxidation. The theory was challenged by the concomitant weight increase and was abandoned before the end of the 18th century following experiments by Antoine Lavoisier in the 1770s and by other scientists. Phlogiston theory led to experiments that ultimately resulted in the identification, and naming (1777), of oxygen by Joseph Priestley and Antoine Lavoisier, respectively.

The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology and chemistry transformed the views of society about nature. The Scientific Revolution took place in Europe in the second half of the Renaissance period, with the 1543 Nicolaus Copernicus publication De revolutionibus orbium coelestium often cited as its beginning.

Robert Boyle was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. He is best known for Boyle's law, which describes the inversely proportional relationship between the absolute pressure and volume of a gas, if the temperature is kept constant within a closed system. Among his works, The Sceptical Chymist is seen as a cornerstone book in the field of chemistry. He was a devout and pious Anglican and is noted for his writings in theology.

Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe. It was dominant before the development of modern science.

In Renaissance alchemy, alkahest was the theorized "universal solvent". It was supposed to be capable of dissolving any composite substance, including gold, without altering or destroying its fundamental components. By extracting from composite substances their fundamental virtues and properties, alchemists hoped to gain control of invaluable medical healing properties. For this reason the alkahest was earnestly sought. At the same time, its very existence was debated among alchemists and philosophers.

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis of the various branches of chemistry. Examples include the discovery of fire, extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.
According to ancient and medieval science, aether, also known as the fifth element or quintessence, is the material that fills the region of the universe beyond the terrestrial sphere. The concept of aether was used in several theories to explain several natural phenomena, such as the propagation of light and gravity. In the late 19th century, physicists postulated that aether permeated space, providing a medium through which light could travel in a vacuum, but evidence for the presence of such a medium was not found in the Michelson–Morley experiment, and this result has been interpreted to mean that no luminiferous aether exists.

The history of thermodynamics is a fundamental strand in the history of physics, the history of chemistry, and the history of science in general. Due to the relevance of thermodynamics in much of science and technology, its history is finely woven with the developments of classical mechanics, quantum mechanics, magnetism, and chemical kinetics, to more distant applied fields such as meteorology, information theory, and biology (physiology), and to technological developments such as the steam engine, internal combustion engine, cryogenics and electricity generation. The development of thermodynamics both drove and was driven by atomic theory. It also, albeit in a subtle manner, motivated new directions in probability and statistics; see, for example, the timeline of thermodynamics.

Iatrochemistry is an archaic pre-scientific school of thought that was supplanted by modern chemistry and medicine. Having its roots in alchemy, iatrochemistry sought to provide chemical solutions to diseases and medical ailments.

The Sceptical Chymist: or Chymico-Physical Doubts & Paradoxes is the title of a book by Robert Boyle, published in London in 1661. In the form of a dialogue, the Sceptical Chymist presented Boyle's hypothesis that matter consisted of corpuscles and clusters of corpuscles in motion and that every phenomenon was the result of collisions of particles in motion. Boyle also objected to the definitions of elemental bodies propounded by Aristotle and by Paracelsus, instead defining elements as "perfectly unmingled bodies". For these reasons Robert Boyle has sometimes been called the founder of modern chemistry.
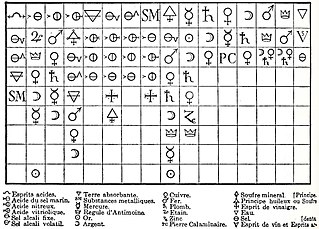
In the history of chemistry, the chemical revolution, also called the first chemical revolution, was the reformulation of chemistry during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, which culminated in the law of conservation of mass and the oxygen theory of combustion.
Corpuscularianism, also known as corpuscularism, is a set of theories that explain natural transformations as a result of the interaction of particles. It differs from atomism in that corpuscles are usually endowed with a property of their own and are further divisible, while atoms are neither. Although often associated with the emergence of early modern mechanical philosophy, and especially with the names of Thomas Hobbes, René Descartes, Pierre Gassendi, Robert Boyle, Isaac Newton, and John Locke, corpuscularian theories can be found throughout the history of Western philosophy.

This timeline of chemistry lists important works, discoveries, ideas, inventions, and experiments that significantly changed humanity's understanding of the modern science known as chemistry, defined as the scientific study of the composition of matter and of its interactions.

A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed.

Alchemy in the medieval Islamic world refers to both traditional alchemy and early practical chemistry by Muslim scholars in the medieval Islamic world. The word alchemy was derived from the Arabic word كيمياء or kīmiyāʾ and may ultimately derive from the ancient Egyptian word kemi, meaning black.

Lawrence M. Principe is the Drew Professor of the Humanities at Johns Hopkins University in the Department of History of Science and Technology and the Department of Chemistry. He is also currently the Director of the Charles Singleton Center for the Study of Premodern Europe, an interdisciplinary center for research at Johns Hopkins. He is the first recipient of the Francis Bacon Medal for significant contributions to the history of science. Principe's research has been supported by the National Science Foundation, the National Endowment for the Humanities, the American Philosophical Society, the Chemical Heritage Foundation, and a 2015-2016 Guggenheim Fellowship. Principe is recognized as one of the foremost experts in the history of alchemy.

The Twelve Keys of Basil Valentine is a widely reproduced alchemical book attributed to Basil Valentine. It was first published in 1599 by Johann Thölde who is likely the book's true author. It is presented as a sequence of alchemical operations encoded allegorically in words, to which images have been added. The first Basil Valentine book to discuss the keys is Ein kurtz summarischer Tractat, von dem grossen Stein der Uralten, 1599.
References
- ↑ J. F. Fulton. Robert Boyle and His Influence on Thought in the Seventeenth Century. Isis, Vol. 18, No. 1 (Jul., 1932), pp. 77-102. Published by: The University of Chicago Press on behalf of The History of Science Society
- ↑ Muir, M.M.P. (1992) [1902]. Story of Alchemy and the Beginnings of Chemistry. Kessinger. p. 157. ISBN 9781564590190. LCCN 03001600.