
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.

Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as halides of carbon without carbon-hydrogen and carbon-carbon bonds, and certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen.

Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.

Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.
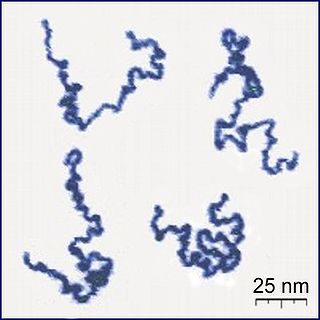
A polymer is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules linked together into chains of repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals.

Fiber or fibre is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate fibers, for example carbon fiber and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene.
In finance, a credit derivative refers to any one of "various instruments and techniques designed to separate and then transfer the credit risk" or the risk of an event of default of a corporate or sovereign borrower, transferring it to an entity other than the lender or debtholder.
In finance, a convertible bond, convertible note, or convertible debt is a type of bond that the holder can convert into a specified number of shares of common stock in the issuing company or cash of equal value. It is a hybrid security with debt- and equity-like features. It originated in the mid-19th century, and was used by early speculators such as Jacob Little and Daniel Drew to counter market cornering.

1,3-Butadiene is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene.

In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. These can be activated by enzyme hydrolysis, which causes the sugar part to be broken off, making the chemical available for use. Many such plant glycosides are used as medications. Several species of Heliconius butterfly are capable of incorporating these plant compounds as a form of chemical defense against predators. In animals and humans, poisons are often bound to sugar molecules as part of their elimination from the body.

Synthetic oil is a lubricant consisting of chemical compounds that are artificially modified or synthesised. Synthetic lubricants can be manufactured using chemically modified petroleum components rather than whole crude oil, but can also be synthesized from other raw materials. The base material, however, is still overwhelmingly crude oil that is distilled and then modified physically and chemically. The actual synthesis process and composition of additives is generally a commercial trade secret and will vary among producers.
Retrosynthetic analysis is a technique for solving problems in the planning of organic syntheses. This is achieved by transforming a target molecule into simpler precursor structures regardless of any potential reactivity/interaction with reagents. Each precursor material is examined using the same method. This procedure is repeated until simple or commercially available structures are reached. These simpler/commercially available compounds can be used to form a synthesis of the target molecule. E.J. Corey formalized this concept in his book The Logic of Chemical Synthesis.
Artificial hair integrations, more commonly known as hair extensions, hair weaves, and fake hair add length and fullness to human hair. Hair extensions are usually clipped, glued, or sewn on natural hair by incorporating additional human or synthetic hair. These methods include tape-in extensions, clip-in or clip-on extensions, micro/nano rings, fusion method, weaving method, and wigs.
A polyolefin is a type of polymer with the general formula (CH2CHR)n where R is an alkyl group. They are usually derived from a small set of simple olefins (alkenes). Dominant in a commercial sense are polyethylene and polypropylene. More specialized polyolefins include polyisobutylene and polymethylpentene. They are all colorless or white oils or solids. Many copolymers are known, such as polybutene, which derives from a mixture of different butene isomers. The name of each polyolefin indicates the olefin from which it is prepared; for example, polyethylene is derived from ethylene, and polymethylpentene is derived from 4-methyl-1-pentene. Polyolefins are not olefins themselves because the double bond of each olefin monomer is opened in order to form the polymer. Monomers having more than one double bond such as butadiene and isoprene yield polymers that contain double bonds (polybutadiene and polyisoprene) and are usually not considered polyolefins. Polyolefins are the foundations of many chemical industries.
Diboron tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula (BF2)2. A colorless gas, the compound has a halflife of days at room temperature. It is the most stable of the diboron tetrahalides, and does not appreciably decompose under standard conditions.

1-Testosterone, also known as δ1-dihydrotestosterone (δ1-DHT), as well as dihydroboldenone, is a synthetic anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 5α-reduced derivative of boldenone (Δ1-testosterone). It differs from testosterone by having a 1(2)-double bond instead of a 4(5)-double bond in its A ring. It was legally sold online in the United States until 2005, when it was reclassified as a Schedule III drug.
Dioxygen complexes are coordination compounds that contain O2 as a ligand. The study of these compounds is inspired by oxygen-carrying proteins such as myoglobin, hemoglobin, hemerythrin, and hemocyanin. Several transition metals form complexes with O2, and many of these complexes form reversibly. The binding of O2 is the first step in many important phenomena, such as cellular respiration, corrosion, and industrial chemistry. The first synthetic oxygen complex was demonstrated in 1938 with cobalt(II) complex reversibly bound O2.

Salicylmethylecgonine, (2′-Hydroxycocaine) is a tropane derivative drug which is both a synthetic analogue and a possible active metabolite of cocaine. Its potency in vitro is around 10x that of cocaine, although it is only around three times more potent than cocaine when administered to mice Note however that the compound 2′-Acetoxycocaine would act as a prodrug to Salicylmethylecgonine in humans, and has a more efficient partition coefficient which would act as a delivery system and would circumvent this reason for a drop in potency. Salicylmethylecgonine also shows increased behavioral stimulation compared to cocaine similar to the phenyltropanes. The hydroxy branch renders the molecule a QSAR of a 10-fold increase over cocaine in its binding potency for the dopamine transporter & a 52-fold enhanced affinity for the norepinephrine transporter. It also has a reduced selectivity for the serotonin transporter though only due to its greater increase at NET binding; its SERT affinity being 4-fold increased compared to cocaine. However, in overall binding affinity it displaces ligands better across the board than cocaine in all monoamine categories.
The Davis–Beirut reaction is N,N-bond forming heterocyclization that creates numerous types of 2H-indazoles and indazolones in both acidic and basic conditions The Davis–Beirut reaction is named after Mark Kurth and Makhluf Haddadin's respective universities; University of California, Davis and American University of Beirut, and is appealing because it uses inexpensive starting materials and does not require toxic metals.

Δ-3-Tetrahydrocannabinol is a synthetic isomer of tetrahydrocannabinol, developed during the original research in the 1940s to develop synthetic routes to the natural products Δ8-THC and Δ9-THC found in the cannabis plant. While the normal trans configuration of THC is in this case flattened by the double bond, it still has two enantiomers as the 9-methyl group can exist in an (R) or (S) conformation. The (S) enantiomer has similar effects to Δ9-THC though with several times lower potency, while the (R) enantiomer is many times less active or inactive, depending on the assay used. It has been identified as a component of vaping liquid products.











