
A therapsid is a member of the clade Therapsida which is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals and their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more underneath the body, as opposed to the sprawling posture of many reptiles and salamanders.

Dinocephalians are a clade of large-bodied early therapsids that flourished in the Early and Middle Permian between 279.5 and 260 million years ago (Ma), but became extinct during the Capitanian mass extinction event. Dinocephalians included herbivorous, carnivorous, and omnivorous forms. Many species had thickened skulls with many knobs and bony projections. Dinocephalians were the first non-mammalian therapsids to be scientifically described and their fossils are known from Russia, China, Brazil, South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Tanzania.

The Beaufort Group is the third of the main subdivisions of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. It is composed of a lower Adelaide Subgroup and an upper Tarkastad Subgroup. It follows conformably after the Ecca Group and unconformably underlies the Stormberg Group. Based on stratigraphic position, lithostratigraphic and biostratigraphic correlations, palynological analyses, and other means of geological dating, the Beaufort Group rocks are considered to range between Middle Permian (Wordian) to Early Triassic (Anisian) in age.

Anteosaurs are a group of large, primitive carnivorous dinocephalian therapsids with large canines and incisors and short limbs, that are known from the Middle Permian of South Africa, Russia, China, and Brazil. Some grew very large, with skulls 50–80 centimetres (20–31 in) long, and were the largest predators of their time. They died out at the end of the Middle Permian, possibly as a result of the extinction of the herbivorous Tapinocephalia on which they may have fed.

Anteosauridae is an extinct family of large carnivorous dinocephalian therapsids that are known from the Middle Permian of Asia, Africa, and South America.These animals were by far the largest predators of the Permian period, with skulls reaching 80 cm in length in adult individuals, far larger than the biggest gorgonopsian.

Caseidae are an extinct family of basal synapsids that lived from the Late Carboniferous to Middle Permian between about 300 and 265 million years ago. Fossils of these animals come from the south-central part of the United States, from various parts of Europe, and possibly from South Africa if the genus Eunotosaurus is indeed a caseid as some authors proposed in 2021. Caseids show great taxonomic and morphological diversity. The most basal taxa were small insectivorous and omnivorous forms that lived mainly in the Upper Carboniferous and Lower Permian, such as Eocasea, Callibrachion, and Martensius. This type of caseid persists until the middle Permian with Phreatophasma and may be Eunotosaurus. During the early Permian, the clade is mainly represented by many species that adopted a herbivorous diet. Some have evolved into gigantic forms that can reach 6–7 metres (20–23 ft) in length, such as Cotylorhynchus hancocki and Alierasaurus ronchii, making them the largest Permian synapsids. Caseids are considered important components of early terrestrial ecosystems in vertebrate history because the numerous herbivorous species in this family are among the first terrestrial tetrapods to occupy the role of primary consumer. The caseids experienced a significant evolutionary radiation at the end of the early Permian, becoming, with the captorhinid eureptiles, the dominant herbivores of terrestrial ecosystems in place of the edaphosaurids and diadectids.

Estemmenosuchidae is an extinct family of large, very early herbivorous therapsids that flourished during the Guadalupian period. They are distinguished by horn-like structures, probably for display or agonistic behavior. Apart from the best known genus, Estemmenosuchus, the group is poorly known. To date, their fossils are known only from the Perm region of Russia.

Anteosaurus is an extinct genus of large carnivorous dinocephalian synapsid. It lived at the end of the Guadalupian during the Capitanian stage, about 265 to 260 million years ago in what is now South Africa. It is mainly known by cranial remains and few postcranial bones. Measuring 5–6 m (16–20 ft) long and weighing about 600 kg (1,300 lb), Anteosaurus was the largest known carnivorous non-mammalian synapsid and the largest terrestrial predator of the Permian period. Occupying the top of the food chain in the Middle Permian, its skull, jaws and teeth show adaptations to capture large prey like the giants titanosuchids and tapinocephalids dinocephalians and large pareiasaurs.

The Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone which correlates to the middle Abrahamskraal Formation, Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a fossiliferous and geologically important geological Group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. The thickest outcrops, reaching approximately 2,000 metres (6,600 ft), occur from Merweville and Leeu-Gamka in its southernmost exposures, from Sutherland through to Beaufort West where outcrops start to only be found in the south-east, north of Oudshoorn and Willowmore, reaching up to areas south of Graaff-Reinet. Its northernmost exposures occur around the towns Fraserburg and Victoria West. The Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone is the second biozone of the Beaufort Group.
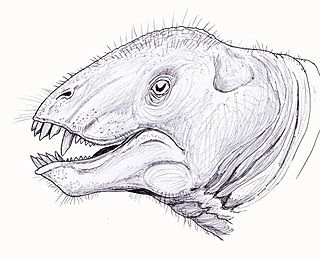
Tapinocaninus is an extinct genus of therapsids in the family Tapinocephalidae, of which it is the most basal member. Only one species is known, Tapinocaninus pamelae. The species is named in honor of Rubidge's mother, Pam. Fossils have been found dating from the Middle Permian.

Australosyodon is an extinct genus of dinocephalian therapsids from the middle Permian of South Africa. The first fossil was discovered in the 1980s near the village of Prince Albert Road in the Karoo region of South Africa.

Microurania is an extinct genus of therapsids from the Middle Permian first named and described by Mikhaïl Ivakhnenko. It is known from a single partial skull found in the region of Orenburg, Russia. According to Kammerer, 2011, it likely represents the remains of a juvenile dinocephalian.

Styracocephalus platyrhynchus (Greek for "spiked-head") is an extinct genus of dinocephalian therapsid that existed during the mid-Permian throughout South Africa, but mainly in the Karoo Basin. It is often referred to by its single known species Styracocephalus platyrhynchus. The Dinocephalia clade consisted of the largest land vertebrates and herbivores during the early to mid-Permian. This period is often also referred to as the Guadalupian epoch, approximately 270 to 260 million years ago.

Criocephalosaurus is an extinct genus of tapinocephalian therapsids that lived in Southern Africa during the Guadalupian epoch of the Permian. They are the latest surviving dinocephalians, extending past the Abrahamskraal Formation into the lowermost Poortjie Member of the Teekloof Formation in South Africa. They are also regarded as the most derived of the dinocephalians, alongside Tapinocephalus, and the most abundant in the fossil record.

The Abrahamskraal Formation is a geological formation and is found in numerous localities in the Northern Cape, Western Cape, and the Eastern Cape of South Africa. It is the lowermost formation of the Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a major geological group that forms part of the greater Karoo Supergroup. It represents the first fully terrestrial geological deposits of the Karoo Basin. Outcrops of the Abrahamskraal Formation are found from the small town Middelpos in its westernmost localities, then around Sutherland, the Moordenaarskaroo north of Laingsburg, Williston, Fraserburg, Leeu-Gamka, Loxton, and Victoria West in the Western Cape and Northern Cape. In the Eastern Cape outcrops are known from Rietbron, north of Klipplaat and Grahamstown, and also southwest of East London.

Pampaphoneus is an extinct genus of carnivorous dinocephalian therapsid belonging to the family Anteosauridae. It lived 268 to 265 million years ago during the Wordian age of the Guadalupian period in what is now Brazil. Pampaphoneus is known by an almost complete skull with the lower jaw still articulated, discovered on the lands of the Boqueirão Farm, near the city of São Gabriel, in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. A second specimen from the same locality was reported in 2019 and 2020 but has not yet been described. It is composed of a skull associated with postcranial remains. It is the first South American species of dinocephalian to have been described. The group was previously known in South America only by a few isolated teeth and a jaw fragment reported in 2000 in the same region of Brazil. Phylogenetic analysis conducted by Cisneros and colleagues reveals that Pampaphoneus is closely related to anteosaurs from European Russia, indicating a closer faunal relationship between South America and Eastern Europe than previously thought, thus promoting a Pangea B continental reconstruction.

Anteosaurinae is an extinct subfamily of dinocephalian therapsids. It is one of two subfamilies in the family Anteosauridae, the other being Syodontinae.

Sinophoneus is an extinct genus of carnivorous dinocephalian therapsid belonging to the family Anteosauridae. It lived 272 to 270 million years ago at the beginning of the Middle Permian in what is now the Gansu Province in northern China. It is known by a skull of an adult individual, as well as by many skulls of juvenile specimens. The latter were first considered as belonging to a different animal, named Stenocybus, before being reinterpreted as immature Sinophoneus. Sinophoneus shows a combination of characters present in other anteosaurs. Its bulbous profile snout and external nostrils located in front of the canine are reminiscent of the basal anteosaur Archaeosyodon, while its massive transverse pterygoids processes with enlarged distal ends are more similar to the more derived anteosaurs Anteosaurus and Titanophoneus. First phylogenetic analyzes identified Sinophoneus as the most basal Anteosaurinae. A more recent analysis positioned it outside the Anteosaurinae and Syodontinae subclades, and recovers it as the most basal Anteosauridae.
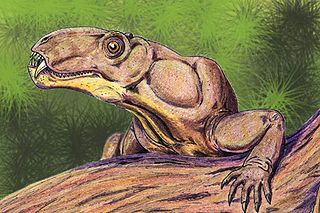
Phthinosuchia is an extinct group of therapsids including two poorly known species, Phthinosuchus discors and Phthinosaurus borrisiaki, from the Middle Permian of Russia. Phthinthosuchus is known a partial crushed skull and Phthinosaurus is known from an isolated lower jaw. The two species have traditionally been grouped together based on their shared primitive characteristics, but more recent studies have proposed that they are more distantly related. Phthinosuchus is either a carnivorous gorgonopsian relative or an anteosaurian dinocephalian while Phthinosaurus is either a herbivorous rhopalodont dinocephalian or a therocephalian.
Parasumina is an extinct genus of anomodont known from the late Capitanian age at the end of the middle Permian period of European Russia. The type and only species is Parasuminia ivakhnenkoi. It was closely related to Suminia, another Russian anomodont, and was named for its resemblance. Little is known about Parasuminia as the only fossils are of fragmentary pieces of the skull and jaw, but the known remains suggest that its head and jaws were deeper and more robust than those of Suminia, and with shorter, stouter teeth. However, despite these differences they appear to have been similar animals with a similarly complex method of processing vegetation.





















