Dinosaurus is an extinct genus of therapsid of controversial affinities. Its type and only species is Dinosaurus murchisonii. It is only known from a partial snout from the Permian of Russia. Its taxonomic history is intertwined with several other poorly-known Russian therapsids, particularly Rhopalodon, Brithopus, and Phthinosuchus.

Therapsida is a clade comprising a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals and their ancestors and close relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more underneath the body, resulting in a more "standing" quadripedal posture, as opposed to the lower sprawling posture of many reptiles and amphibians.

Gorgonopsia is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to the Upper Permian, possibly even up to the Early Triassic, roughly between 265 and 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw.

Microurania is an extinct genus of therapsids from the Middle Permian first named and described by Mikhaïl Ivakhnenko. It is known from a single partial skull found in the region of Orenburg, Russia. According to Kammerer, 2011, it likely represents the remains of a juvenile dinocephalian.

Venyukovia is an extinct genus of venyukovioid therapsid, a basal anomodont from the Middle Permian of Russia. The type and sole species, V. prima, is known only by a partial lower jaw with teeth. Venyukovia has often been incorrectly spelt as 'Venjukovia' in English literature. This stems from a spelling error made by Russian palaeontologist Ivan Efremov in 1940, who mistakenly replaced the 'y' with a 'j', which subsequently permeated through therapsid literature before the mistake was caught and corrected. Venyukovia is the namesake for the Venyukovioidea, a group of small Russian basal anomodonts also including the closely related Otsheria, Suminia, Parasuminia and Ulemica, although it itself is also one of the poorest known. Like other venyukovioids, it had large projecting incisor-like teeth at the front and lacked canines, although the remaining teeth are simple compared to some other venyukovioids, but may resemble those of Otsheria.
Cerdodontenuidens is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian therapsids. However, some consider this genus to be a nomen dubium. The holotype skull is of a crushed skull of a small therocephalian.
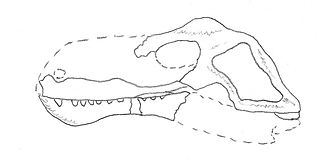
Dimacrodon is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsid from the latest Early Permian San Angelo Formation of Texas. It is distinguished by toothless, possibly beaked jaw tips, large lower canines and a thin bony crest on top of its head. Previously thought to be an anomodont therapsid related to dicynodonts, it was later found to lack any diagnostic features of anomodonts or even therapsids and instead appears to be a 'pelycosaur'-grade synapsid of uncertain classification.
Eosyodon is a dubious genus of extinct non-mammalian synapsids from the Permian of Texas. Its type and only species is Eosyodon hudsoni. Though it was originally interpreted as an early therapsid, it is probably a member of Sphenacodontidae, the family of synapsids that includes Dimetrodon.
Elephantosaurus is an extinct genus of dicynodont from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) Bukobay Formation. The holotype and only known specimen, catalogued as PIN 525/25, is a fragment of the skull that includes portions of the left interorbital region and nasal bones, and suggests a very large animal with a skull at least 30 centimetres (12 in) wide. The bones of the skull roof are also unusually thick. While usually considered a member of the Stahleckeriidae, generally due to its size, it probably falls just outside the group due to its frontal bone contributing substantially to the margin of the eye socket.

Hipposaurus is an extinct genus of basal therapsids known from the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone of the Main Karoo Basin, South Africa. Chronologically this is within the Capitanian stage of the Guadalupian Series. The genus was first described by S.H. Haughton as H. boonstrai on the basis of a skull and associated skeleton and was later considered a gorgonopsian in the family 'Ictidorhinidae' by Robert Broom. It is now considered a basal biarmosuchian, but its affinities remain uncertain. Some authors note the similarity of its braincase with that of Herpetoskylax. H. boonstrai is currently known from only two specimens in the Iziko South African Museum, Cape Town.

Glanosuchus is a genus of scylacosaurid therocephalian from the Late Permian of South Africa. The type species G. macrops was named by Robert Broom in 1904. Glanosuchus had a middle ear structure that was intermediate between that of early therapsids and mammals. Ridges in the nasal cavity of Glanosuchus suggest it had an at least partially endothermic metabolism similar to modern mammals.
Lanthanostegus is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsids from the Capitanian Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone, Koonap Formation of South Africa. The type and the only species is Lanthanostegus mohoii.
Orthopus is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsids. It is based on a partial humerus that closely resembles Estemmenosuchus, in the limited comparisons possible.

Niaftasuchus is an extinct genus of therapsids. Its type and only named species is Niaftasuchus zekkeli.

Progalesaurus is an extinct genus of galesaurid cynodont from the early Triassic. Progalesaurus is known from a single fossil of the species Progalesaurus lootsbergensis, found in the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone of the Balfour Formation. Close relatives of Progalesaurus, other galesaurids, include Galesaurus and Cynosaurus. Galesaurids appeared just before the Permian-Triassic extinction event, and disappeared from the fossil record in the Middle-Triassic.

Scymnosaurus is a dubious genus of therocephalian therapsids based upon various fossils of large early therocephalians. The genus was described by Robert Broom in 1903 with S. ferox, followed by S. watsoni in 1915 and a third, S. major, by Lieuwe Dirk Boonstra in 1954. Each of these species are considered nomen dubia today and based upon specimens belonging to two separate families of therocephalians. S. ferox and S. major represent specimens of Lycosuchidae incertae sedis, while S. watsoni is Scylacosauridae incertae sedis. Broom named a fourth species in 1907 from KwaZulu-Natal, S. warreni, though he later referred it to Moschorhinus as a valid species in 1932 but now is recognised as being synonymous with M. kitchingi.

Xyrospondylus is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsids belonging to the Edaphosauridae. The type species, X. ecordi, was named in 1982; it was originally named as a species of Edaphosaurus in 1957.

Lumkuia is an extinct genus of cynodont, fossils of which have been found in the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the South African Karoo Basin that date back to the early Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, Lumkuia fuzzi, which was named in 2001 on the basis of the holotype specimen BP/1/2669, which can now be found at the Bernard Price Institute in Johannesburg, South Africa. The genus has been placed in its own family, Lumkuiidae. Lumkuia is not as common as other cynodonts from the same locality such as Diademodon and Trirachodon.

Herpetoskylax is an extinct genus of biarmosuchian therapsids which existed in South Africa. The type species is Herpetoskylax hopsoni. It lived in the Late Permian Period.
Eutheriodontia is a clade of therapsids which appear during the Middle Permian and which includes therocephalians and cynodonts, this latter group including mammals and related forms.















