
Tabulata, commonly known as tabulate corals, are an order of extinct forms of coral. They are almost always colonial, forming colonies of individual hexagonal cells known as corallites defined by a skeleton of calcite, similar in appearance to a honeycomb. Adjacent cells are joined by small pores. Their distinguishing feature is their well-developed horizontal internal partitions (tabulae) within each cell, but reduced or absent vertical internal partitions. They are usually smaller than rugose corals, but vary considerably in shape, from flat to conical to spherical.

Stromatoporoidea is an extinct clade of sea sponges common in the fossil record from the Middle Ordovician to the Late Devonian. They can be characterized by their densely layered calcite skeletons lacking spicules. Stromatoporoids were among the most abundant and important reef-builders of their time, living close together in flat biostromes or elevated bioherms on soft tropical carbonate platforms.

Carbonate hardgrounds are surfaces of synsedimentarily cemented carbonate layers that have been exposed on the seafloor. A hardground is essentially, then, a lithified seafloor. Ancient hardgrounds are found in limestone sequences and distinguished from later-lithified sediments by evidence of exposure to normal marine waters. This evidence can consist of encrusting marine organisms, borings of organisms produced through bioerosion, early marine calcite cements, or extensive surfaces mineralized by iron oxides or calcium phosphates. Modern hardgrounds are usually detected by sounding in shallow water or through remote sensing techniques like side-scan sonar.

Hexagonaria is a genus of colonial rugose coral. Fossils are found in rock formations dating to the Devonian period, about 350 million years ago. Specimens of Hexagonaria can be found in most of the rock formations of the Traverse Group in Michigan. Fossils of this genus form Petoskey stones, the state stone of Michigan. They can be seen and found in most Midwestern U.S. states.

Pleurodictyum is an extinct genus of tabulate corals, characterized by polygonal corallites. Colonies commonly encrust hard substrates such as rocks, shells and carbonate hardgrounds.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2012.
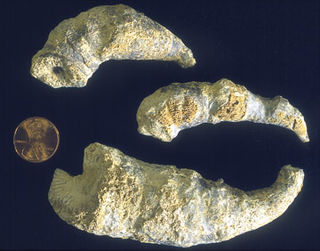
Caninia is an extinct genus of rugose coral. Its fossils occur worldwide from the Devonian to the Permian periods.

Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2013.

Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2014.

The Ludlowville Formation is a geologic formation in New York, Ohio and Pennsylvania. It dates to the Devonian period.
The Onate Formation is a geologic formation that is exposed in most of the highlands of south-central New Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the middle Devonian period.
The Sly Gap Formation is a geologic formation in south-central New Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Frasnian Age of the late Devonian period.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2015.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2016.
This list of fossil fish described in 2018 is a list of new taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, acanthodians, fossil cartilaginous fish, bony fish, and other fish of every kind that are scheduled to be described during the year 2018, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of fish that are scheduled to occur in 2018.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2019.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2020.
Beresellaceae is an extinct family of organisms of uncertain affinity, sometimes placed within the Metazoa, but tentatively assigned to the green alga order Dasycladales. Beresellids were cosmopolitan and their fossils are found in strata ranging in age from the late Devonian to the early Permian.
Sphaerospongia is an extinct genus of organism found in marine beds of Devonian age. Its classification is enigmatic, but it is typically placed among the sponges or the receptaculites. The organism has a surface covered with hexagonal plates, and some early taxonomists placed it among the echinoderms. It is found in close association with the horn coral Tabulophyllum traversensis in the Onate Formation of New Mexico, US, where it provides a substrate for the coral.
Heliolites is a large and heterogenous genus of extinct tabulate corals in the family Heliolitidae. Specimens have been found in Ordovician to Devonian beds in North America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and Australia. The genus is particularly abundant in the Wellin Member of the Hanonet Formation of Belgium.








