
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

The indigenous peoples of New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands:
- a first wave from the Malay Archipelago perhaps 50,000 years ago when New Guinea and Australia were a single landmass called Sahul ...
- and, much later, a wave of Austronesian people from the north who introduced Austronesian languages and pigs about 3,500 years ago. They also left a small but significant genetic trace in many coastal Papuan peoples.

The Papua New Guinea national football team is the national team of Papua New Guinea and is controlled by the Papua New Guinea Football Association. Its nickname is the Kapuls, which is Tok Pisin for Cuscus.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua or Indonesian New Guinea, is the western portion of the Melanesian island of New Guinea which is administered by Indonesia. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua. Lying to the west of Papua New Guinea and considered a part of the Australian continent, the territory is mostly in the Southern Hemisphere and includes the Schouten and Raja Ampat archipelagoes. The region is predominantly covered with ancient rainforest where numerous traditional tribes live such as the Dani of the Baliem Valley although a large proportion of the population live in or near coastal areas with the largest city being Jayapura.

The Papua New Guinea national cricket team, nicknamed the Barramundis, is the team that represents the country of Papua New Guinea in international cricket. The team is organised by Cricket PNG, which has been an Associate Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) since 1973. Papua New Guinea previously had One-Day International (ODI) status, which it gained by finishing fourth in 2014 World Cup Qualifier. Papua New Guinea lost both their ODI and T20I status in March 2018 after losing a playoff match against Nepal during the 2018 Cricket World Cup Qualifier, a result that earned ODI and T20I status for their opponents. On 26 April 2019, at the final World Cricket League 2 fixture; PNG defeated Oman to finish at the fourth position and reclaim their ODI status.

The Papua New Guinea Football Association, PNGFA is the governing body of football (soccer) in Papua New Guinea.

Papua New Guinea has 326 local-level governments (LLGs) comprising 6,112 wards as of 2018.

This page is a list of districts of Papua New Guinea.
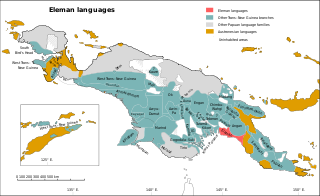
The Eleman languages are a family spoken around Kerema Bay, Papua New Guinea.

The continent of Australia, sometimes known in technical contexts by the names Sahul, Australia-New Guinea, Australinea, Meganesia, or Papualand to distinguish it from the country of Australia, is located within the Southern and Eastern Hemispheres. The name "Sahul" takes its name from the Sahul Shelf, which is part of the continental shelf of the Australian continent. The continent includes mainland Australia, Tasmania, the island of New Guinea, the Aru Islands, the Ashmore and Cartier Islands, most of the Coral Sea Islands, and some other offshore continental islands. Situated in the geographical region of Oceania, Australia is the smallest of the seven traditional continents.

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, and West Papua. The largest cities on the island are Jayapura and Port Moresby.

Talanga is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae described by Frederic Moore in 1885.

The Papua New Guinea national rugby sevens team competes in the Pacific Games, Commonwealth Games, Challenger Series and the Oceania Sevens. They finished third in 2009 and fourth in 2010, 2015 and 2016 in the Oceania Sevens.

Neochera dominia is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics from India to Queensland and the Solomons.

Asota heliconia is a moth in the family Erebidae. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics east to Queensland and the Solomons.

Talanga quadristigmalis is a species of moth of the family Crambidae. It was described by George Hamilton Kenrick in 1907 and is found in Papua New Guinea.

Talanga exquisitalis is a species of moth of the family Crambidae. It was described by George Hamilton Kenrick in 1907 and is found in Papua New Guinea.
Talanga nubilosa is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Eugene G. Munroe in 1968. It is found in Papua New Guinea.
Talanga sabacusalis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1859. It is found on Borneo, Java, Sumatra, Sulawesi and in Papua New Guinea, Cambodia, the Philippines, as well as Australia, where it has been recorded from Queensland.
A tree in the Moraceae family, Ficus bernaysii is found from New Guinea to the Solomon Islands, growing in lowland rainforest. It is dioecious, and grows cauliflorous fruit. It is fed on by a wide range of animals.














