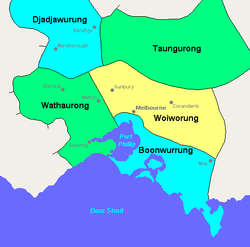
History
The Taungurung people used the King and Howqua River valleys as a major route for trade or war between tribes. The Howqua River valley contains a number of archaeological sites of significance including at least two quarry sites for greenstone, an exceptionally hard rock used for stone axes, spears and other cutting tools which the Taungurung traded with other tribes. There are many other significant cultural both tangible and in tangible across their country.
A raiding party of up to 40 Taungurung is believed to have been killed in May–June 1839 on Dja Dja Wurrung territory at the Campaspe Plains massacre.
In February 1859 some Wurundjeri elders, led by Simon Wonga (aged 35) and brother Tommy Munnering (aged 24) petitioned Protector William Thomas to secure land on behalf of the Taungurung clans for the Kulin at the junction of the Acheron and Goulburn rivers in Taungurung territory. Initial representations to the Victorian Government were positive, however the intervention of the most powerful squatter in Victoria, Hugh Glass, resulted in their removal to a colder site, Mohican Station, which was not suitable for agricultural land and had to be abandoned.
In March 1863 after three years of upheaval, the surviving leaders, among them Simon Wonga and William Barak, led forty Wurundjeri, Taungurung (Goulburn River) and Boonwurrung people over the Black Spur and squatted on a traditional camping site on Badger Creek near Healesville and requested ownership of the site. This became Coranderrk Station.
The Taungurung Clans Aboriginal Corporation was registered as a Registered Aboriginal Party by the Victorian Aboriginal Heritage Council on 16 July 2009. [8]
In 2021, the Taungurung Land and Waters council adopted a flag consisting of a rectangle diagonally divided by a yellow wavy line. (Heraldic) The right side is ocher with the 7 stars arranged into the constellation of the Pleiades, the left side is black. [9]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.