
Redlichiida is an order of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. Species assigned to the order Redlichiida are among the first trilobites to appear in the fossil record, about halfway during the Lower Cambrian. Due to the difficulty to relate sediments in different areas, there remains some discussion, but among the earliest are Fallotaspis, and Lemdadella, both belonging to this order. The first representatives of the orders Corynexochida and Ptychopariida also appear very early on and may prove to be even earlier than any redlichiid species. In terms of anatomical comparison, the earliest redlichiid species are probably ancestral to all other trilobite orders and share many primitive characters. The last redlichiid trilobites died out before the end of the Middle Cambrian.

Paradoxides is a genus of large to very large trilobite found throughout the world during the Middle Cambrian period. One record-breaking specimen of Paradoxides davidis, described by John William Salter in 1863, is 37 cm (15 in). The cephalon was semicircular with free cheeks ending in long, narrow, recurved spines. Eyes were crescent shaped providing an almost 360° view, but only in the horizontal plane. Its elongate thorax was composed of 19–21 segments and adorned with longish, recurved pleural spines. Its pygidium was comparatively small. Paradoxides is a characteristic Middle-Cambrian trilobite of the 'Atlantic' (Avalonian) fauna. Avalonian rocks were deposited near a small continent called Avalonia in the Paleozoic Iapetus Ocean. Avalonian beds are now in a narrow strip along the East Coast of North America, and in Europe.

Analox is a genus of eodiscinid trilobites belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida It lived during the Botomian stage. It can easily be distinguished from other trilobites by the two furrows that extend forwards and sidewards from the front of the glabella.
Meniscuchus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 522 to 516 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period. Meniscuchus has been found in the USA, Canada, Russia and Australia.
Parapagetia is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period.

Dicerodiscus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the early part of the Botomian stage, in China. Four species have been assigned to it. Dicerodiscus is unique for an eodiscoid in having conspicuous and curved spines that are attached anteriorly, and at their base are directed outward perpendicular to the midline, before gradually bending further backwards.
Semadiscus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It has been collected from the Lower Cambrian of Canada (Newfoundland), Russia, and the United States. Only the headshield is known, and it may well be that it would be better to include it in Serrodiscus.
Egyngolia is a genus of very small sized trilobites, that lived during the Lower Cambrian in what are today the Russia Federation, Mongolia, and South Australia.

Meteoraspis is an extinct genus of ptychopariid trilobites of the family Tricrepicephalidae. The various species lived from 501 to 497 million years ago during the Dresbachian faunal stage of the late Cambrian Period. Fossils of Meteoraspis are characteristic of Late Cambrian strata in North America, though they are found in Late Cambrian strata elsewhere in the world, such as M. nevensis from Victoria Land, Antarctica.

Conocoryphe is a genus of primarily eyeless trilobites belonging to the family Conocoryphidae. They lived during the Middle Cambrian period, about 505 million years ago. These arthropods lived on the sea bottom (epifaunal) and lived off dead particulate organic matter.
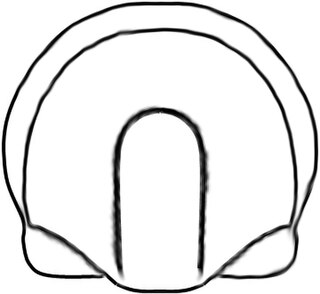
Mallagnostus Howell, 1935, is a trilobite genus belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864) according to Whittington et al. 1997. It lived during the late Lower Cambrian, with remains found in USA, Canada (Newfoundland), Spain, England, Russia, Mongolia, and the early Middle Cambrian as reported from China and Russia (Yakutia).

Geragnostus is a genus of very small agnostid trilobites whose fossils are found Ordovician-aged marine strata from Eurasia, North America and Argentina.

Pliomera is a genus of trilobites that lived during the Middle Ordovician on the paleocontinent Baltica, now Norway, Sweden, Estonia and the Russian Federation, and in Argentina. It can be recognized for its pentagonal glabella widest between the frontal corners, with an inverted V-shaped occipital ring. In front of the occipital furrow that crosses the entire glabella, two pairs of dead-ending furrows create three side lobes left and right. The front of the glabella also has three dead-ending furrows, a very short one on the midline and left and right a longer one, directed inward and slightly backward. The eyes are small and are not connected to the glabella by an eye ridge. The thorax and pygidium are very regularly divided into up to 23 rather narrow segments, without a furrow within each of the pleurae. The pleurae are clearly wider than the axis. The pygidium ends in downward pointing toothlike spines.
Tannudiscus Pokrovskaya (1959) is a genus of eodiscinid trilobites belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida. It lived during the late Lower Cambrian, with remains found in Canada (Newfoundland), China (Gansu), The United Kingdom (England), and the Russian Federation.

Psychopyge is a genus of trilobite, that lived during the upper Emsian and has been found in Germany and Morocco. It is characterized by the swordlike extension from the front of the head.

Cedaria is an extinct genus of trilobites from the late Cambrian.

Kendallina is a genus of parabolinoidid trilobite with an inverted egg-shaped outline, a wide headshield, small eyes, small deflected spines, 12 thorax segments and a small, short tailshield. It lived during the Late Cambrian in what are today Canada and the United States.

Orygmaspis is a genus of asaphid trilobite with an inverted egg-shaped outline, a wide headshield, small eyes, long genal spines, 12 spined thorax segments and a small, short tailshield, with four pairs of spines. It lived during the Late Cambrian in what are today Canada and the United States.

Tricrepicephalus is an extinct genus of ptychopariid trilobites of the family Tricrepicephalidae with species of average size. Its species lived from 501 to 497 million years ago during the Dresbachian faunal stage of the late Cambrian Period. Fossils of Tricrepicephalus are widespread in Late Cambrian deposits in North America, but is also known from one location in South America. Tricrepicephalus has an inverted egg-shaped exoskeleton, with three characteristic pits in the fold that parallels the margin of the headshield just in front of the central raised area. The articulating middle part of the body has 12 segments and the tailshield carries two long, tubular, curved pygidial spines that are reminiscent of earwig's pincers that rise backwards from the plain of the body at approximately 30°.
Anabaraspis is a genus of redlichiid trilobite, A. splendens occurs in the uppermost Lower Cambrian and lowest Middle Cambrian of Russia. In Anabaraspis, there is an extended area in front of the glabella which is not differentiated in a border and a preglabellar field. It is a unique character in the family Paradoxididae.














