
Redlichiida is an order of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. Species assigned to the order Redlichiida are among the first trilobites to appear in the fossil record, about halfway during the Lower Cambrian. Due to the difficulty to relate sediments in different areas, there remains some discussion, but among the earliest are Fallotaspis, and Lemdadella, both belonging to this order. The first representatives of the orders Corynexochida and Ptychopariida also appear very early on and may prove to be even earlier than any redlichiid species. In terms of anatomical comparison, the earliest redlichiid species are probably ancestral to all other trilobite orders and share many primitive characters. The last redlichiid trilobites died out before the end of the Middle Cambrian.

The Paradoxididae are a family of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. They occurred during the late Lower Cambrian (Toyonian) and disappeared at the end of the Middle Cambrian. Representatives of this family have been found in the paleocontinents of Avalonia, Baltica, and Gondwana, now Canada, USA, England, Wales, Morocco, Spain, Czech Republic, Poland, Russia, Mongolia, and Turkey. Species in this family can typically grow large to very large, are relatively flat, have an inverted egg-shaped outline, opisthoparian sutures, a glabella that in early genera has parallel sides and expands forward in later representatives, and approaches or reaches the frontal border. All species have an almost semicircular headshield with long backward-directed genal spines. The articulate middle part of the body consists of 15 to 21 segments ending in sickle-shaped spines that to the back curve increasingly further backwards. The tailshield is small.

Acimetopus is a genus of eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864). It lived during the Botomian stage. = late Lower Cambrian Stage 4 ; the upper Botomian boundary corresponds to base of the Middle Cambrian, Miaolingian Series and Wuliuan stage.
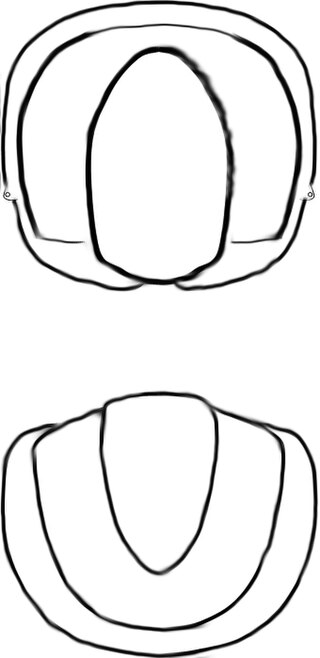
Oodiscus is an extinct genus of small size trilobite, with three known species. It lived during the Toyonian in what are now Canada and the USA.
Meniscuchus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 522 to 516 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period. Meniscuchus has been found in the USA, Canada, Russia and Australia.
Parapagetia is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period.

Dicerodiscus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the early part of the Botomian stage, in China. Four species have been assigned to it. Dicerodiscus is unique for an eodiscoid in having conspicuous and curved spines that are attached anteriorly, and at their base are directed outward perpendicular to the midline, before gradually bending further backwards.
Semadiscus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It has been collected from the Lower Cambrian of Canada (Newfoundland), Russia, and the United States. Only the headshield is known, and it may well be that it would be better to include it in Serrodiscus.
Egyngolia is a genus of very small sized trilobites, that lived during the Lower Cambrian in what are today the Russia Federation, Mongolia, and South Australia.

Nevadella is an extinct genus of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with species of average size. It lived during the late Atdabanian stage, which lasted from 530 to 524 million years ago during the early part of the Cambrian Period.
Acmarhachis is a genus of trilobites in the order Agnostida, which lived in what are now Australia, Canada, China (Anhui), Kazakhstan, Russia (Kharaulakh), and the US. It was described by Resser in 1938, and the type species is Acmarhachis typicalis.

Eodiscina is trilobite suborder. The Eodiscina first developed near the end of the Lower Cambrian period and became extinct at the end of the Middle Cambrian. Species are tiny to small, and have a thorax of two or three segments. Eodiscina includes six families classified under one superfamily, Eodiscoidea.
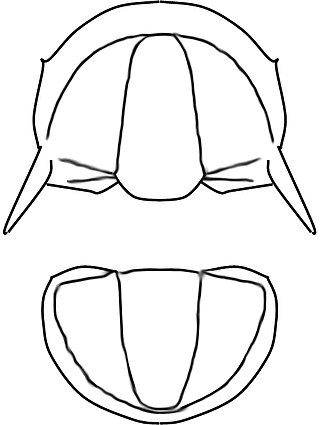
Litometopus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Botomian stage.

Toragnostus is a genus of trilobites restricted to the late Middle Cambrian. Its remains have been found in the United States, Greenland, Denmark, China, Sweden, the Russian Federation, and Kazakhstan. Its headshield and tailshield are almost completely effaced and it has two thorax segments.

Eodiscidae is a family of agnostid trilobites that lived during the final Lower Cambrian and the Middle Cambrian. They are small or very small, and have a thorax of two or three segments. Eodiscidae includes nine genera.

Cnemidopyge is a genus of trilobites that lived during the Ordovician. Like all Raphiophorids it is blind, with a cephalon that is subtriangular to subsemicircular, carrying genal spines and a forward directed rapier-like spine on the central raised area, with the front of the glabella inflated and the natural fracture lines of the cephalon coinciding with its margin. It may be easily distinguished from other raphiophorids by the rectangular thorax with 6 segments, where other genera have a different number of segments and segments change in width over the length of the thorax. Uniquely in this genus, the inner pleural region of the frontal segment is enlarged. Also the axis and pleural fields of the pygidium are strongly segmented.
The Calodiscidae Kobayashi, 1943 [nom. transl. Öpik, 1975 ex Calodiscinae Kobayashi, 1943] are a family of trilobites belonging to the order Agnostida that lived during the Lower Cambrian. They are small or very small, and have a thorax of two or three segments. The Calodiscidae includes five genera.

Cedaria is an extinct genus of trilobites from the late Cambrian.
Anabaraspis is a genus of redlichiid trilobite, A. splendens occurs in the uppermost Lower Cambrian and lowest Middle Cambrian of Russia. In Anabaraspis, there is an extended area in front of the glabella which is not differentiated in a border and a preglabellar field. It is a unique character in the family Paradoxididae.

The Paradoxidoidea Hawle & Corda 1847, are a superfamily of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. They occurred during the late Lower Cambrian (Toyonian) and disappeared at the end of the Middle Cambrian.












