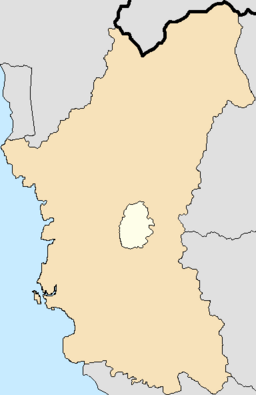
Perak is a state of Malaysia on the west coast of the Malay Peninsula. Perak has land borders with the Malaysian states of Kedah to the north, Penang to the northwest, Kelantan and Pahang to the east, and Selangor to the south. Thailand's Yala and Narathiwat provinces both lie to the northeast. Perak's capital city, Ipoh, was known historically for its tin-mining activities until the price of the metal dropped, severely affecting the state's economy. The royal capital remains Kuala Kangsar, where the palace of the Sultan of Perak is located. As of 2018, the state's population was 2,500,000. Perak has diverse tropical rainforests and an equatorial climate. The state's main mountain ranges are composed of the Titiwangsa, Bintang and Keledang Ranges, where all of them are part of the larger Tenasserim Hills system that connects Myanmar, Thailand and Malaysia.

Kedah, also known by its honorific Darul Aman and historically as Queda, is a state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km2, and consists of a mainland portion and the Langkawi islands. The mainland has relatively flat terrain, which is used to grow rice, while Langkawi is composed of mostly of uninhabited islands.

Terengganu is a sultanate and federal state of Malaysia. The state is also known by its Arabic honorific, Dāru l-Īmān. The coastal city of Kuala Terengganu, at the mouth of the Terengganu River, is both the state and royal capital as well as the most populous city in Terengganu. Other major cities and towns include Jerteh, Kuala Dungun, Chukai, Kuala Berang, Marang, and Permaisuri. At 13,035 square kilometres in size and a population of over 1.2 million people in 2023, Terengganu is Malaysia's 7th largest state and 10th most populated. Terengganu, along with Kelantan, Perlis, and the Federal Territory of Putrajaya, is one of the most homogeneous states/territories in the country of which 95% of the population are ethnic Malay-Muslims with its own distinct language/dialect, culture, history, and tradition.

The Titiwangsa Mountains, also known as Banjaran Besar by locals, is the chain of mountains that forms the backbone of the Malay Peninsula. The northern section of the range is in southern Thailand, where it is known as the Sankalakhiri Range.

Kenyir Lake is an artificial lake located in Hulu Terengganu, Terengganu, Malaysia, nestled deep in the Pantai Timur Range. The lake was created in 1985 by the Kenyir Dam on the Kenyir River, the upper stream of the Terengganu River. The lake provides water to the nearby Sultan Mahmud Power Station. It is the largest man-made lake in mainland Southeast Asia with an area of 260,000 hectares.

Hulu Perak District is a district in Perak, Malaysia. It is the largest district in Perak. In the east of the district it borders the districts of Jeli and Gua Musang in Kelantan, to the west it borders Baling and Kulim Districts of Kedah, to the south it borders the district of Kuala Kangsar while to the south-west it borders the district of Larut, Matang and Selama. Hulu Perak also shares a border with Yala province's Betong district on the border with Thailand. The seat of the district is Gerik, which is also the largest town of the district.

The Gombak District is an administrative district located in the state of Selangor, Malaysia. The district was created on February 1, 1974, the same day when Kuala Lumpur was declared a Federal Territory. Until 1997, Rawang was the district capital; the capital has been moved to Bandar Baru Selayang. Gombak borders Kuala Lumpur to the southeast and the Genting Highlands to the east. Both Gombak and Kuala Lumpur, along with some other districts in Selangor, are situated within the Klang Valley. Other localities in Gombak district include Batu Arang, Kuang, Rawang, Kundang, Gombak Town, Selayang, Batu Caves and Hulu Kelang.
East–West Highway or also known as Gerik–Jeli Highway, Kulim–Baling Highway and Titi Karangan–Gerik Highway, Federal Route 4, Asian Highway Route 140 is the 215 kilometres (134 mi) federal highway constructed by the Malaysian Public Works Department (JKR) to shorten the journey from Kota Bharu, Kelantan to northwestern towns and cities of Malaysia such as Alor Star, Kedah and Penang. The highway connects Gerik, Perak in the west to Jeli, Kelantan in the east, before being extended further to Lunas, Kedah.
Federal Route 4 is a federal road in the north of Peninsula Malaysia. The 307 kilometres (191 mi) road connects Butterworth, Penang to Pasir Puteh in Kelantan. The highway also goes close to the border with Thailand and meets Jalan Kompleks CIQ Bukit Bunga at Bukit Bunga.

Second East–West Highway, also known as Simpang Pulai–Kuala Berang Highway, Federal Route 185 and Federal Route 36, is a highway in Peninsular Malaysia which connects Simpang Pulai in Perak to Kuala Jeneris in Terengganu. It overlaps with Federal Route 8 Federal Route 8 between Gua Musang and Sungai Relau. It is notorious for its many sharp corners which increase the risk of road accidents.

Gerik is a mukim and the district capital of Hulu Perak District, Perak, Malaysia. The town is also known as Rest Town due to its strategic location next to East-West Highway Federal Route 4, the main route linking Kedah, Penang and Kelantan.
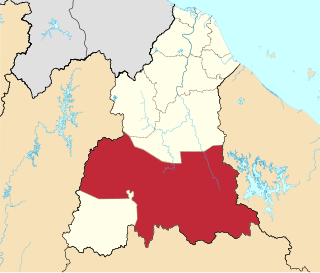
Gua Musang is a town, district and parliamentary constituency in southern Kelantan, Malaysia. It is the largest district in Kelantan. Gua Musang is administered by the Gua Musang District Council. Gua Musang district is bordered by the state of Pahang to the south, Terengganu to the east, Perak to the west and the Kelantanese districts of Kuala Krai and Jeli to the north. It is a small railway town about 140 km south of state capital Kota Bharu. Gua Musang is represented by Mohd Azizi Abu Naim in the Dewan Rakyat. The town lies on the KTM East Coast Line, from Tumpat, near the border with Thailand, to Gemas, Negeri Sembilan.
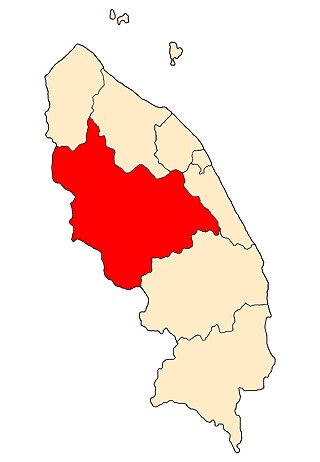
Hulu Terengganu is an interior district of Terengganu, Malaysia. The seat of the district is Kuala Berang, located about 40 km (25 mi) from the state capital, Kuala Terengganu. The local government of this district is Hulu Terengganu District Council.

Setiu is one of the districts in Terengganu, Malaysia. This district is bordered by Besut to the north, Hulu Terengganu to the south, and on the east, Kuala Nerus District.

Belum-Temengor is the largest continuous forest complex in Peninsular Malaysia. Specifically, it is located in the Malaysian state of Perak and crosses into Southern Thailand. Belum-Temenggor is divided into two sections. Belum is located up north, right by the Malaysia-Thailand border, while Temenggor is south of Belum. The Royal Belum State Park is entirely contained within the forest complex. Bang Lang National Park is on the Thailand side of the border.

Terengganu Malay is a Malayic language spoken in the Malaysian state of Terengganu all the way southward to coastal Pahang and northeast Johor. It is the native language of Terengganu Malays and highly localized Chinese Peranakan community as well as a second language among the smaller Indian minority.

The Temiar are a Senoic group indigenous to the Malay Peninsula and one of the largest of the eighteen Orang Asli groups of Malaysia. They reside mainly in Perak, Pahang and Kelantan. Their total population is estimated at around 40,000 to 120,000, most of which live on the fringes of the rainforest, while a small number have been urbanised.
Ulu Titi Basah is the southernmost high peak of Thailand. The peak is 1,533 metres (5,030 ft) tall and is located on the Malaysia–Thailand border between Betong District of Yala province and Hulu Perak in the state of Perak.
The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to Selangor.