Kedah, also known by its honorific Darul Aman and historically as Queda, is a state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km2, and consists of a mainland portion and the Langkawi islands. The mainland has relatively flat terrain, which is used to grow rice, while Langkawi is composed of mostly of uninhabited islands.

The Jelebu District is the second largest district in Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia after Jempol, with a population over 40,000. Jelebu borders on the Seremban District to its west and Kuala Pilah District to its south, Jempol District to its southeast, Bentong and Bera Districts, Pahang to its east and Hulu Langat District, Selangor to the north. Jelebu is a suburban district with blossoming semi-agricultural industry. Jelebu is also a parliamentary constituency of the Dewan Rakyat in the Malaysian Parliament. Kuala Klawang is the principal town of the district.
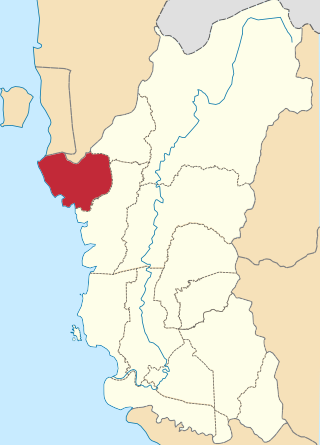
The Kerian District is an administrative district in Perak, Malaysia. It covers the northwestern corner of Perak, bordering the states of Penang and Kedah to the north; the main town of Parit Buntar is located a mere 37 km (23 mi) southeast of George Town, Penang's capital city. The district is well known for Bukit Merah, a popular tourist destination.

The Kinta District is a district in Perak, Malaysia. It contains the state capital Ipoh. Kinta is the most populated district in Perak and also the seventh most populated district in Malaysia. Kinta houses Ipoh, Perak's largest city and state capital while Batu Gajah is a seat in Kinta district.

The Batang Padang District is a district in Perak, Malaysia. This district is administered by a local council, namely, the Tapah District Council, based in Tapah. The major towns of Batang Padang are Bidor, Tapah and Sungkai.
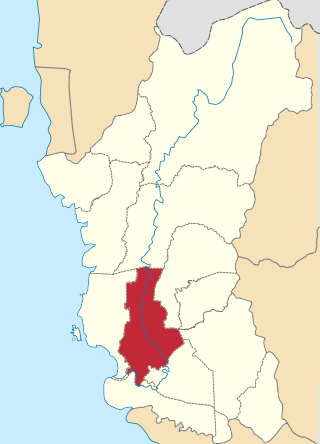
Perak Tengah District is a district in Perak, Malaysia. It is administered by the Perak Tengah District Council, which is based at the town of Seri Iskandar. Parit is however the largest settlement in the area. The district is well known for its historical sites in the Pasir Salak. Smaller towns in the district include Bota, Lambor and Kampung Gajah.

Pontian District is a district located in southwest part of the Malaysian state of Johor. It borders Batu Pahat and Kluang Districts to the north and Kulai and Johor Bahru Districts to the east.
East–West Highway or also known as Gerik–Jeli Highway, Kulim–Baling Highway and Titi Karangan–Gerik Highway, Federal Route 4, Asian Highway Route 140 is the 215 kilometres (134 mi) federal highway constructed by the Malaysian Public Works Department (JKR) to shorten the journey from Kota Bharu, Kelantan to northwestern towns and cities of Malaysia such as Alor Star, Kedah and Penang. The highway connects Gerik, Perak in the west to Jeli, Kelantan in the east, before being extended further to Lunas, Kedah.

The Jempol District is the largest district in the Malaysian state of Negeri Sembilan. The district borders Jelebu District to the northwest, Kuala Pilah District to the west, Tampin District to the south, Bera District, Pahang to the northeast and Segamat District, Johor to the east. Bandar Seri Jempol and Bahau are the principal towns in Jempol.

Gerik is a mukim and the district capital of Hulu Perak District, Perak, Malaysia. The town is also known as Rest Town due to its strategic location next to East-West Highway Federal Route 4, the main route linking Kedah, Penang and Kelantan.

Pengkalan Hulu, formerly known as Kroh or Keroh, is a town and a mukim in Hulu Perak District, Perak, Malaysia, bordering Thailand and Kedah. The nearest town on the Thailand side is Betong in Yala province.

Setiu is one of the districts in Terengganu, Malaysia. This district is bordered by Besut to the north, Hulu Terengganu to the south, and on the east, Kuala Nerus District.

Temenggor Lake is a lake in Hulu Perak District, Perak, Malaysia. It is the second largest lake in Peninsular Malaysia after Kenyir Lake in Hulu Terengganu District, Terengganu. This man-made lake is located south of the 1,533 m high Ulu Titi Basah peak. The lake was created by the construction of Temenggor Dam to generate electric power. The lake is located about 45 km from the Hulu Perak district capital, Gerik. There is a bridge on the East-West Highway, which crosses the lake and passing through a man-made island called Banding Island.

The Larut, Matang and Selama District is a district of Perak, Malaysia. Taiping is the capital town of this district. Larut, Matang and Selama used to be three small different districts and they merged into one larger district later. Larut, Matang and Selama houses Taiping, Perak's second largest city and former state capital. Other towns in the region include Changkat Jering, Terong, Matang, Kuala Sepetang and Selama. The region borders the state of Kedah on the north, the Kerian District on the northwest, the Hulu Perak and Kuala Kangsar District on the east, and the Manjung District on the south.
Ulu Titi Basah is the southernmost high peak of Thailand. The peak is 1,533 metres (5,030 ft) tall and is located on the Malaysia–Thailand border between Betong District of Yala province and Hulu Perak in the state of Perak.
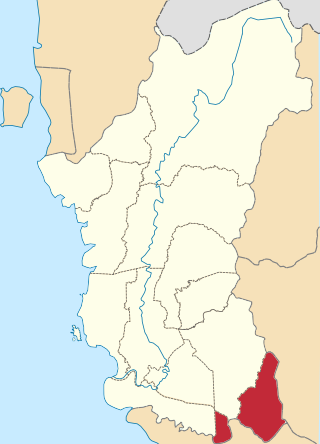
The Muallim District is the eleventh district of the state of Perak, Malaysia, situated at the southeastern tip of the state, bordering the state of Selangor. It was proclaimed by the current Sultan of Perak, Sultan Nazrin Muizzuddin Shah on 11 January 2016 at the Tanjung Malim District Council Building. The district was previously part of the neighbouring Batang Padang district.

Lenggong is a federal constituency in Hulu Perak District, Perak, Malaysia, that has been represented in the Dewan Rakyat of the Malaysian Parliament since 2004. Represented by Dato Shamsul Anuar bin Haji Nasarah from UMNO. Lenggong also contributes two seats to the Perak State Legislative Assembly: Kota Tampan and Kenering, which were also held by UMNO.

The Kingdom of Reman or Kingdom of Rahman was a landlocked semi-independent Malay kingdom in the northern Malay Peninsula.
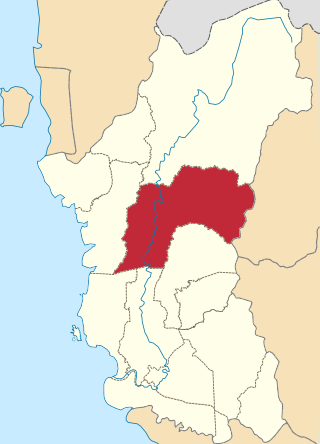
The Kuala Kangsar District is a district in Perak, Malaysia. Kuala Kangsar shares its borders with Larut, Matang and Selama at the west, Hulu Perak at the north, Gua Musang of Kelantan at the east, Kinta at the south, Perak Tengah and Manjung at the southwest. The seat of this district is the town of Kuala Kangsar.
Reman Malay, also known by several names such as Patani, Baling, Grik, and Tukugho, is a Malayic language spoken in the states of Kedah and Perak in northern Peninsular Malaysia. In the state of Kedah it is spoken in the districts of Baling, Padang Terap, Sik, and Yan, while in Perak it is spoken in Hulu Perak, but also in some areas within Kerian and Larut, Matang and Selama districts, especially in the towns of Batu Kurau and Bukit Gantang. Despite being located within these two states, Reman Malay is not closely related to neighbouring Kedahan and Perakian varieties but instead more closely related or an offshoot of Kelantan–Pattani Malay.