Keretapi Tanah Melayu Berhad (KTMB) or Malayan Railway Limited, colloquially referred to simply as KTM, is the main rail operator in Peninsular Malaysia. The railway system dates back to the British colonial era, when it was first built to transport tin. Previously known as the Federated Malay States Railways (FMSR) the Malayan Railway Administration (MRA), and the Malayan Railway, Keretapi Tanah Melayu acquired its current name in 1962. The organisation was corporatised in 1992, but remains wholly owned by the Malaysian government.

Ipoh is the capital city of the Malaysian state of Perak. Located by the Kinta River, it is nearly 200 km (120 mi) north of Kuala Lumpur and 150 km (93 mi) southeast of George Town in neighbouring Penang. As of the 2020 census Ipoh had a population of 759,952, making it the eighth-largest city in Malaysia by population.

Kedah, also known by its honorific Darul Aman and historically as Queda, is a state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km2, and consists of a mainland portion and the Langkawi islands. The mainland has relatively flat terrain, which is used to grow rice, while Langkawi is composed of mostly of uninhabited islands.

Sungai Petani is a town in Kuala Muda District, Kedah, Malaysia. Sungai Petani is Kedah's largest city and is located about 55 km south of Alor Setar, the capital of Kedah, and 33 km northeast of George Town, the capital city of the neighbouring state of Penang.
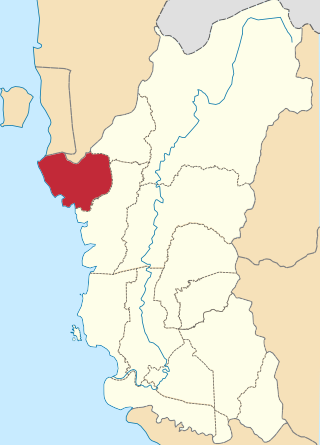
The Kerian District is an administrative district in Perak, Malaysia. It covers the northwestern corner of Perak, bordering the states of Penang and Kedah to the north; the main town of Parit Buntar is located a mere 37 km (23 mi) southeast of George Town, Penang's capital city. The district is well known for Bukit Merah, a popular tourist destination.

Tanjong Malim, or Tanjung Malim, is a town in Muallim District, Perak, Malaysia. It is approximately 70 km (43 mi) north of Kuala Lumpur and 120 km south of Ipoh via the North–South Expressway. It lies on the Perak-Selangor state border, with Sungai Bernam serving as the natural divider.

Taiping is a town located in Larut, Matang and Selama District, Perak, Malaysia. It is located approximately 48 km (30 mi) northwest of Ipoh, the capital of Perak, and 78 km (48 mi) southeast of George Town, Penang. With a population of 245,182, it is the second largest town in Perak after Ipoh, the state capital.

The North–South Expressway Northern Route is an interstate controlled-access highway running parallel to the northwestern coast of Peninsular Malaysia. The 460-kilometre (290-mile) expressway forms the north section of the North–South Expressway, passing through the northwestern states of Kedah, Penang, Perak and Selangor. The expressway begins at the Bukit Kayu Hitam checkpoint in Kedah, where the Malaysia–Thailand border lies, and ends at Bukit Lanjan in Selangor state where the expressway interchanges with the New Klang Valley Expressway. The expressway is operated by PLUS Expressways.
Malaysian National Projects are major national and giant projects which are important in the development of Malaysia.

The Bandar Baharu District is a district containing a town of the same name and a state assembly constituency at the southernmost end of Kedah, Malaysia. The Bandar Baharu District is located along the Kedah-Penang-Perak border tripoint, 37 km (23 mi) southeast of George Town, Penang's capital city.

The Kerian River, alternately Krian, is a river in the northern part of the Malaysian state of Perak. The river originates from the Bintang Range. It flows westerly and discharges into the Strait of Malacca. The main tributaries are the Selama River, Ijok River, Samagagah River and Ulu Mengkuang River.

Bagan Serai is a mukim in Kerian District, Perak, Malaysia. It is located 52 km (32 mi) southeast of George Town, the capital city of the neighbouring state of Penang. As such, the town is also part of Greater Penang, Malaysia's second largest conurbation, with the town's logistical needs being served by Penang's well-developed transportation infrastructure. There is the birthplace of the No.1 badminton player, Lee Chong Wei.

The Roman Catholic Diocese of Penang is situated in the northern as well as the east coast region of Peninsular Malaysia covering 4 northern states, namely Perlis, Kedah, Penang and Perak as well as the east coast state of Kelantan. It was created on 25 February 1955 together with the Archdiocese of Kuala Lumpur. It is under the ecclesiastical province of Kuala Lumpur.

The Parit Buntar railway station is a Malaysian train station located at and named after the town of Parit Buntar, Perak.

The Bukit Mertajam railway station is a Malaysian railway station located at Bukit Mertajam, Central Seberang Perai District, Penang.

The Butterworth railway station is a Malaysian railway station located at and named after the town of Butterworth, Penang.

The Sungai Petani railway station is a Malaysian train station located at and named after the city of Sungai Petani. The station is on Keretapi Tanah Melayu's West Coast Line and is served by the KTM ETS and the KTM Komuter Northern Sector services. It was also previously served by the International Express.

The Greater Penang Conurbation, also known as the George Town Conurbation, is the built-up urban or metropolitan area within and around the Malaysian state of Penang. Encompassing all of Penang, and parts of the neighbouring states of Kedah and Perak, the conurbation was home to over 2.84 million people as of 2020, the second largest in the country after the Klang Valley.

The KTM Komuter Northern Sector is one of the five KTM Komuter services run by Malaysian rail operator Keretapi Tanah Melayu (KTM). The service was introduced on 11 September 2015 following the completion of the Ipoh-Padang Besar Electrification and Double-Tracking Project in December 2014, which also saw the extension of ETS services to Padang Besar from Ipoh.