
The COVID-19 pandemic in Singapore is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The first case in Singapore was confirmed on 23 January 2020. Early cases were primarily imported until local transmission began to develop in February and March. In late March and April, COVID-19 clusters were detected at multiple migrant worker dormitories, which soon contributed to an overwhelming proportion of new cases in the country.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Malaysia is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. As of 28 November 2022, with over 4,945,000 confirmed COVID-19 cases, over 27,000 active cases, over 36,648 deaths, and more than 66 million tests, the country is currently ranked third in the number of COVID-19 cases in Southeast Asia behind Vietnam and Indonesia, and fourth in the number of COVID-19 deaths in Southeast Asia behind Indonesia, the Philippines, and Vietnam.

During the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries and regions imposed quarantines, entry bans, or other travel restrictions for citizens of or recent travelers to the most affected areas. Some countries and regions imposed global restrictions that apply to all foreign countries and territories, or prevent their own citizens from travelling overseas.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Samoa is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Samoa on 18 November 2020. The country reported its second case on 27 November.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Tuvalu is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Tuvalu on 20 May 2022.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Niue is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Niue reported its first confirmed case on 9 March 2022.

The first COVID-19 case in the Indian state of Bihar was reported in Munger on 22 March 2020, a 38-year-old tested positive for COVID-19, he was also the first victim. He had travel history to Qatar. The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has confirmed a total of 62,031 cases as of 4 August 2020, including 20,922 active cases, 349 deaths and 40,760 recoveries. The virus has spread in 38 districts of the state, of which Patna district has the highest number of cases.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in Singapore in 2020.

The Health Protection (England) Regulations 2020 is a statutory instrument (SI) enacted on 4 July 2020 by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care, Matt Hancock, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The regulations aimed to reduce the possibility of infection spreading from travellers from overseas. They imposed requirements on certain categories of travellers arriving in England from outside the Common Travel Area. Travellers falling within the regulations had to provide specified information to the British government on entry, and some had to undergo a fourteen-day period of self-isolation.
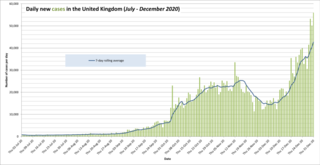
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom from July 2020 to December 2020.
The Global Travel Taskforce is an advisory body of the government of the United Kingdom. Secretary of State for Transport, Grant Shapps announced the formation of the group on 7 October 2020 as a cross-government response to an identified need to enable the safe and sustainable recovery of international travel and to introduce a COVID-19 testing system for travellers visiting the UK. In a Written Statement to Parliament of 7 October 2020, the Transport Secretary pledged to formally report to the Prime Minister by early November 2020 with the taskforce's recommendations as to how the country can help global travel resume safe operation. The Government intends that the work of the taskforce will be performed in collaboration with the transport and tourism industries along with the private sector, specifically in relation to COVID-19 testing.

The Government of Ghana initially responded to the virus through a nationwide disinfection and fumigation exercise which began in April 2020. In order to curb the spread of the virus, the government enforced lockdowns, aggressive contact tracing, public bans and social measures such as encouraging the wearing of face masks. By April, it began the gradual reopening of the country; lifting all lockdowns while maintaining protocols such as social distancing. Throughout the pandemic, the government partnered with the private sector in order to roll out economic reliefs and recovery programs as a result of the impact of the pandemic on Ghana's economy. There was also an expansion of medical facilities and the improvement of testing logistics.

The COVID-19 pandemic has had a deep impact on the Irish economy, leading it into a recession. Essential public health measures announced by the Irish Government to contain the spread of COVID-19 resulted in the largest monthly increase in unemployment in the history of the Republic of Ireland during March 2020. By 24 April, there were more than one million people in receipt of support interventions to the labour market, including those in receipt of the COVID-19 Pandemic Unemployment Payment and the COVID-19 Temporary Wage Subsidy Scheme. While there were job losses in all sectors, individuals working in tourism, hospitality, food and retail have seen the largest job losses.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in Scotland during 2021. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales.

The New Zealand Government responded to the COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand in various ways. In early February 2020, the Government imposed travel restrictions on China in response to the global COVID-19 pandemic originating in Wuhan and also repatriated citizens and residents from Wuhan. Following the country's first case which originated in Iran, the Government imposed travel restrictions on Iran.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in England from July 2020 to December 2020. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales.

This article documents the chronology of the response to the COVID-19 pandemic in May 2021, which originated in Wuhan, China in December 2019. Some developments may become known or fully understood only in retrospect. Reporting on this pandemic began in December 2019.

The Health Protection (England) Regulations 2021 was a statutory instrument (SI) enacted on 17 May 2021 by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care, Matt Hancock, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, revoking and replacing The Health Protection (England) Regulations 2020.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom from July 2021 to December 2021.
This article documents the chronology and epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2, the virus which causes the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic in Australia during the first half of 2021.







