
The Glypheoidea, is a group of lobster-like decapod crustaceans which forms an important part of fossil faunas, such as the Solnhofen limestone. These fossils included taxa such as Glyphea, and Mecochirus, mostly with elongated chelipeds. This group of decapods is a good example of a living fossil, or a lazarus taxon, since until their discovery in the 1970s, the group was considered to have become extinct in the Eocene. The superfamily Glypheoidea comprises five families. The two extant species, Neoglyphea inopinata and Laurentaeglyphea neocaledonica, are both in the family Glypheidae.
Liopleurodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous pliosaurid pliosaurs that lived from the Callovian stage of the Middle Jurassic to the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic period. The type species is L. ferox, which is probably the only valid species. Some studies also include the second species L. pachydeirus, but this latter is considered as a probable junior synonym of L. ferox due to its lack of viable diagnosis. As the holotype specimen of L. ferox consists of a single tooth preserving questionable distinctive features, recent studies therefore recommend the necessary identification of a neotype in order to preserve the validity of the genus. Numerous fossil specimens attributed to Liopleurodon, even including numerous skeletons, have been discovered in Europe, Russia, and Mexico. Other additional species were even proposed, but these are currently seen as coming from other pliosaurid genera.

Titanosaurus is a dubious genus of sauropod dinosaurs, first described by Richard Lydekker in 1877. It is known from the Maastrichtian Lameta Formation of India.

Mosasaurus is the type genus of the mosasaurs, an extinct group of aquatic squamate reptiles. It lived from about 82 to 66 million years ago during the Campanian and Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous. The genus was one of the first Mesozoic marine reptiles known to science—the first fossils of Mosasaurus were found as skulls in a chalk quarry near the Dutch city of Maastricht in the late 18th century, and were initially thought to be crocodiles or whales. One skull discovered around 1780 was famously nicknamed the "great animal of Maastricht". In 1808, naturalist Georges Cuvier concluded that it belonged to a giant marine lizard with similarities to monitor lizards but otherwise unlike any known living animal. This concept was revolutionary at the time and helped support the then-developing ideas of extinction. Cuvier did not designate a scientific name for the animal; this was done by William Daniel Conybeare in 1822 when he named it Mosasaurus in reference to its origin in fossil deposits near the Meuse River. The exact affinities of Mosasaurus as a squamate remain controversial, and scientists continue to debate whether its closest living relatives are monitor lizards or snakes.

Dakosaurus is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. It was large, with teeth that were serrated and compressed lateromedially. The genus was established by Friedrich August von Quenstedt in 1856 for an isolated tooth named Geosaurus maximus by Theodor Plieninger in 1846. Dakosaurus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. The extent of its adaptation to a marine lifestyle means that it is most likely that it mated at sea, but since no eggs or nests have been discovered that have been referred to Dakosaurus, whether it gave birth to live young at sea like dolphins and ichthyosaurs or came ashore like turtles is not known yet. The name Dakosaurus means "biter lizard", and is derived from the Greek dakos ("biter") and σαῦρος -sauros ("lizard").

Macrurosaurus is the name given to a genus of dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous. It was a titanosauriform which lived in what is now England. The type species, M. semnus, was named in 1876. A second species, M. platypus, may also exist.

Poekilopleuron is a genus of carnosaurian theropod dinosaur, which lived during the middle Bathonian of the Jurassic, about 168 to 166 million years ago. The genus has been used under many different spelling variants, although only one, Poekilopleuron, is valid. The type species is P. bucklandii, named after William Buckland, and many junior synonyms of it have also been erected. Little material is currently known, as the holotype was destroyed in World War II, although many casts of the material still exist.

Metriorhynchus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform that lived in the oceans during the Late Jurassic. The type species, M. brevirostris was named in 1829 as a species of Steneosaurus before being named as a separate genus by the German palaeontologist Christian von Meyer in 1832. The name Metriorhynchus means "Moderate snout", and is derived from the Greek Metrio- ("moderate") and -rhynchos ("snout").
Teleosaurus is an extinct genus of teleosaurid crocodyliform found in the Middle Jurassic Calcaire de Caen Formation of France. It was approximately 3 metres (10 ft) in length. The holotype is MNHN AC 8746, a quarter of a skull and other associated postcranial remains, while other fragmentary specimens are known. The type species is T. cadomensis, but a second species, T. geoffroyi may also exist. It was previously considered a wastebasket taxon, with many other remains assigned to the genus.
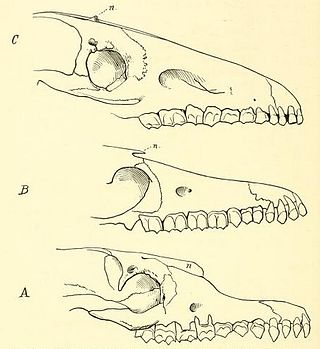
Scalabrinitherium is an extinct genus of mammals of the family Macraucheniidae. Fossils of this animal were found among the fossils of prehistoric xenarthrans in the Ituzaingó Formation of Argentina.

Isurus is a genus of mackerel sharks in the family Lamnidae, commonly known as the mako sharks. They are largely pelagic, and are fast, predatory fish capable of swimming at speeds of up to 50 km/h (31 mph).

Interatherium is an extinct genus of interatheriid notoungulate from the Early to Middle Miocene (Colhuehuapian-Mayoan). Fossils have been found in the Santa Cruz, Collón Curá and Sarmiento Formations in Argentina.
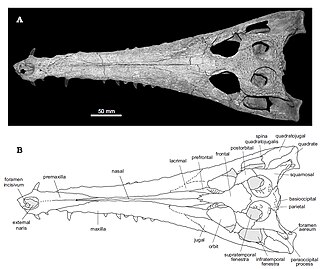
Eosuchus is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph, traditionally regarded as a gavialoid crocodilian. It might have been among the most basal of all gavialoids, lying crownward of all other known members of the superfamily, including earlier putative members such as Thoracosaurus and Eothoracosaurus. Fossils have been found from France as well as eastern North America in Maryland, Virginia, and New Jersey. The strata from which specimens have been found date back to the late Paleocene and early Eocene epochs.

Xenastrapotherium is an extinct genus of astrapothere, a type of hoofed herbivorous mammal, native to South America, which lived in the Middle to Late Miocene period, typically during the Laventan stage. It is a member of the family Astrapotheriidae in the subfamily Uruguaytheriinae, large astrapotheres, equipped with a trunk-like nose and protruding teeth, similar to the elephants, but their tusks were the canine teeth, not the incisors. Xenastrapotherium was a genus widely distributed in northern South America, in contrast to other species of astrapotheres which lived in the area of the Southern Cone of the continent. It differed from other astrapotheres by having two lower incisors on each side of the jaw and the tusks have a pronounced longitudinal curvature, although their general shape and size are probably very similar to Astrapotherium, whose weight would be 900 to 1,500 kilograms, comparable to the current black rhinoceros.
Plesiocetus is a genus of extinct rorquals found worldwide. It has had a chequered taxonomic history, having served as a wastebasket genus for a handful of mysticete species.

Miocochilius is an extinct genus of small notoungulate mammals (typotheres) native to South America. The genus lived during the Middle Miocene epoch. The genus contains two described species, the type species M. anomopodus described in 1953 by Ruben Arthur Stirton and M. federicoi, described and included in the genus by Darin A. Croft.

Proexochokefalos is an extinct genus of machimosaurid teleosauroid from the Jurassic of France
Proterotherium is an extinct genus of litoptern mammal of the family Proterotheriidae that lived during the Late Miocene of Argentina and Chile. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Ituzaingó Formation of Argentina, and the Galera Formation of Chile.
Taubatherium is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the order Notoungulata. It lived during the Late Oligocene, in what is today Brazil, in South America.
Neuryurus is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived from the Late Pliocene to the Early Holocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.














